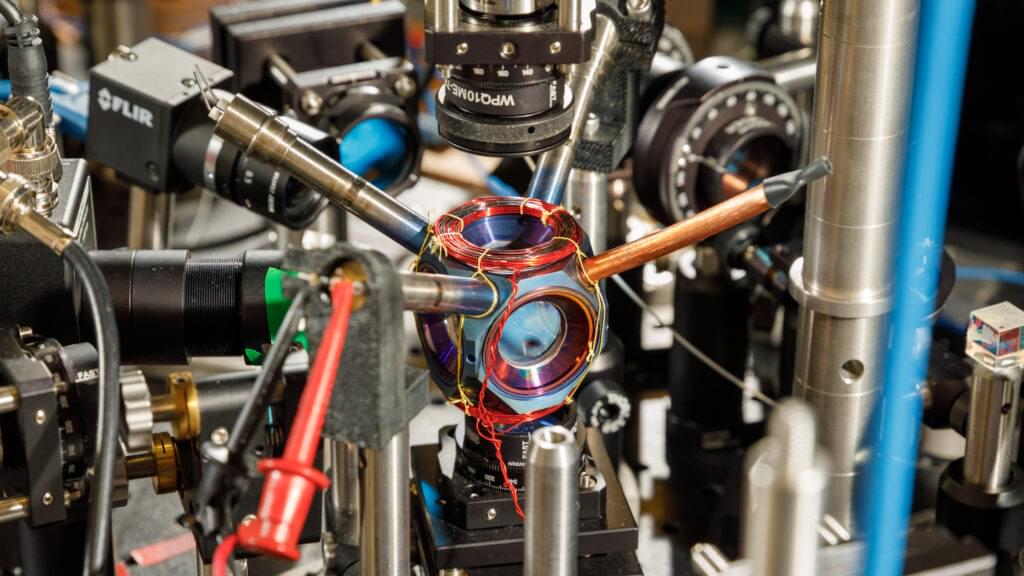
Quantum tech could provide high-precision alternatives to GPS for targeting or sonar for hunting submarines. But the same hyper-sensitivity that makes them such good sensors also makes them fatally vulnerable to interference – so far. A new DARPA program aims to change that.
Category: electronics – Page 4
Khan, M.U., Hassan, B., Alazzam, A. et al. Brain inspired iontronic fluidic memristive and memcapacitive device for self-powered electronics. Microsyst Nanoeng 11, 37 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41378-025-00882-x.
Bread is full of carbon, which just so happens to be a pretty good conductor when properly processed.
Keeping up with the Joneses…
The big elephant in the room here is Micro-LED. That’s because, like QDEL, Micro-LED pixels are self-emissive, with each pixel containing a tiny red, blue, and green LED, which combine to produce different colors as needed. It also means that Micro-LED displays have that pixel-level control for true blacks.
But QDEL could win here, too. Quantum dots seem to be able to produce more saturated and more pure colors than LEDs, which is why quantum dots are used on many high-end TVs today. Of course, it’s entirely possible that Micro-LED technology could be combined with a quantum dot layer for purer and more vibrant colors, which would create a stunning image with a high level of brightness.
Likely, however, QDEL could end up doing a similar job as Micro-LED for much cheaper. Micro-LED has proven expensive to produce. While QDEL isn’t being used on consumer screens just yet, it could end up being much cheaper given the fact that quantum dots at this point are relatively easy to manufacture.
Water isn’t just liquid, ice, or vapor — under extreme conditions, it can transform into exotic phases, such as the newly observed plastic ice VII.
This hybrid phase, predicted years ago but only recently confirmed using cutting-edge neutron spectrometers, exhibits both solid-like structure and liquid-like molecular motion.
Beyond the familiar: water’s many phases.
