CryocrastinationDescription: Biostasis techniques such as cryopreservation, which allow recently-living organisms to be stored indefinitely without deteriora…
Category: life extension – Page 180

Waging war on chronic inflammation
Fresh from announcing positive Phase 1 trial results for its inflammation-targeting drug candidate, Utah-based biotech Halia Therapeutics is now pursuing Phase 2 studies in a range of indications. The Salt Lake City company’s lead compound is an inhibitor of the NLRP3 inflammasome, a known driver of systemic chronic inflammation, which is linked to conditions including fibrotic disease, Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s and many others.
Halia is taking a unique approach to the NLRP3 inflammasome by targeting the protein NEK7, which plays a key role in gene’s activity. In preclinical models, the company has shown its approach disrupts the formation of the NLRP3 inflammasome and promotes its disassembly once activated, reducing the overall inflammatory response. In its recent Phase 1 trial, in addition to showing positive safety and tolerability data, Halia’s drug demonstrated positive effects in blood samples taken from healthy volunteers, showing “over 90% suppression of multiple NLRP3-mediated cytokines and chemokines.”
Longevity. Technology: Chronic inflammation is a frequent topic of discussion in longevity circles. The term “inflammaging” refers to the increase of inflammatory cytokines in our bodies as we age, which is linked to chronic morbidity, disability, frailty and premature death. While there is no doubt that Halia believes that its approach can potentially impact many diseases, does the company have aging itself in its sights? We caught up with CEO Dr David Bearss to find out.
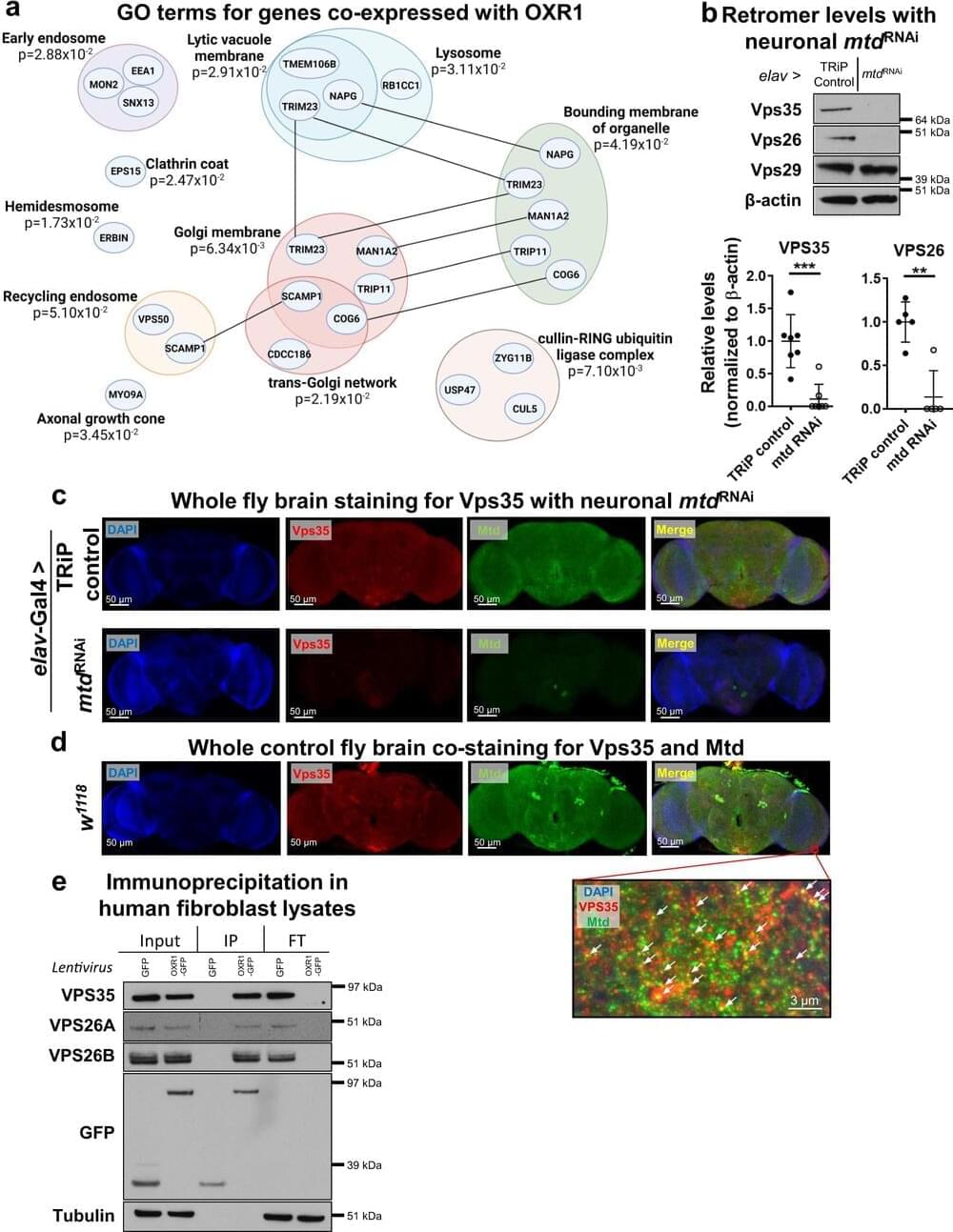
Scientists identify how dietary restriction slows brain aging and increases lifespan
Restricting calories is known to improve health and increase lifespan, but much of how it does so remains a mystery, especially in regard to how it protects the brain. Buck Institute for Research on Aging scientists have uncovered a role for a gene called OXR1 that is necessary for the lifespan extension seen with dietary restriction and is essential for healthy brain aging.
“When people restrict the amount of food that they eat, they typically think it might affect their digestive tract or fat buildup, but not necessarily about how it affects the brain,” said Kenneth Wilson, Ph.D., Buck postdoc and first author of the study, published in Nature Communications. “As it turns out, this is a gene that is important in the brain.”
The team additionally demonstrated a detailed cellular mechanism of how dietary restriction can delay aging and slow the progression of neurodegenerative diseases. The work, done in fruit flies and human cells, also identifies potential therapeutic targets to slow aging and age-related neurodegenerative diseases.

