A team of researchers condensed one billion years of Earth’s evolution and tectonic plate movements into a short forty-second video.





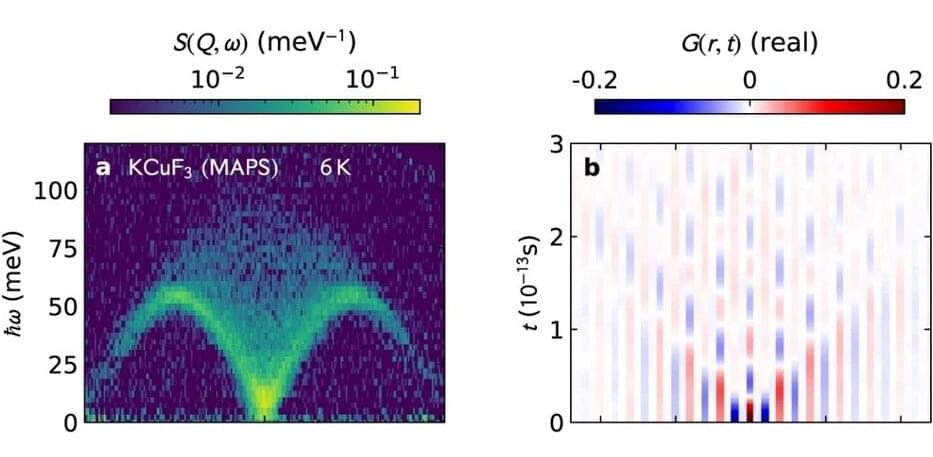
Neutron scattering is considered the method of choice for investigating magnetic structures and excitations in quantum materials. Now, for the first time, the evaluation of measurement data from the 2000s with new methods has provided much deeper insights into a model system—the 1D Heisenberg spin chains. A new toolbox for elucidating future quantum materials has been achieved.
Potassium copper fluoride (KCuF3 ) is considered the simplest model material for realizing the so-called Heisenberg quantum spin chain: The spins interact with their neighbors antiferromagnetically along a single direction (one-dimensional), governed by the laws of quantum physics.
“We carried out the measurements on this simple model material at the ISIS spallation neutron source some time ago when I was a postdoc, and we published our results in 2005, 2013 and again in 2021, comparing to new theories each time they became available,” says Prof. Bella Lake, who heads the HZB-Institute Quantum Phenomena in Novel Materials. Now with new and extended methods, a team led by Prof. Alan Tennant and Dr. Allen Scheie has succeeded in gaining significantly deeper insights into the interactions between the spins and their spatial and temporal evolution.

The accident at reactor four of the Chernobyl Nuclear Power Plant in 1986 generated the largest release of radioactive material into the environment in human history. The impact of the acute exposure to high doses of radiation was severe for the environment and the human population. But more than three decades after the accident, Chernobyl has become one of the largest nature reserves in Europe. A diverse range of endangered species finds refuge there today, including bears, wolves, and lynxes.
Radiation can damage the genetic material of living organisms and generate undesirable mutations. However, one of the most interesting research topics in Chernobyl is trying to detect if some species are actually adapting to live with radiation. As with other pollutants, radiation could be a very strong selective factor, favoring organisms with mechanisms that increase their survival in areas contaminated with radioactive substances.

