Jun 5, 2016
Actuators inspired by muscle
Posted by Shailesh Prasad in categories: materials, robotics/AI
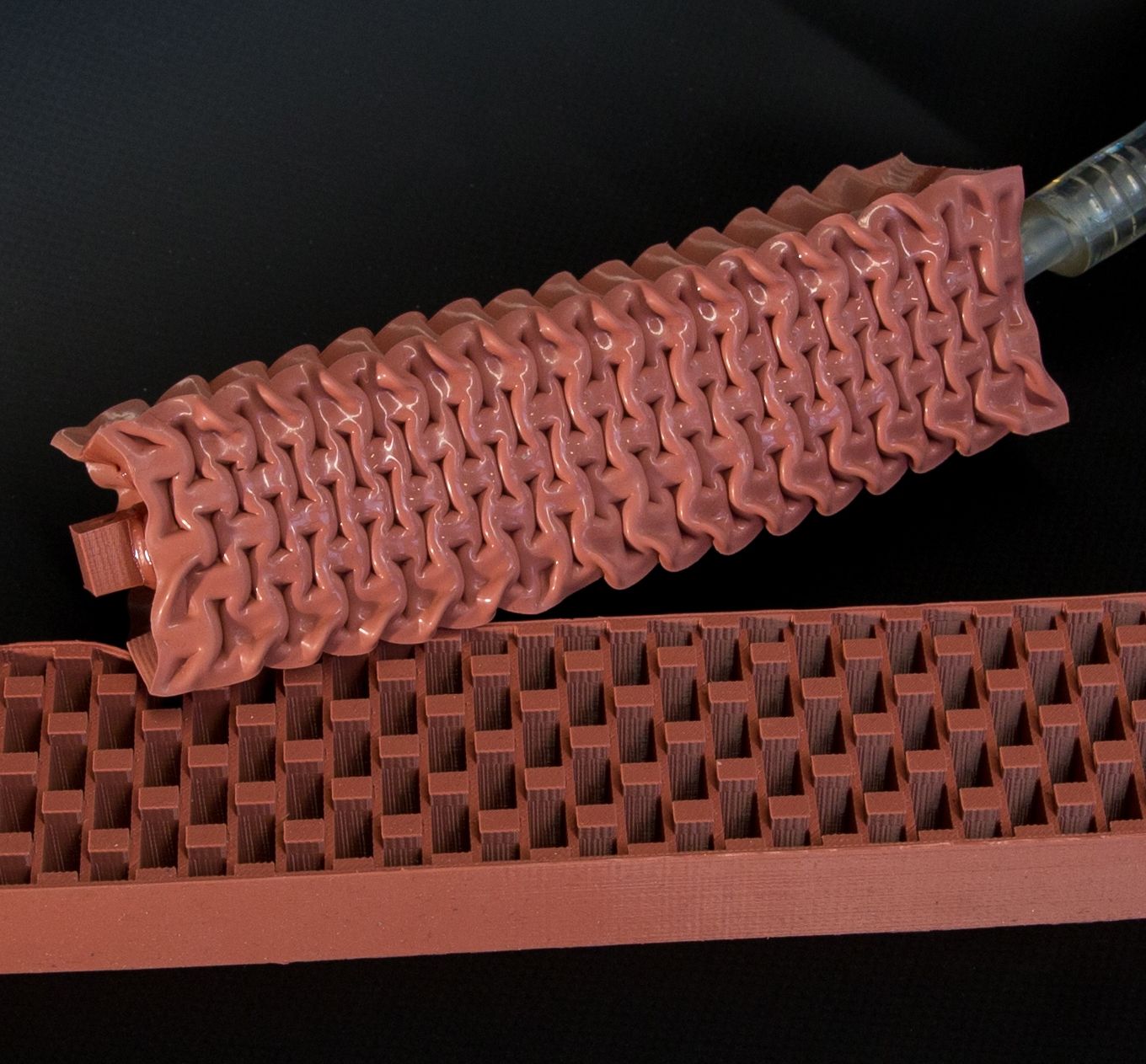
To make robots more cooperative and have them perform tasks in close proximity to humans, they must be softer and safer. A new actuator developed by Harvard researchers generates movements similar to those of skeletal muscles using vacuum power to automate soft, rubber beams.
Like real muscles, the actuators are soft, shock absorbing, and pose no danger to their environment or humans working collaboratively alongside them or the potential future robots equipped with them. The work was reported June 1 in the journal Advanced Materials Technologies.
The new actuators could pave the way for entirely soft-bodied robots that are safer than their conventional rigid counterparts.