Meta’s push to put computing into a headset will end in tears.



Nvidia’s software restriction to limit Ethereum mining over the RTX 3,000 graphics cards is officially dead because it’s now irrelevant.
On Friday, an Nvidia spokesperson confirmed that the company had removed the “Lite Hash Rate” limiter after users began reporting (Opens in a new window) the absence of the mining restriction in the latest Nvidia drivers releases for Windows and Linux.
“We don’t believe it’s necessary in the current environment,” the Nvidia spokesperson told PCMag without elaborating.
At 200 times stronger than steel, graphene has been hailed as a super material of the future since its discovery in 2004. The ultrathin carbon material is an incredibly strong electrical and thermal conductor, making it a perfect ingredient to enhance semiconductor chips found in many electrical devices.
But while graphene-based research has been fast-tracked, the nanomaterial has hit roadblocks: in particular, manufacturers have not been able to create large, industrially relevant amounts of the material. New research from the laboratory of Nai-Chang Yeh, the Thomas W. Hogan Professor of Physics, is reinvigorating the graphene craze.
In two new studies, the researchers demonstrate that graphene can greatly improve electrical circuits required for wearable and flexible electronics such as smart health patches, bendable smartphones, helmets, large folding display screens, and more.
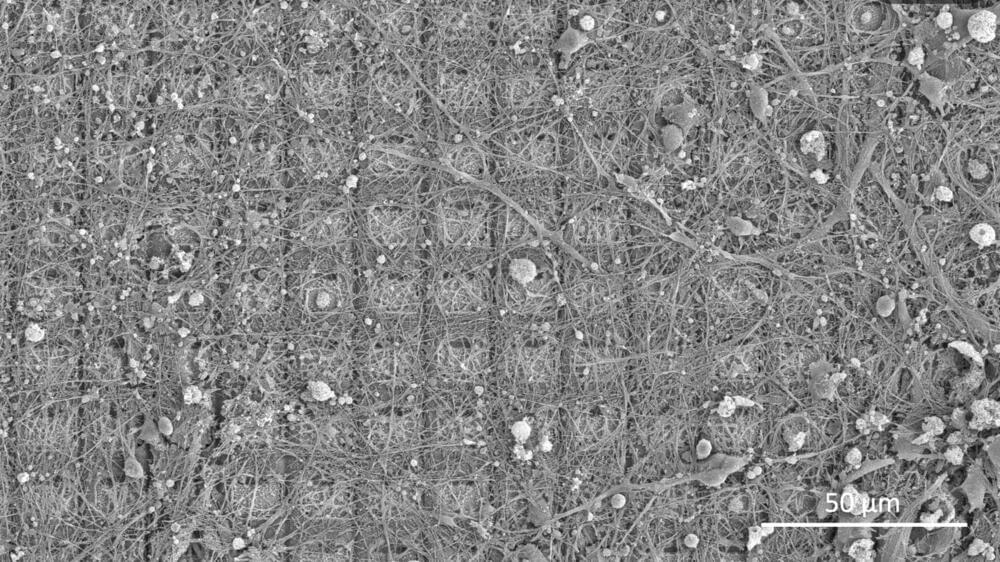
A dish of living brain cells has learned to play the 1970s arcade game Pong.
About 800,000 cells linked to a computer gradually learned to sense the position of the game’s electronic ball and control a virtual paddle, a team reports in the journal Neuron.
The novel achievement is part of an effort to understand how the brain learns, and how to make computers more intelligent.

