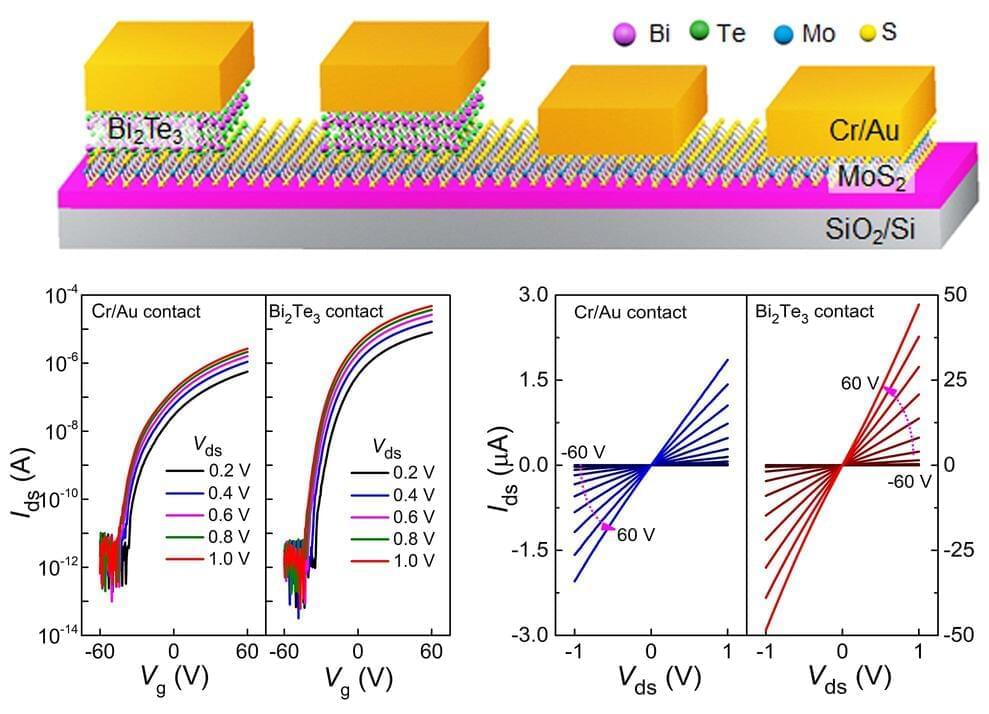
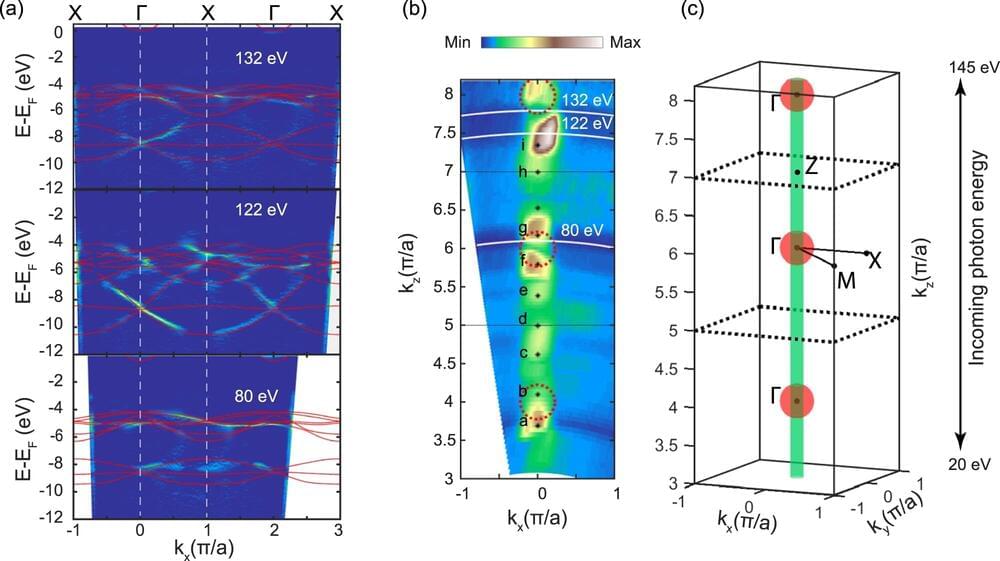
A team of researchers in China have developed a high-conductivity material that could greatly reduce contact resistance and Schottky barrier height within critical parts of electronic and optoelectronic microchips, paving the way for computer and digital imaging components that consume less power relative to their performance than existing chipsets.
The material, molybdenum disulfide (MoS2) is so thin that it falls into a classification of two-dimensional. That is, it is grown in sheets extending in two directions, X and Y, but virtually immeasurable on a Z axis because the material is often only a single molecule or atom in height.
The team, led by Professor Dong Li and Professor Anlian Pan, College of Materials Science and Engineering at Hunan University, published their findings in Nano Research.