In a new study, researchers from Australia and Canada have identified a ‘sweet spot’, using holes, where the qubit is least sensitive to noise.




Bottom dollar.
Bloomberg today reported that a shortage of inexpensive display driver chips has delayed production of the LCD panels used in, well, pretty much every product category you can think of. Displays are ubiquitous, and many devices can’t function without them. But for the displays to work, they require a display driver — no, not Nvidia or AMD display drivers, those are software. We’re talking about a tiny chip that sends instructions and signals to the display.
That’s a fairly simple function, at least compared to those performed by the vastly more powerful components inside the device proper, which is why many display drivers cost $1. But a component’s price doesn’t always reflect its importance, as anyone who’s built a high-end PC, bought one of the best gaming monitors, and then realized they forgot to get a compatible cable can attest. That missing link is both cheap and vital.
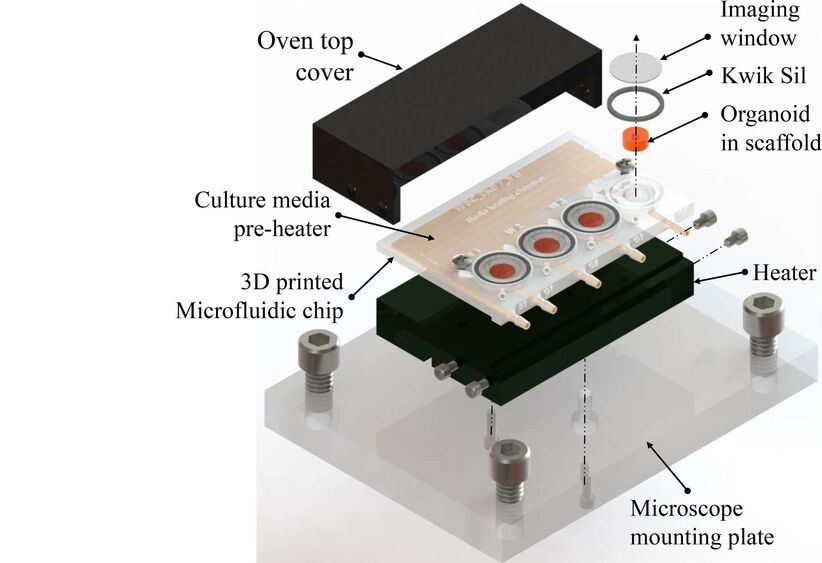
Scientists from MIT and the Indian Institute of Technology Madras have grown small amounts of self-organizing brain tissue, known as organoids, in a tiny 3D-printed system that allows observation while they grow and develop. The work is reported in Biomicrofluidics.
Current technology for real-time observation of growing organoids involves the use of commercial culture dishes with many wells in a glass-bottomed plate placed under a microscope. The plates are costly and only compatible with specific microscopes. They do not allow for the flow or replenishment of a nutrient medium to the growing tissue.
Recent advances have used a technique known as microfluidics, where a nutrient medium is delivered through small tubes connected to a tiny platform or chip. These microfluidic devices are, however, expensive and challenging to manufacture.

Klas Moser.
What Musk is doing beside realizing his own dreams is inspiring thousands of young bright kids to keep on studying to realize their own dreams and I am sure that this is exactly what we humans need to create a better world on Earth as well.
This whol… See More.
2 Replies.
Rob Enderle.
It better come with a decent meal and reclining seats for that price. It’s a one-way trip too, so you better LOVE Mars.
View 4 more replies.

What’s New: Intel today announced that it has signed an agreement with Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) to perform in its Data Protection in Virtual Environments (DPRIVE) program. The program aims to develop an accelerator for fully homomorphic encryption (FHE). Microsoft is the key cloud ecosystem and homomorphic encryption partner leading the commercial adoption of the technology once developed by testing it in its cloud offerings, including Microsoft Azure and the Microsoft JEDI cloud, with the U.S. government. The multiyear program represents a cross-team effort across multiple Intel groups, including Intel Labs, the Design Engineering Group and the Data Platforms Group, to tackle “the final frontier” in data privacy, which is computing on fully encrypted data without access to decryption keys.
“Fully homomorphic encryption remains the holy grail in the quest to keep data secure while in use. Despite strong advances in trusted execution environments and other confidential computing technologies to protect data while at rest and in transit, data is unencrypted during computation, opening the possibility of potential attacks at this stage. This frequently inhibits our ability to fully share and extract the maximum value out of data. We are pleased to be chosen as a technology partner by DARPA and look forward to working with them as well as Microsoft to advance this next chapter in confidential computing and unlock the promise of fully homomorphic encryption for all.” – Rosario Cammarota, principal engineer, Intel Labs, and principal investigator, DARPA DPRIVE program
The first wireless commands to a computer have been demonstrated in a breakthrough for people with paralysis.
The system is able to transmit brain signals at “single-neuron resolution and in full broadband fidelity”, say researchers at Brown University in the US.
A clinical trial of the BrainGate technology involved a small transmitter that connects to a person’s brain motor cortex.

Using measurements of resistance versus applied gate voltage at temperatures of 390 mK, the researchers showed that superconductivity in the improved NbN layer could survive applied magnetic fields as high as 17.8 Tesla. Meanwhile, the improved GaN semiconductor was of high enough quality to exhibit the quantum Hall effect at lower applied magnetic fields of 15 T. “Both these improvements mean the quantum Hall effect and superconductivity can occur at the same time in the heterostructure over a certain ‘window’ of temperatures and magnetic fields (that is, below 1 K and between magnetic fields of 15 to 17.8 T),” study lead author Phillip Dang tells Physics World.
According to the team, the new GaN/NbN heterostructure could be used in quantum computing and low-temperature electronics. Reporting their work in Science Advances, the researchers say they now plan to further investigate the interaction between superconductivity and the quantum Hall effect in this material.

Intel Corp Chief Executive Officer Pat Gelsinger will virtually attend a meeting being put together by President Joe Biden’s administration for April 12 to discuss the semiconductor supply chain issues disrupting U.S. automotive factories, according to a person familiar with the matter. Reuters previously reported the meeting will include Biden’s national security adviser, Jake Sullivan, and a top economic aide, Brian Deese, as well as chipmakers and automakers. Gelsinger last month said Intel will spend $20 billion to build two new chip factories in Arizona.
Exactly one week after new Chief Executive Pat Gelsinger unveiled plans to reinvent Intel Corp., Arm Ltd. announced version 9 of its architecture and put forth its vision for the next decade. We believe Arm’s direction is strong and compelling as it combines an end-to-end capability, from edge to cloud to the data center to the home and everything in between.
Moreover, it doubles down on Arm’s model of enabling ecosystem partners to add significant value while at the same time maintaining software compatibility with previous generations. We see this as extremely important because the variety of use cases requiring specialized silicon is rapidly expanding in the marketplace, and the Arm architecture is by far in our view the best-positioned to capitalize on this coming wave.
In this Breaking Analysis, we’ll explain why we think this announcement is so important and what it means for Intel and the broader technology landscape. We’ll also share with you some feedback we received from theCUBE community on last week’s episode and a little inside baseball on how Intel, IBM Corp., Samsung Electronics Co. Ltd., Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Co. Ltd. and the U.S. government might be thinking about the shifting landscape of semiconductor technology.