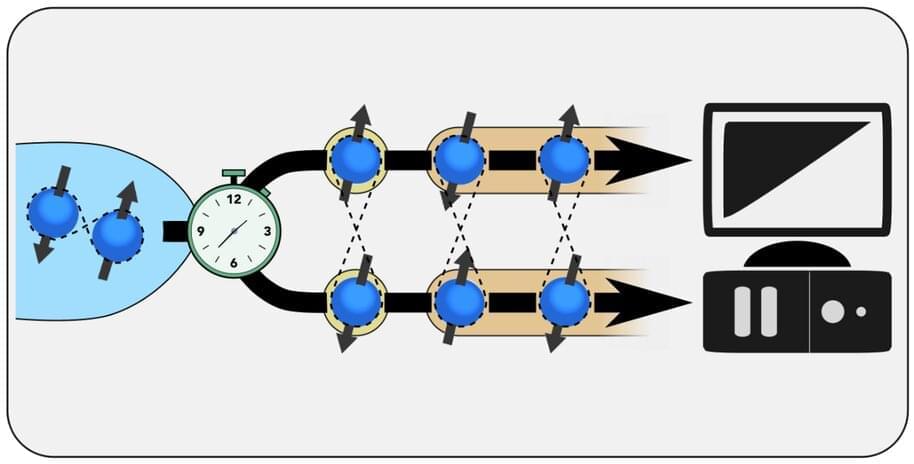
Quantum computer and many other quantum technologies rely on the generation of quantum-entangled pairs of electrons. However, the systems developed so far typically produce a noisy and random flow of entangled electrons, which hinders synchronized operations on the entangled particles. Now, researchers from Aalto University in Finland propose a way to produce a regular flow of spin-entangled electrons.
Their solution is based on a dynamically driven Cooper pair splitter. In a Cooper pair splitter, two quantum dots near a superconductor are used to generate and separate a pair of entangled electrons known as a Cooper pair. When the Cooper pair splitter is driven with a static voltage, the result is a random and noisy process.
A theoretical analysis by the Aalto team showed that driving the system dynamically with external gate voltages makes it possible to control the timing of the splitting process. As a result, exactly one pair of entangled electrons can be extracted during each splitting cycle, leading to a completely noiseless and regular flow of spin-entangled electrons.