In addition to having access to large colonies of monkeys and other species, animal researchers in China face less public scrutiny than counterparts in the United States and Europe. Ji, who says his primate facility follows international ethical standards for animal care and use, notes that the Chinese public has long supported monkey research to help human health. “Our religion or our culture is different from that of the Western world,” he says. Yet he also recognizes that opinions in China are evolving. Before long, he says, “We’ll have the same situation as the Western world, and people will start to argue about why we’re using a monkey to do an experiment because the monkey is too smart, like human beings.”
This story, one in a series, was supported by the Pulitzer Center.
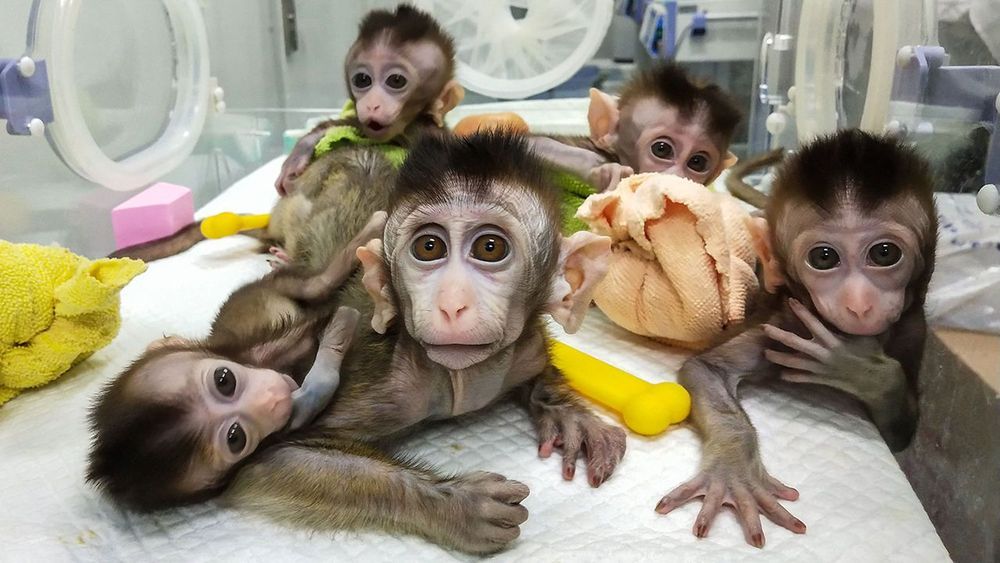
BEIJING, GUANGZHOU, JIANGMEN, KUNMING, AND SHANGHAI—Early one February morning, researchers harvest six eggs from a female rhesus macaque—one of 4000 monkeys chirping and clucking in a massive outdoor complex of metal cages here at the Yunnan Key Laboratory of Primate Biomedical Research. On today’s agenda at the busy facility, outside Kunming in southwest China: making monkey embryos with a gene mutated so that when the animals are born 5 months later, they will age unusually fast. The researchers first move the eggs to a laboratory bathed in red light to protect the fragile cells. Using high-powered microscopes, they examine the freshly gathered eggs and prepare to inject a single rhesus sperm into each one. If all goes well, the team will introduce the genome editor CRISPR before the resulting embryo begins to grow—early enough for the mutation for aging to show up in all cells of any offspring.
But as often happens when eggs are retrieved, all does not go well. Only one egg in this morning’s batch is mature enough to fertilize. “We were a little unlucky today,” says Niu Yuyu, who with facility director Ji Weizhi runs the gene-editing research. The group can afford a little bad luck, though. Through a combination of patience, ingenuity, and enormous animal resources, the team has already used CRISPR to create an astonishing range of genome-edited monkeys to serve as models for studying human diseases.