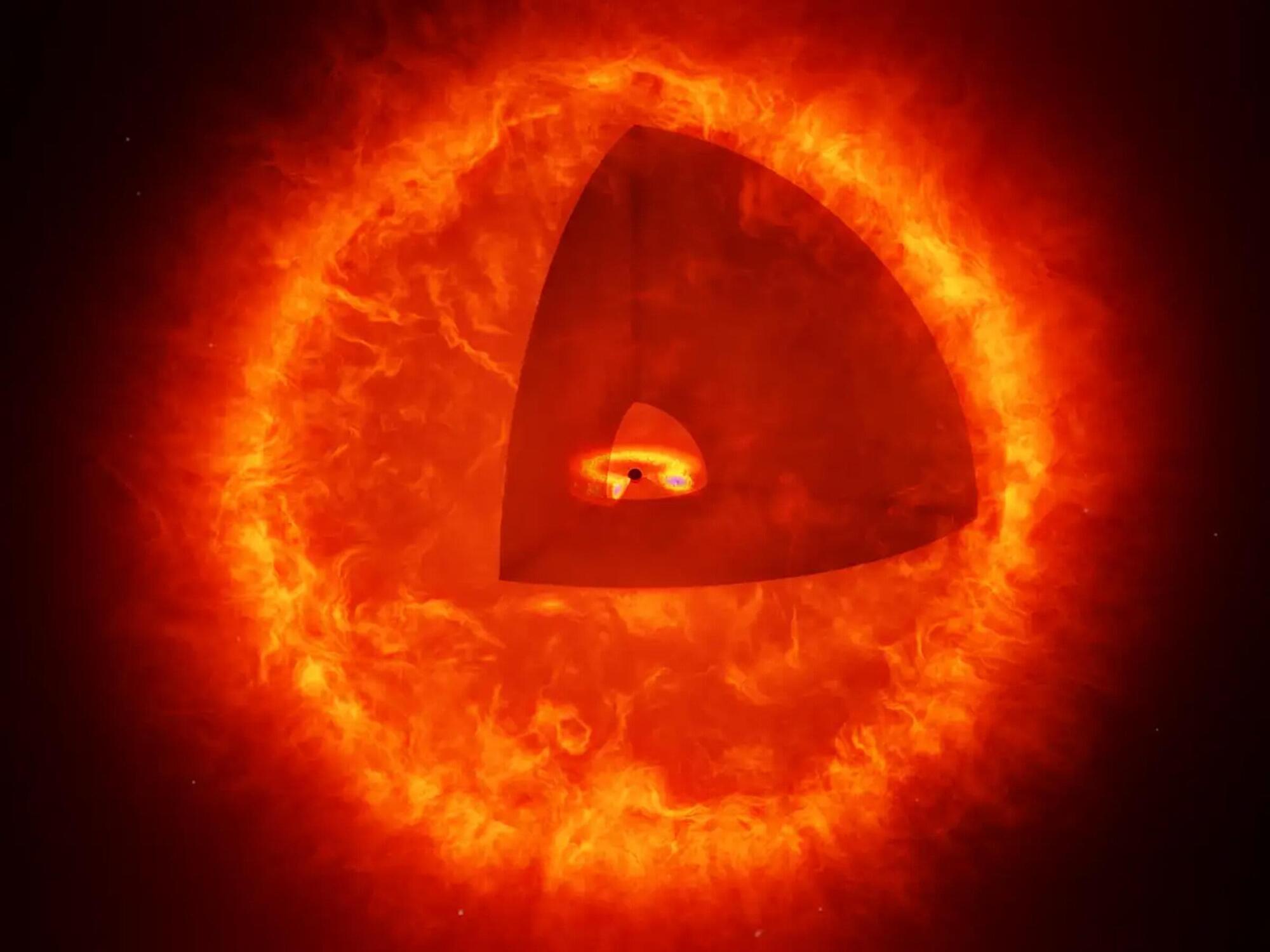
The last gasp of a primordial black hole may be the source of the highest-energy “ghost particle” detected to date, a new MIT study proposes.
In a paper appearing today in Physical Review Letters, MIT physicists put forth a strong theoretical case that a recently observed, highly energetic neutrino may have been the product of a primordial black hole exploding outside our solar system.
Neutrinos are sometimes referred to as ghost particles, for their invisible yet pervasive nature: They are the most abundant particle type in the universe, yet they leave barely a trace. Scientists recently identified signs of a neutrino with the highest energy ever recorded, but the source of such an unusually powerful particle has yet to be confirmed.