Most exoplanets that have been discovered over the last few decades happened to go around stars that are roughly the same size as the Sun. Some are a bit bigger and many a lot smaller. Planets have been discovered around pulsars, the extreme end product of supernovae, so astronomers expect that planets are to be found around the massive star that will one day explode as a supernova. Two such planets have recently been discovered and the whole setup looks like a blown-up version of our own Solar System.
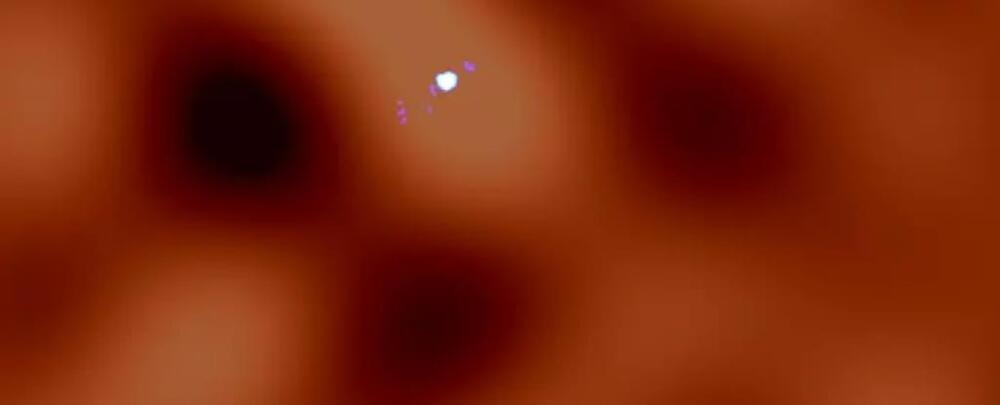
The star in question is called μ2 Sco which is part of the Scorpius-Centaurus association. This is a group of young stars, no older than 20 million years. Among them, μ2 Sco (pronounced Mew two, yes like the legendary Pokemon) is a massive, blue, hot star that weighs about nine times our Sun. The observations conducted in this study suggest the presence of two candidate companions.
These are called CC0 and μ2 Sco b. The first has not been confirmed completely yet. It appears to have a mass of about 18.5 times that of Jupiter. The team is confident in the detection of the second one, which has a mass of about 14.4 Jupiters, so it gets the proper planet name. The team uses the term planet.