Borophene is already thinner and more conductive than graphene, and scientists have altered it to make it even more special.


Questions to inspire discussion.
What is the potential impact of humanoid robots on human labor?
—Humanoid robots are on the verge of disrupting human labor across various industries, leading to a new era of material superabundance and prosperity within the next 10 to 20 years.
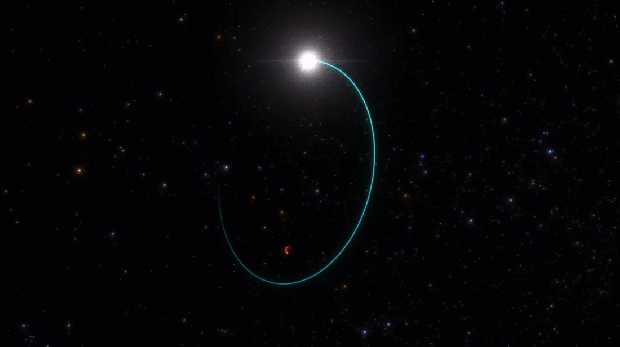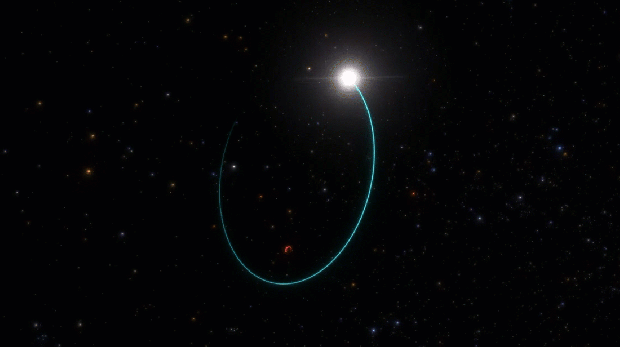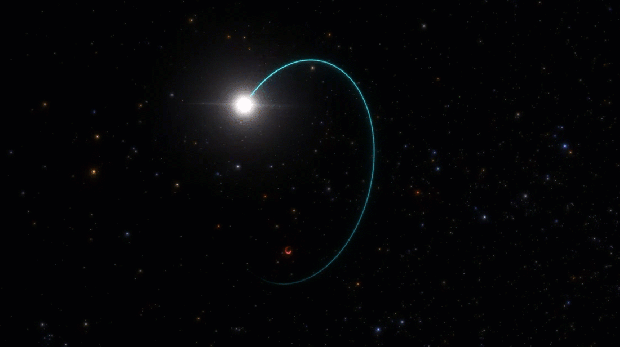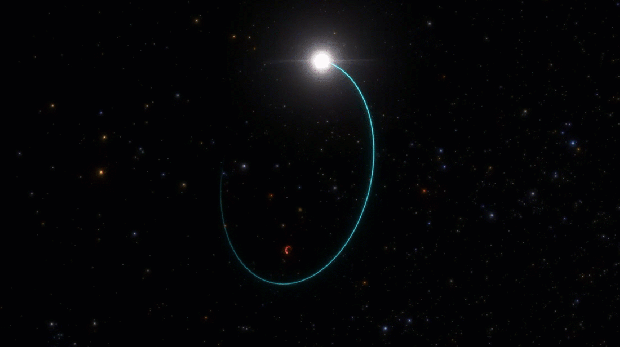
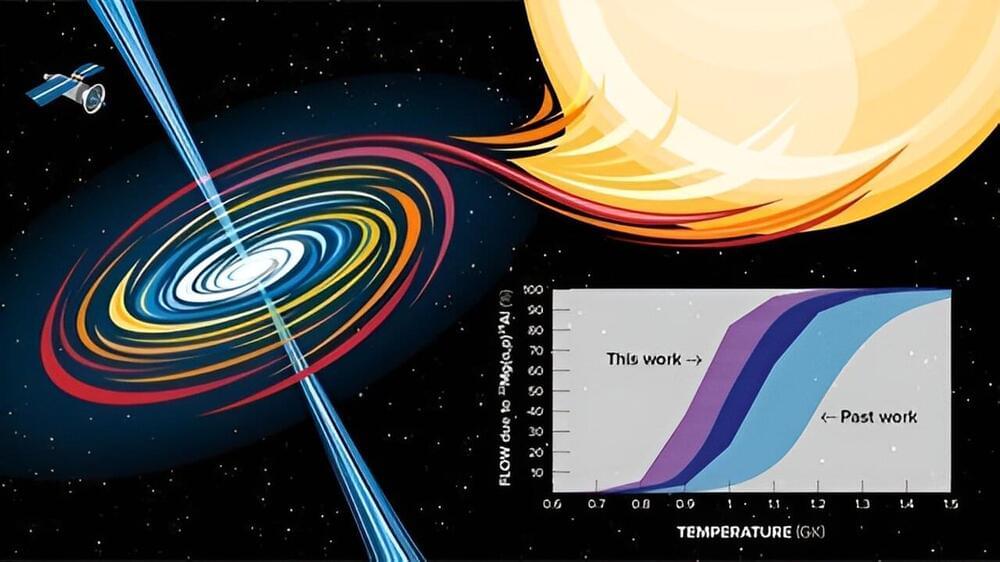
The newfound black hole, an intense, light-trapping abyss which has been named Gaia BH3, lurks just 1,926 light-years from Earth in the Aquila constellation. (That makes it the second closest black hole to Earth after Gaia BH1, which resides at 1,500 light-years away and is three times lighter than Gaia BH3.) The so-called “sleeping giant” — so named because unlike its ilk, the dormant black hole doesn’t appear to be shredding its companion star to pieces — birthed out of the imminent collapse of a once-massive star. It is the first direct link between a black hole and a progenitor star that was deprived of metals heavier than hydrogen and helium, according to the new study published in April in the journal Astronomy and Astrophysics.
