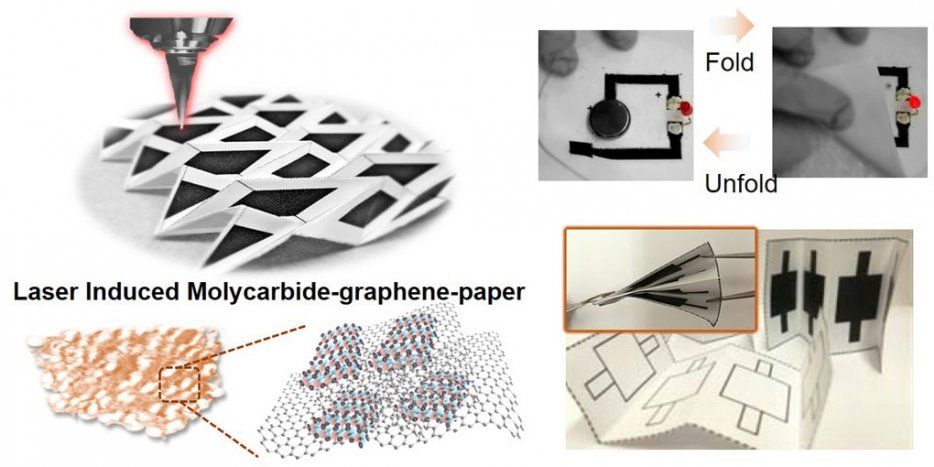
UC Berkeley engineers have given new meaning to the term “working paper.” Using inexpensive materials, they have fabricated foldable electronic switches and sensors directly onto paper, along with prototype generators, supercapacitors and other electronic devices for a range of applications.
Research to develop paper electronics has accelerated in the last 10 years. Besides its availability and low cost, paper offers an intriguing potential: simply folding it could switch circuits on and off or otherwise change their activity—a kind of electronic origami.
But most efforts to fabricate electrodes onto paper with sufficient conductivity for practical use have employed expensive metals such as gold or silver as the conducting material, swamping the potential savings of paper as a substrate.