Cells Across the Body Talk to Each Other About Aging
The research builds on a recent body of work that suggests that #mitochondria are social organelles that can talk to one another even when they are in different tissues.
Biologists discovered that mitochondria in different tissues talk to each other to repair injured cells. When their signal fails, the biological clock starts winding down.

Immune Cells Hold the Key to Biological Aging
Summary: Scientists are using epigenetic clocks to reveal our biological age, a true marker of health.
A new study delves into the immune system’s role in understanding and improving the accuracy of these clocks. Their innovative approach sheds light on the relationship between immune cell composition and biological age, with a focus on the balance between naïve and memory immune cells.
This research has significant implications for aging insights, health interventions, and targeted cancer treatments.
AI is helping decode the oldest story in the world
German researchers are developing an algorithm to help decode ancient cuneiform tablets — including those containing the oldest known work of world literature.
Ancient poem: The Epic of Gilgamesh is a Babylonian poem first written in cuneiform characters on clay tablets around 4,000 years ago. It tells the story of Gilgamesh, the king of the city of Uruk, and his quest for immortality.
Over the centuries, the poem was copied onto countless other tablets in both the original Sumerian language as well as Akkadian.
Tea Consumption Is Associated With Slower Biological Aging
Join us on Patreon! https://www.patreon.com/MichaelLustgartenPhDDiscount Links: Green Tea: https://www.ochaandco.com/?ref=conqueragingTelomere, Epigenetic Te…
Elon Musk Discusses Abundance, AGI, and Media in 2024 with Peter Diamandis
In this episode, Peter and Elon hop on X Spaces to discuss Data-driven optimism, solving grand challenges, uplifting humanity, Digital Super Intelligence, Longevity, Education, and Abundance in 2024.
Elon Musk is a businessman, founder, investor, and CEO. He co-founded PayPal, Neuralink and OpenAI; founded SpaceX, and is the CEO of Tesla and the Chairman of X.
Listen to spaces on X: https://x.com/PeterDiamandis/status/1742713338549997884?s=20