The discovery confirms a leading theory of stellar evolution that posits high-mass black holes are remnants of stars that are low on metals. Such metal-poor stars have damped mass-eroding winds compared to their metal-rich counterparts, and thus have more material available to form heavier black holes. Astronomers normally time announcements of science discoveries at the same time as data release, in this case no sooner than early 2026, but “you cannot hide this kind of discovery from the community for two years,” says Panuzzo. “It is a unique case of publication based on the preliminary data because the data is exceptional and also something that’s very interesting for the community.”
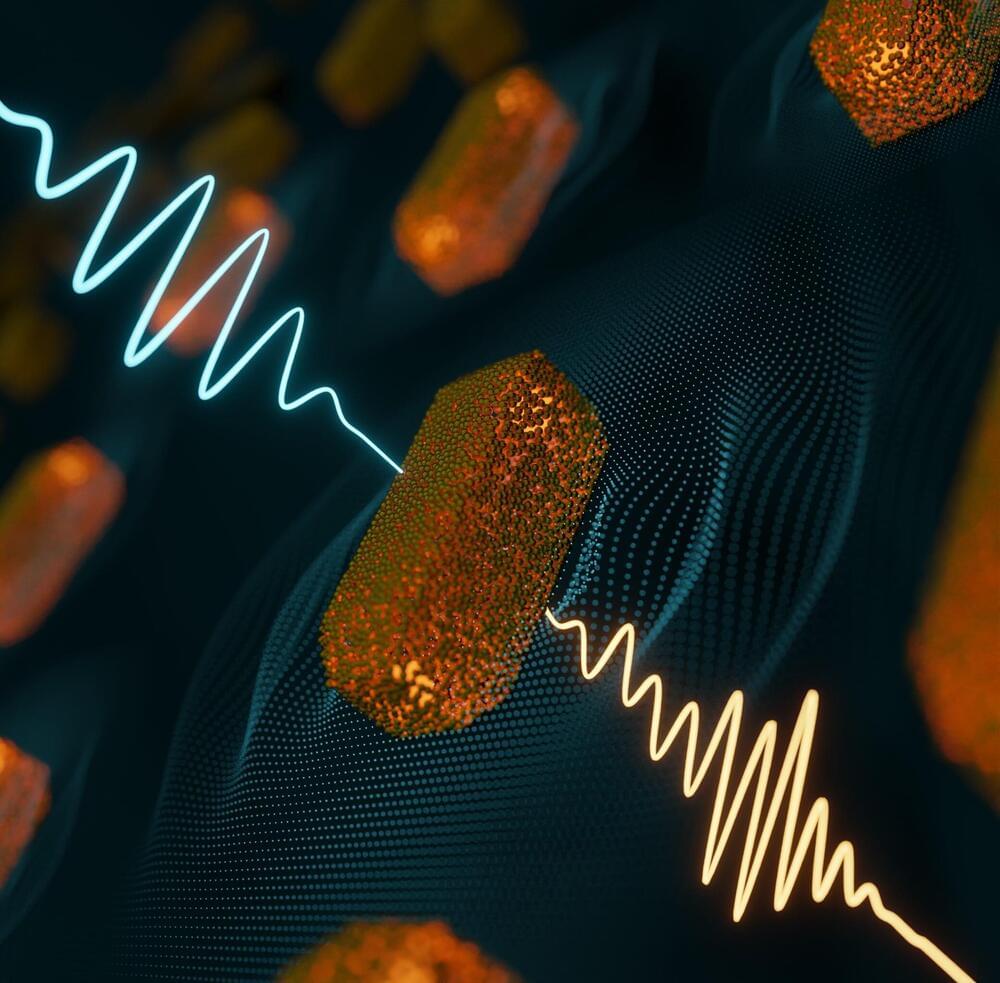
“We employed this configuration for the first time to characterize the signal field emerging from a resonantly excited plasmonic sample,” says Francesca Calegari, lead scientist at DESY, physics Professor at Universität Hamburg and a spokesperson of the Cluster of Excellence “CUI: Advanced Imaging of Matter.”