Circa 2017 face_with_colon_three
To demonstrate this, researchers stored historic audio recordings on these molecules for the first time and then retrieved them with 100 percent accuracy. The experiment showed that DNA not only offers a place to save a dense package of information in a tiny space, but because it can last for hundreds of years, it reduces the risk that it will go out of date or degrade in the way that cassette tapes, compact discs, and even computer hard drives can.
“DNA is intrinsically and exquisitely a stable molecule,” Emily Leproust, CEO of the biotech firm Twist Bioscience, which works on DNA synthesis, told Seeker. Her company collaborated with Microsoft, the University of Washington, and the Montreux Jazz Digital Project on the DNA data feat.
The two performances they stored and retrieved, “Smoke on the Water” by Deep Purple and “Tutu” by Miles Davis, are the first DNA-saved files to be added to UNESCO’s Memory of the World Archive, a collection of audio and visual pieces of cultural significance. Both were performed at the Montreux Jazz Festival, an annual event in Switzerland.
Circa 2017 face_with_colon_three
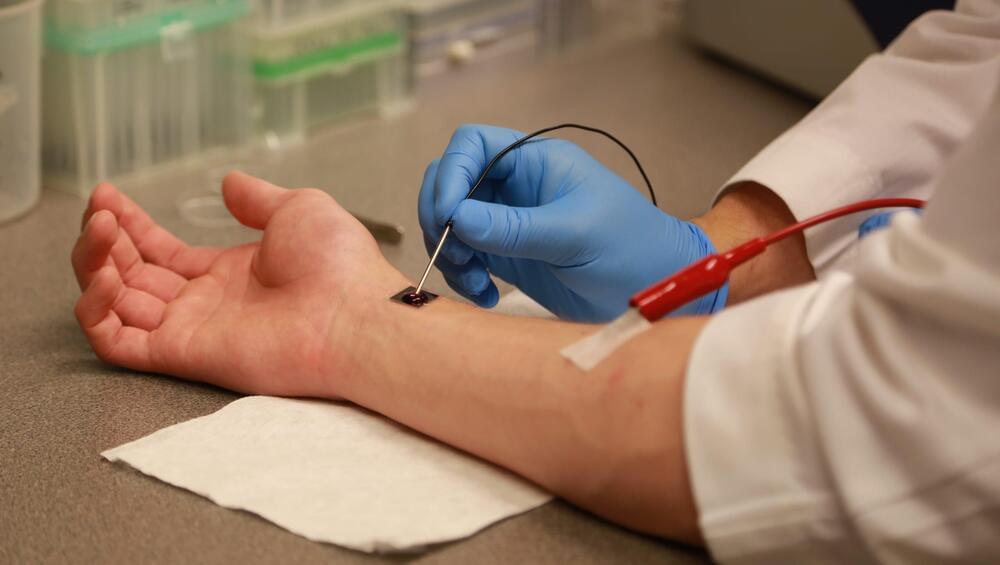
A new device developed at The Ohio State University can start healing organs in a “fraction of a second,” researchers say.
The technology, known as Tissue Nanotransfection (TNT), has the potential to save the lives of car crash victims and even deployed soldiers injured on site. It’s a dime-sized silicone chip that “injects genetic code into skin cells, turning those skin cells into other types of cells required for treating diseased conditions,” according to a release.
In lab tests, one touch of TNT completely repaired injured legs of mice over three weeks by turning skin cells into vascular cells.

A classic thought experiment in the philosophy of mind is reduplication, in which a person (or her mind) is duplicated such that two or more descendant people of shared mental ancestry now exist where previously there was one. The philosophical quandary is to resolve what happened to the original person’s identity. Did she survive and if so, in which of the resulting people’s minds? Which of the two resulting people is the original and which is a mere copy of denigrated identity status? Alternatively, is there something fundamentally wrong with the wording of such questions, such that we should we adopt a different perspective on the nature of personal identity that offers alternative solutions to the reduplication quandary? Reduplication further arises not only in abstract philosophical musings, but also in the futuristic and variously conceivable (depending on the reader’s tastes), technology of mind uploading, in which a person’s physical brain is emulated via the technology of whole brain emulation. While mind uploading might produce a single result, such as if the original brain is destroyed by the uploading process and only one upload is created, we can also conceive of either nondestructive scenarios (in which the original brain is not destroyed) or scenarios that produce multiple uploads. Either case results in multiple descendant minds, each operating in distinct physical systems (brains or cloned brains, or computers of some sort). The philosophy of personal identity has produced several possible stances on the nature of personal identity. The most popular are body identity and psychological identity, with other options including closest continuer identity, space-time worm identity and branching identity. However, there is always room for new theories to enter the discussion. The way in which blockchains work, and Bitcoin’s mining process and protocol for handling orphaned blocks, suggests a new theory of identity along with a new solution to the reduplication problem. The proposed blockchain solution to personal identity has applications to the handling of the reduplication problem as it may arise during a futuristic mind uploading procedure.
A blockchain holds a hashed transaction ledger, essentially the history of all transactions encoded to prevent any subsequent alteration of the history. In this way, all transactions back to the beginning of the ledger’s history can be confirmed by any interested party. Deceit, fraud, and other attempts to undermine the history simply don’t work, and consequently blockchains enable a variety of interactions with the currently most popular being digital currency. In addition to more conventional applications, blockchains could also be used to assign identity status (original or copy) to the descendent minds of a mind uploading procedure. Each descendant could then venture out into the world confident that their identity status will be honored by all third parties thereafter. Let us call this the blockchain theory of personal identity.

After spending two years on the ocean’s floor, Microsoft’s underwater data center had a much lower server failure rate than land-based data centers.