Researchers have calculated the likelihood that a quantum state will decay when its evolution is inhibited by a dearth of final states.
Quantum systems are fragile, meaning a specific quantum state generally decays into other states over time. This decay process is formalized by Fermi’s golden rule (FGR), which in its traditional formalization applies when there exists an infinite continuum of states for the quantum system state to decay to—for example, when an excited atom emits a photon into a vacuum. Now Tobias Micklitz at the Brazilian Center for Research in Physics and colleagues have developed and solved a model showing how a quantum system evolves when its initial state is instead coupled to a finite set of states spread across discrete energy levels [1]. Micklitz says that their model could be the foundation for models of more complex, many-body quantum systems.
FGR-obeying systems occupy one end of a scale, where the coupling strength between the systems’ initial and final states is large relative to the energy gap between the various final states (zero for a continuum of states). At the other end of the scale, the coupling strength is much lower relative to this gap. A system that sits in this second regime remains in its initial state, as there are too few available final states for it to decay into.
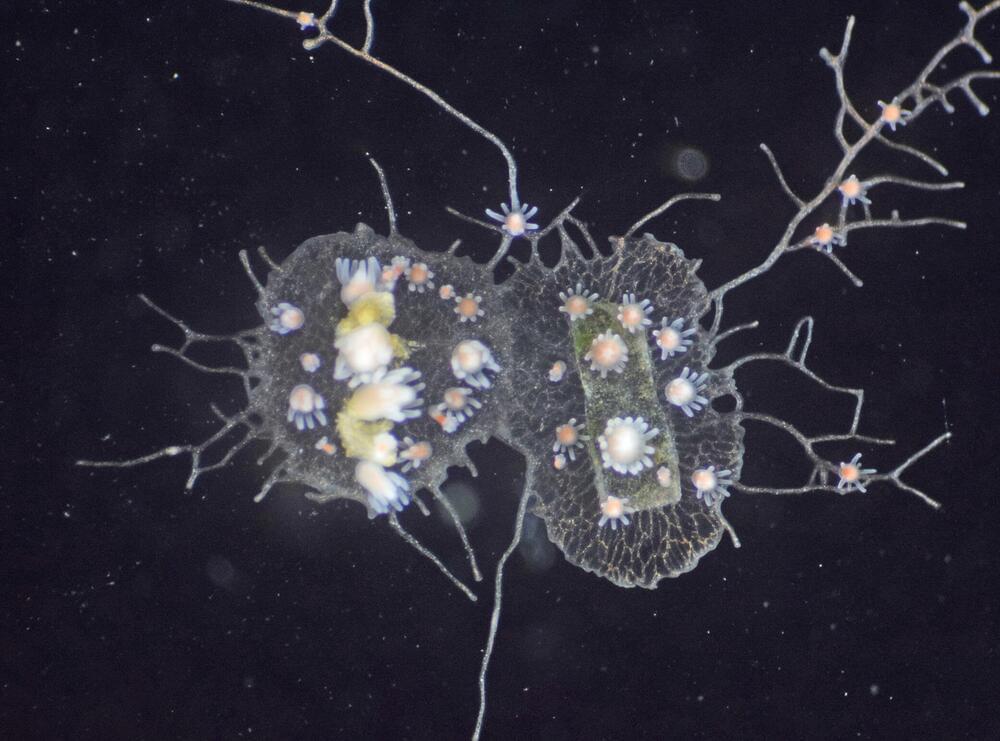
How a tiny marine invertebrate distinguishes its own cells from competitors’ bears striking similarities to the human immune system, according to a new study led by University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine researchers.
The findings, published now in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, suggest that the building blocks of our immune system evolved much earlier than previously thought and could help improve understanding of transplant rejection, one day guiding development of new immunotherapies.
“For decades, researchers have wondered whether self-recognition in a marine creature called Hydractinia symbiolongicarpus was akin to the processes that control whether a piece of skin can be successfully grafted from one person to another,” said senior author Matthew Nictora, Ph.D., assistant professor of surgery and immunology at the Thomas E. Starzl Transplantation Institute. “Our study shows for the first time that a special group of proteins called the immunoglobulin superfamily— which are important for adaptive immunity in mammals and other vertebrates—are found in such a distantly-related animal.”
Call them the Firstborn. Though they were not remotely human, they were flesh and blood, and when they looked out across the deeps of space, they felt awe, and wonder— and loneliness. As soon as they possessed the power, they began to seek for fellowship among the stars.
In their explorations, they encountered life in many forms, and watched the workings of evolution on a thousand worlds. They saw how often the first faint sparks of intelligence flickered and died in the cosmic night.
And because, in all the Galaxy, they had found nothing more precious than Mind, they encouraged its dawning everywhere. They became farmers in the fields of stars; they sowed, and sometimes they reaped.
And sometimes, dispassionately, they had to weed.
The great dinosaurs had long since passed away, their morning promise annihilated by a random hammerblow from space, when the survey ship entered the Solar System after a voyage that had already lasted a thousand years. It swept past the frozen outer planets, paused briefly above the deserts of dying Mars, and presently looked down on Earth.
Spread out beneath them, the explorers saw a world swarming with life. For years they studied, collected, catalogued. When they had learned all that they could, they began to modify. They tinkered with the destiny of many species, on land and in the seas. But which of their experiments would bear fruit, they could not know for at least a million years.

Chromosome-level engineering is a completely different beast: it’s like rearranging multiple paragraphs or shifting complete sections of an article and simultaneously hoping the changes add capabilities that can be passed onto the next generation.
Reprogramming life isn’t easy. Xiao Zhu’s DNA makeup is built from genetic letters already optimized by eons of evolutionary pressure. It’s no surprise that tinkering with an established genomic book often results in life that’s not viable. So far, only yeast have survived the rejiggering of their chromosomes.
The new study, published in Science, made the technology possible for mice. The team artificially fused together chunks from mice chromosomes. One fused pair made from chromosomes four and five was able to support embryos that developed into healthy—if somewhat strangely behaved—mice. Remarkably, even with this tectonic shift to their normal genetics, the mice could reproduce and pass on their engineered genetic quirks to a second generation of offspring.