Computer scientists established a new boundary on computationally verifiable knowledge. In doing so, they solved major open problems in quantum mechanics and pure mathematics.



Google plans to add a Zoom-like gallery view to its business- and education-focused Meet videoconferencing service and let users start calls and join meetings right from Gmail, Google’s GM and VP of G Suite Javier Soltero told Reuters in an interview. The additions come amid huge growth for Meet as families, students, and workers use the service while at home due to the COVID-19 pandemic.
The upcoming gallery view will let users display up to 16 meeting participants in one frame, according to Reuters. That functionality is coming later this month, said Soltero. Zoom’s gallery view, by contrast, lets you see the thumbnails of up to 49 people in one screen, if you have a powerful enough CPU to display them all.
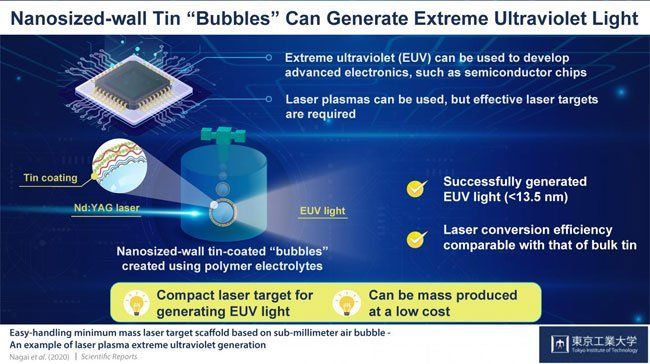
Scientists at Tokyo Institute of Technology (Tokyo Tech) have generated low-cost extreme ultraviolet (EUV) light by creating tin thin-film spheres using a polymer electrolyte “soap bubble” as a template and irradiating it with a laser.
#EUV #photonics
The team from Tokyo Tech, working with colleagues from University College Dublin, set out to find efficient, scalable, low-cost laser targets that could be used to generate EUV. The scientists created a tin-coated microcapsule or “bubble” — a low-density structure weighing as little as 4.2 nanograms and with a high level of controllability. For the bubble, they used polymer electrolytes, which are a dissolution of salts in a polymer matrix. The salts act as surfactants to stabilize the bubble.
The scientists coated the bubble with tin nanoparticles. “We produced polyelectrolyte microcapsules composed of poly(sodium 4-styrene-sulfonate) and poly(allylamine hydrochloride) and then coated them in a tin oxide nanoparticle solution,” professor Keiji Nagai said.
To test the bubble, the scientists irradiated it using a neodymium-YAG laser. This resulted in the generation of EUV light within the 13.5-nm range. The team further found that the structure was compatible with the conventional EUV light sources that are used to manufacture semiconductor chips.

Cooling atoms to ultracold temperatures is a routine task in atomic physics labs, but molecules are a trickier proposition. Researchers in the US have now used a widely-applicable combination of methods to make molecules colder than ever before – a feat that could pave the way for applications in areas as diverse as high-temperature superconductivity and quantum computing.
In everyday life, we do not see the bizarre effects of quantum mechanics because the quantum states of the particles around us are constantly collapsing, or decohering, as they interact. At temperatures near absolute zero, however, some identical particles will simultaneously occupy the lowest energy quantum state available. This phenomenon is known as quantum degeneracy, and it was experimentally demonstrated in 1995, when groups led by Eric Cornell and Carl Wieman (then at the University of Colorado, Boulder) and Wolfgang Ketterle of the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) created the first Bose-Einstein condensates (BECs) with rubidium and sodium atoms, respectively.
Other groups have subsequently made condensates using other atomic species, and various techniques have been developed to cool atoms to quantum degeneracy. In one of the simplest methods, a sample of atoms is confined in a magnetic or optical trap. Hotter atoms with more kinetic energy are more readily able to escape, or evaporate, from this trap, so the remaining atoms become cooler. In another method, known as sympathetic cooling, one type of atom is cooled directly and allowed to thermalize with atoms of another type, thereby cooling them by extracting their kinetic energy.