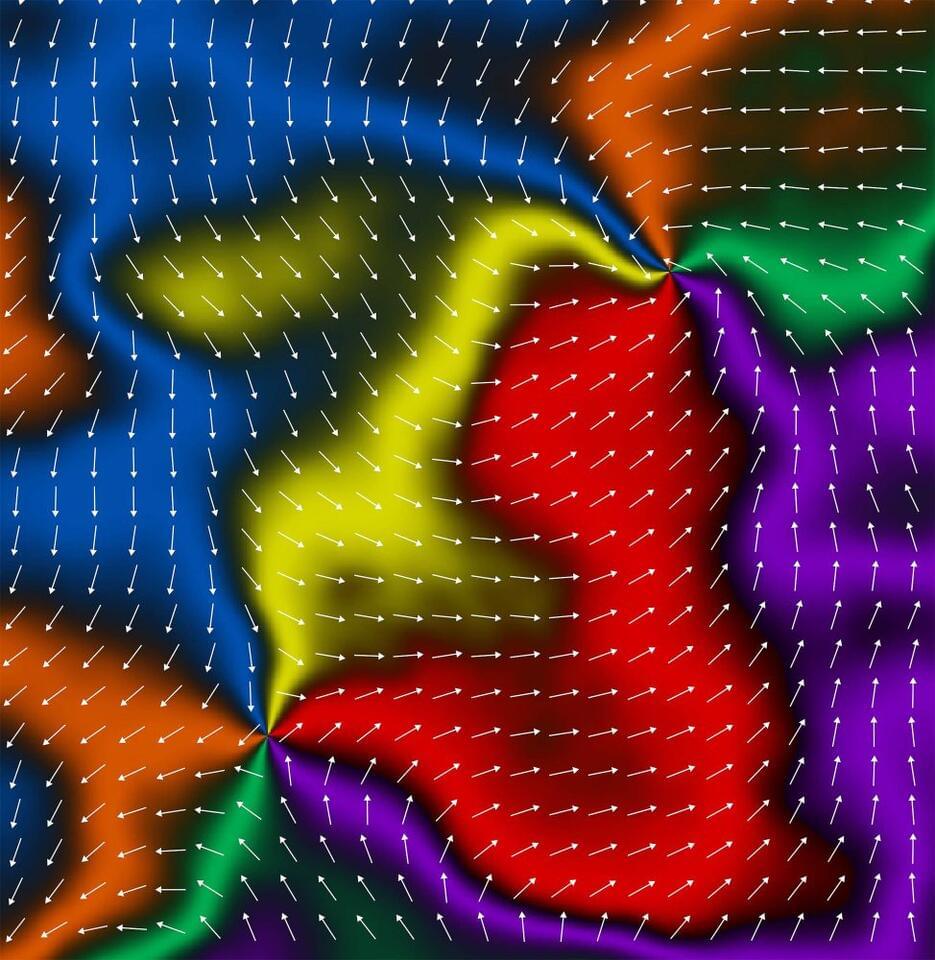
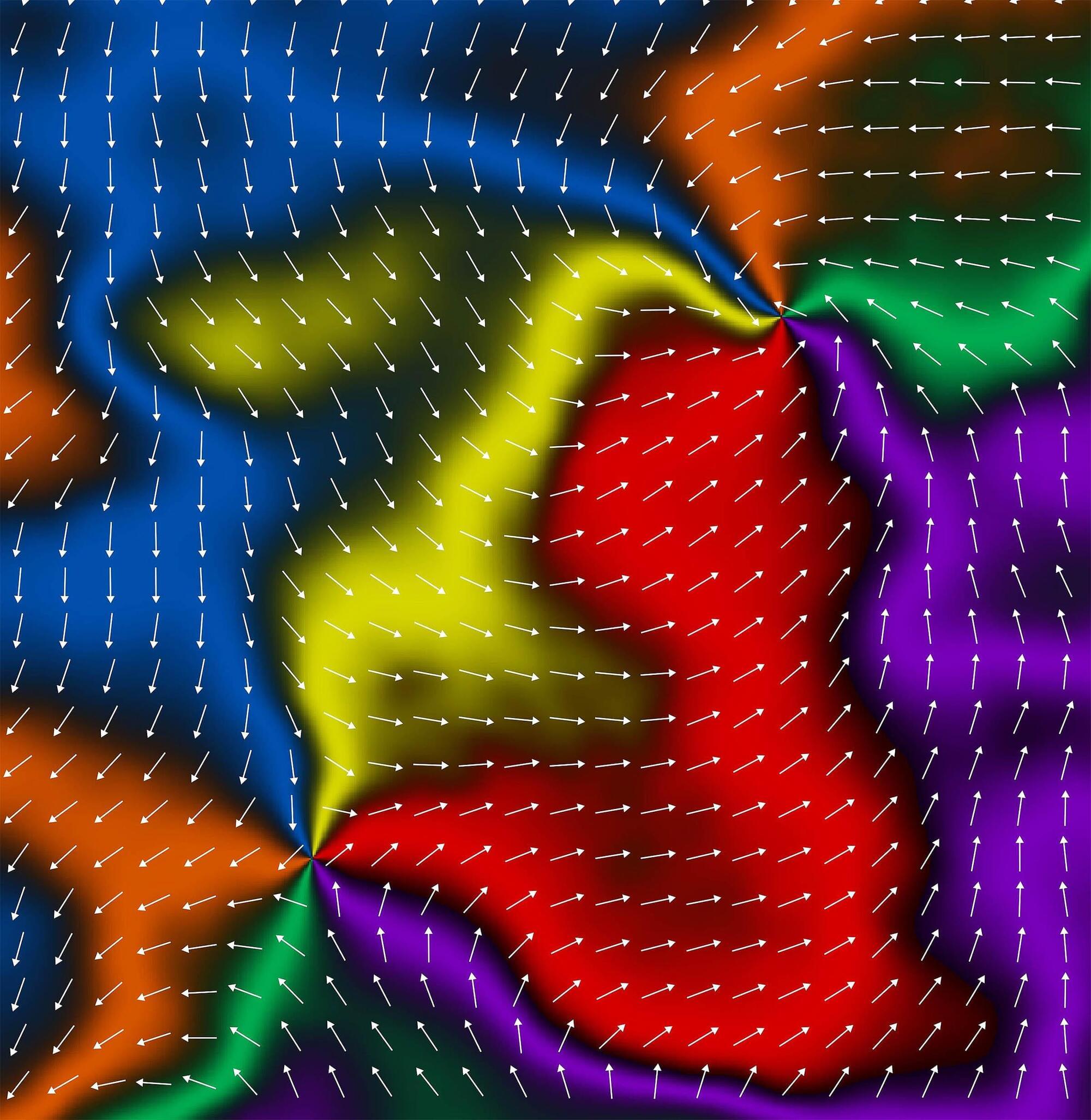
Researchers in Sweden have reported control over a new kind of magnetism with the potential to boost electronic performance. Their work shows that this new class of magnetism, called altermagnetism, can increase memory device operation speeds by up to a thousand times.
Scientists say it stands apart from the two widely known forms of magnetic order and may open doors to faster, more efficient technologies.
Scientists from the University of Nottingham’s School of Physics and Astronomy have confirmed this third category in microscopic devices, and their findings have been published in Nature. Professor Peter Wadley from the same institution led the research.
DARPA’s RoQS program aims to develop resilient quantum sensors that maintain their high sensitivity while resisting environmental disruptions.
QUT researchers created a biosensor using engineered proteins to detect and extract rare earth elements, offering a potential solution to growing demand and environmental challenges.
QUT synthetic biologists have developed a prototype for an innovative biosensor capable of detecting rare earth elements, with the potential for modification to suit various other applications.
Lanthanides (Lns) are essential elements used in electronics, electric motors, and batteries. However, current extraction methods are costly, environmentally damaging, and unable to meet the growing demand.
Scientists report that a new class of magnetism, called altermagnetism, can increase memory device operation speeds by up to a thousand times.