The difference of the reconstructed pulse with plasmon interaction to the reference pulse allowed the scientists to trace the emergence of the plasmon and its fast decay which they confirmed by electrodynamic model calculations.
“Our approach can be used to characterize arbitrary plasmonic samples in ambient conditions and in the far-field,” adds CUI scientist Prof. Holger Lange. Additionally, the precise characterization of the laser field emerging from nanoplasmonic materials could constitute a new tool to optimize the design of phase-shaping devices for ultrashort laser pulses.
Astronomy Magazine — Project Lyra is the cover feature!
A big thank you to Maciej Rebisz for the images and the entire Project Lyra team for the research work!
Project Lyra develops concepts for reaching interstellar objects such as 1I / ‘Oumuamua and 2I / Borisov with a spacecraft, based on near-term technologies. But what is an interstellar object?
On October 19th 2017, the University of Hawaii’s Pan-STARRS 1 telescope on Haleakala discovered a fast-moving object near the Earth, initially named A/2017 U1. It is now designated as 1I/’Oumuamua. This object was found to be not bound to the solar system. It has a velocity at infinity of ~26 km/s and an incoming radiant (direction of motion) near the solar apex in the constellation Lyra. Due to the non-observation of a tail in the proximity of the Sun, the object does not seem to be a comet but an asteroid. More recent observations from the Palomar Observatory indicate that the object is reddish, similar to Kuiper belt objects. This is a sign of space weathering.
When will such an object visit us again? End of 2019, a second interstellar object, 2I/Borisov was discovered, which is a comet. As 1I/‘Oumuamua and 2I/Borisov are the nearest macroscopic samples of interstellar material, the scientific returns from sampling the object are hard to overstate. Detailed study of interstellar materials at interstellar distances are likely decades away, even if Breakthrough Initiatives’ Project Starshot, for example, is vigorously pursued. Hence, an interesting question is if there is a way to exploit this unique opportunity by sending a spacecraft to 1I/’Oumuamua to make observations at close range.
NYU Abu Dhabi researchers have unveiled a novel 2D material improving optical modulation for advanced systems and communications.
Responding to the increasing demand for efficient, tunable optical materials capable of precise light modulation to create greater bandwidth in communication networks and advanced optical systems, a team of researchers at NYU Abu Dhabi’s Photonics Research Lab (PRL) has developed a novel, two-dimensional (2D) material capable of manipulating light with exceptional precision and minimal loss.
Tunable optical materials (TOMs) are revolutionizing modern optoelectronics, electronic devices that detect, generate, and control light. In integrated photonics circuits, precise control over the optical properties of materials is crucial for unlocking groundbreaking and diverse applications in light manipulation. Two-dimensional materials like Transition Metal Dichalcogenides (TMDs) and graphene exhibit remarkable optical responses to external stimuli. However, achieving distinctive modulation across a short-wave infrared (SWIR) region while maintaining precise phase control at low signal loss within a compact footprint has been a persistent challenge.
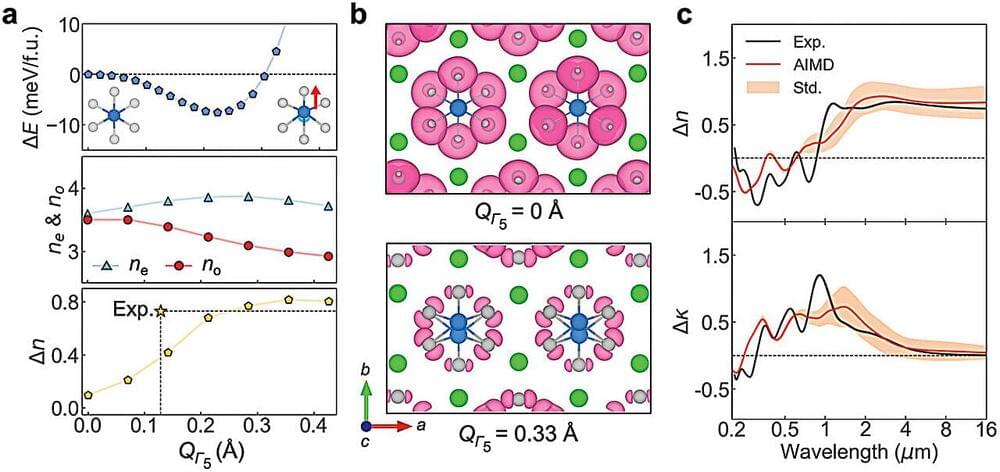
While we usually think of disorder as a bad thing, a team of materials science researchers led by Rohan Mishra, from Washington University in St. Louis, and Jayakanth Ravichandran, from the University of Southern California, have revealed that—when it comes to certain crystals—a little structural disorder might have big impacts on useful optical properties.