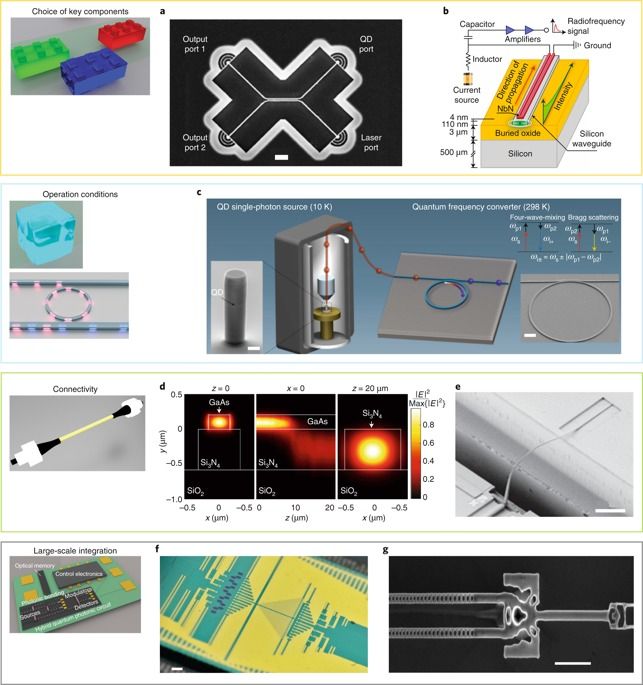
Recent developments in chip-based photonic quantum circuits have radically impacted quantum information processing. However, it is challenging for monolithic photonic platforms to meet the stringent demands of most quantum applications. Hybrid platforms combining different photonic technologies in a single functional unit have great potential to overcome the limitations of monolithic photonic circuits. Our Review summarizes the progress of hybrid quantum photonics integration, discusses important design considerations, including optical connectivity and operation conditions, and highlights several successful realizations of key physical resources for building a quantum teleporter. We conclude by discussing the roadmap for realizing future advanced large-scale hybrid devices, beyond the solid-state platform, which hold great potential for quantum information applications.

We are cousins of bats lol.
Dr David Haussler, Howard Hughes Medical Institute investigator working at University of California, Santa Cruz, co-authors report on computer analysis designed to reconstruct genome of 80-million-year-old mammal; holds that program has 98.5 percent accuracy rate and over next four years will formulate entire genome of ancestral mammal from total of 37 current mammalian species, including humans; research is published in journal Genome Research; graph (M)
Test Coronavirus in minutes:
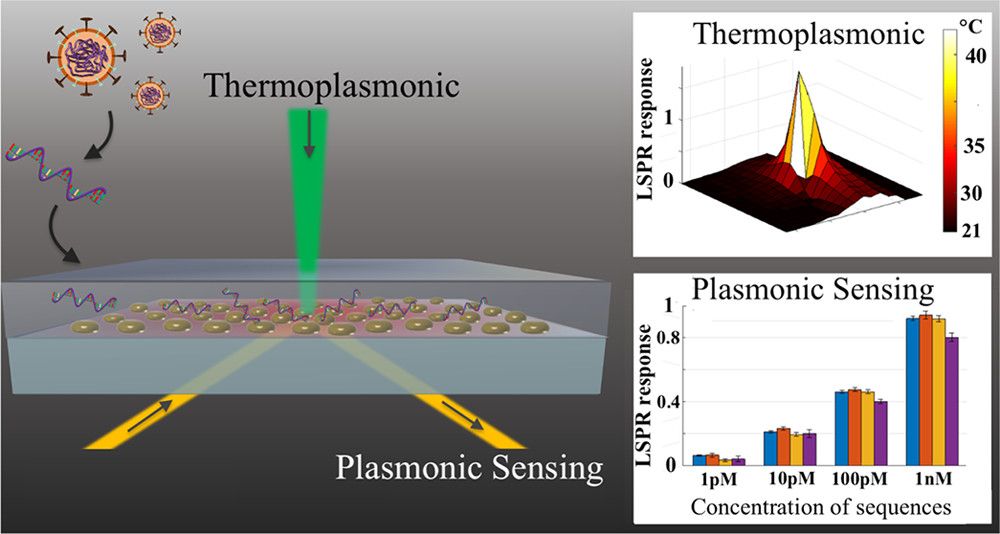
The ongoing outbreak of the novel coronavirus disease (COVID-19) has spread globally and poses a threat to public health in more than 200 countries. Reliable laboratory diagnosis of the disease has been one of the foremost priorities for promoting public health interventions. The routinely used reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) is currently the reference method for COVID-19 diagnosis. However, it also reported a number of false-positive or –negative cases, especially in the early stages of the novel virus outbreak. In this work, a dual-functional plasmonic biosensor combining the plasmonic photothermal (PPT) effect and localized surface plasmon resonance (LSPR) sensing transduction provides an alternative and promising solution for the clinical COVID-19 diagnosis. The two-dimensional gold nanoislands (AuNIs) functionalized with complementary DNA receptors can perform a sensitive detection of the selected sequences from severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) through nucleic acid hybridization. For better sensing performance, the thermoplasmonic heat is generated on the same AuNIs chip when illuminated at their plasmonic