A heptagonal-lattice superconducting circuit, and the mathematics that describe it, provide tools for studying quantum mechanics in curved space.
According to John Wheeler’s summary of general relativity, “space-time tells matter how to move; matter tells space-time how to curve.” How this relationship plays out at the quantum scale is not known, because extending quantum experiments to curved space poses a challenge. In 2019, Alicia Kollár and colleagues at Princeton University met that challenge with a photonic circuit that represents the negatively curved space of an expanding universe [1]. Now, Igor Boettcher and colleagues at the University of Maryland, College Park, describe those experiments with a new theoretical framework [2]. Together, the studies offer a toolkit for studying quantum mechanics in curved space that could help answer fundamental questions about cosmology.
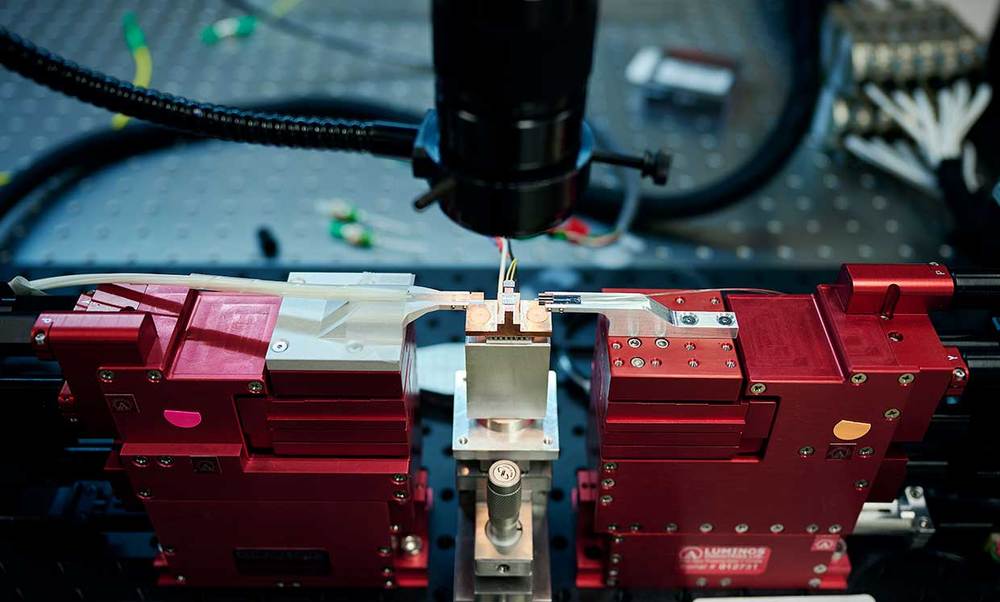
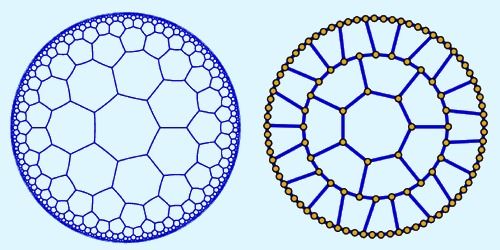
In a universe that expands at an accelerating rate, space curves away from itself at every point, producing a saddle-like, hyperbolic geometry. To project hyperbolic space onto a plane, Kollár’s team etched a centimeter-sized chip with superconducting resonators arranged in a lattice of heptagonal tiles. By decreasing the tile size toward the edge of the chip, the researchers reproduced a perplexing property of hyperbolic space: most of its points exist on its boundary. As a result, photons moving through the circuit behave like particles moving in negatively curved space.