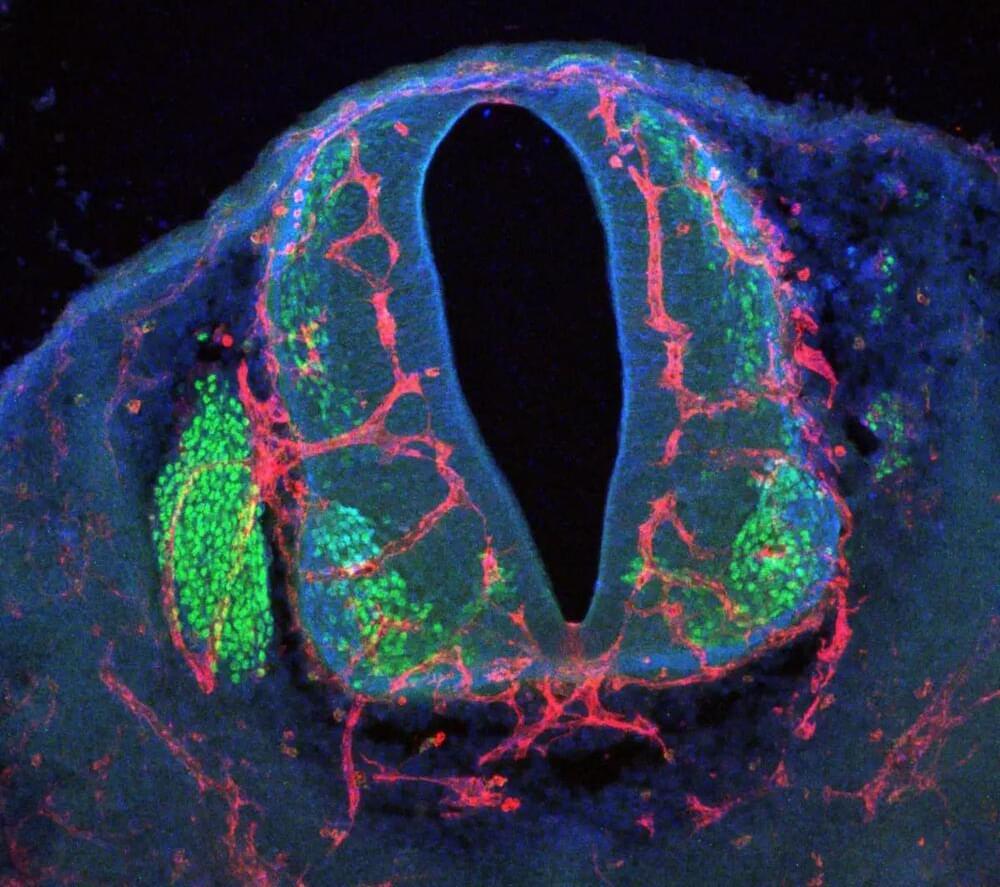
Nerve cells require vast amounts of energy and oxygen which they receive through the bloodstream. This results in nerve tissue being densely intertwined with numerous blood vessels. However, what prevents neurons and vascular cells from interfering with each other during growth? Researchers from the Universities of Heidelberg and Bonn, in collaboration with international partners, have uncovered a mechanism that ensures this coordination. The findings have recently been published in the journal Neuron.
Nerve cells are highly energy-intensive, requiring a large amount of fuel. Approximately 20% of the calories we consume through food are dedicated to our brain, as the generation of voltage pulses (action potentials) and transmission between neurons is incredibly energy-demanding. For this reason, nerve tissue is usually crisscrossed by numerous blood vessels. They ensure a supply of nutrients and oxygen.
During embryonic development, a large number of vessels sprout in the brain and spinal cord, but also in the retina of the eye. Additionally, masses of neurons are formed there, which network with each other and with structures such as muscles and organs. Both processes have to be considerate of each other so as not to get in each other’s way. “We have identified a new mechanism that ensures this,” explains Prof. Dr. Carmen Ruiz de Almodóvar, member of the Cluster of Excellence ImmunoSensation2 and the Transdisciplinary Research Area Life & Health at the University of Bonn.