resonance frequency. The localized PPT heat is capable to elevate the in situ hybridization temperature and facilitate the accurate discrimination of two similar gene sequences. Our dual-functional LSPR biosensor exhibits a high sensitivity toward the selected SARS-CoV-2 sequences with a lower detection limit down to the concentration of 0.22 pM and allows precise detection of the specific target in a multigene mixture. This study gains insight into the thermoplasmonic enhancement and its applicability in the nucleic acid tests and viral disease diagnosis.
Article Views are the COUNTER-compliant sum of full text article downloads since November 2008 (both PDF and HTML) across all institutions and individuals. These metrics are regularly updated to reflect usage leading up to the last few days.
Citations are the number of other articles citing this article, calculated by Crossref and updated daily. Find more information about Crossref citation counts.
The Altmetric Attention Score is a quantitative measure of the attention that a research article has received online. Clicking on the donut icon will load a page at altmetric.com with additional details about the score and the social media presence for the given article. Find more information on the Altmetric Attention Score and how the score is calculated.
PsiQuantum is a little-known quantum computing startup, however it recently had no trouble raising almost a quarter of a billion dollars from Microsoft’s M12 venture fund and other investors. That is in addition to a whopping $230 million it received last year from a fund formed by Andy Rubin, developer of the Android operating system.
The company was founded in 2016 by British professor Jeremy O’Brien and three other academics, Terry Rudolph, Mark Thompson, and Pete Shadbolt. In just a few years, they have quietly grown the company from a few employees to a robust technical staff of more than 100.
Compared to today’s modest quantum computing capabilities, PsiQuantum’s elevator pitch for investors sounds like a line from a science fiction movie. O’Brien not only says he is going to build a fault-tolerant quantum computer with a staggering one million qubits, he also says he is going to do it within five years. O’Brien’s technology of choice for this claim is silicon photonics, which uses particles of light called photons to perform quantum calculations. Theoretically, photons behave as both waves and particles, but that’s a subject for another article. Quantum computing technologies in use today are primarily superconductors and trapped ion. However, there is plenty of research that shows photonics holds a lot of promise.
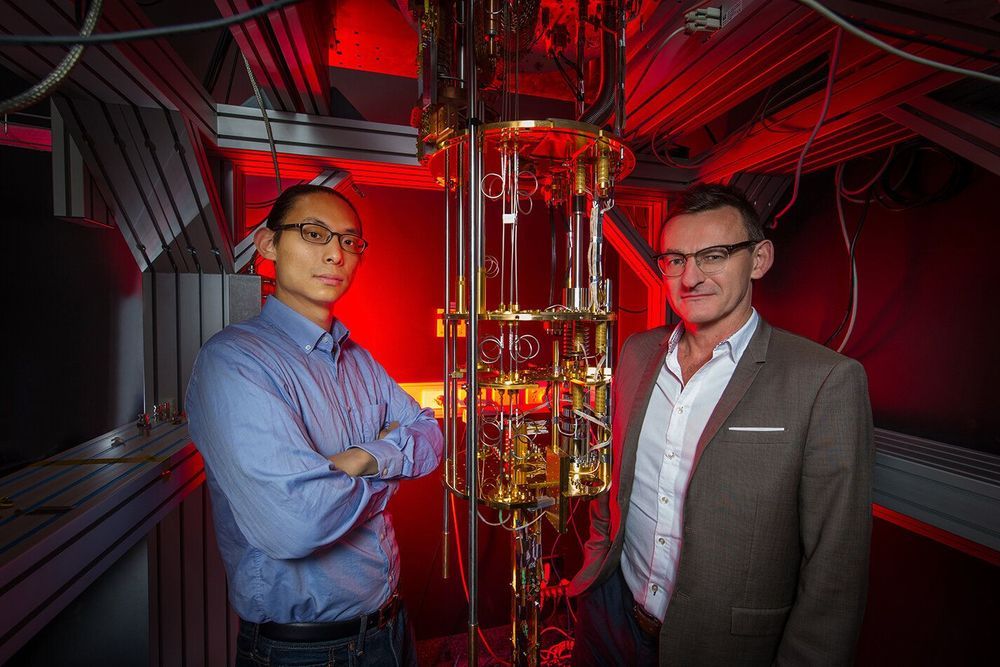
Most quantum computers being developed around the world will only work at fractions of a degree above absolute zero. That requires multi-million-dollar refrigeration and as soon as you plug them into conventional electronic circuits they’ll instantly overheat.
But now researchers led by Professor Andrew Dzurak at UNSW Sydney have addressed this problem.
“Our new results open a path from experimental devices to affordable quantum computers for real world business and government applications,” says Professor Dzurak.
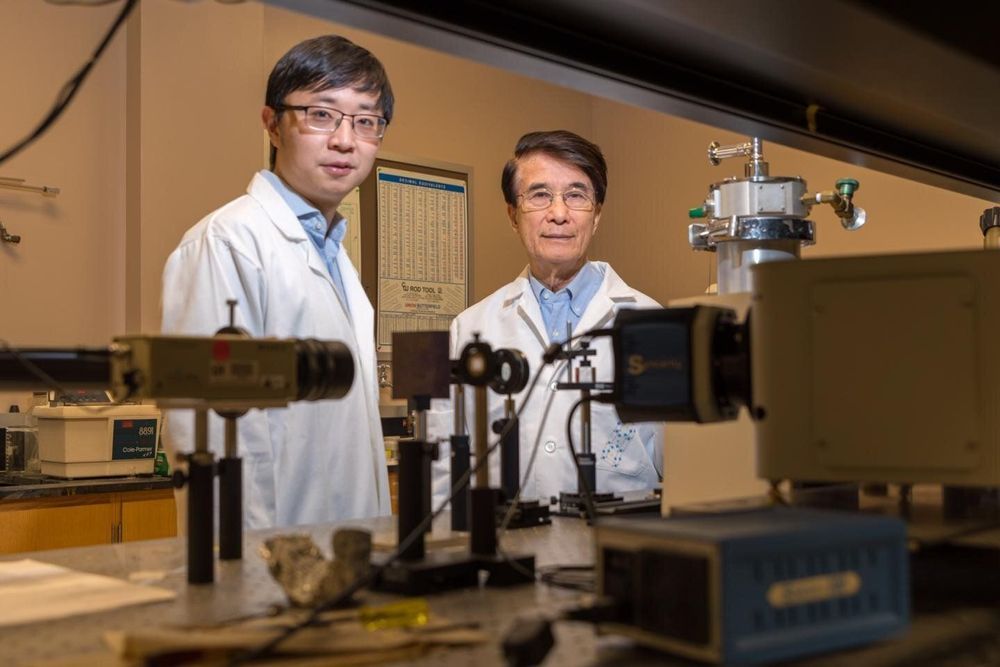
The demands for data storage and processing have grown exponentially as the world becomes increasingly connected, emphasizing the need for new materials capable of more efficient data storage and data processing.
An international team of researchers, led by physicist Paul Ching-Wu Chu, founding director of the Texas Center for Superconductivity at the University of Houston, is reporting a new compound capable of maintaining its skyrmion properties at room temperature through the use of high pressure. The results also suggest the potential for using chemical pressure to maintain the properties at ambient pressure, offering promise for commercial applications.
The work is described in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.