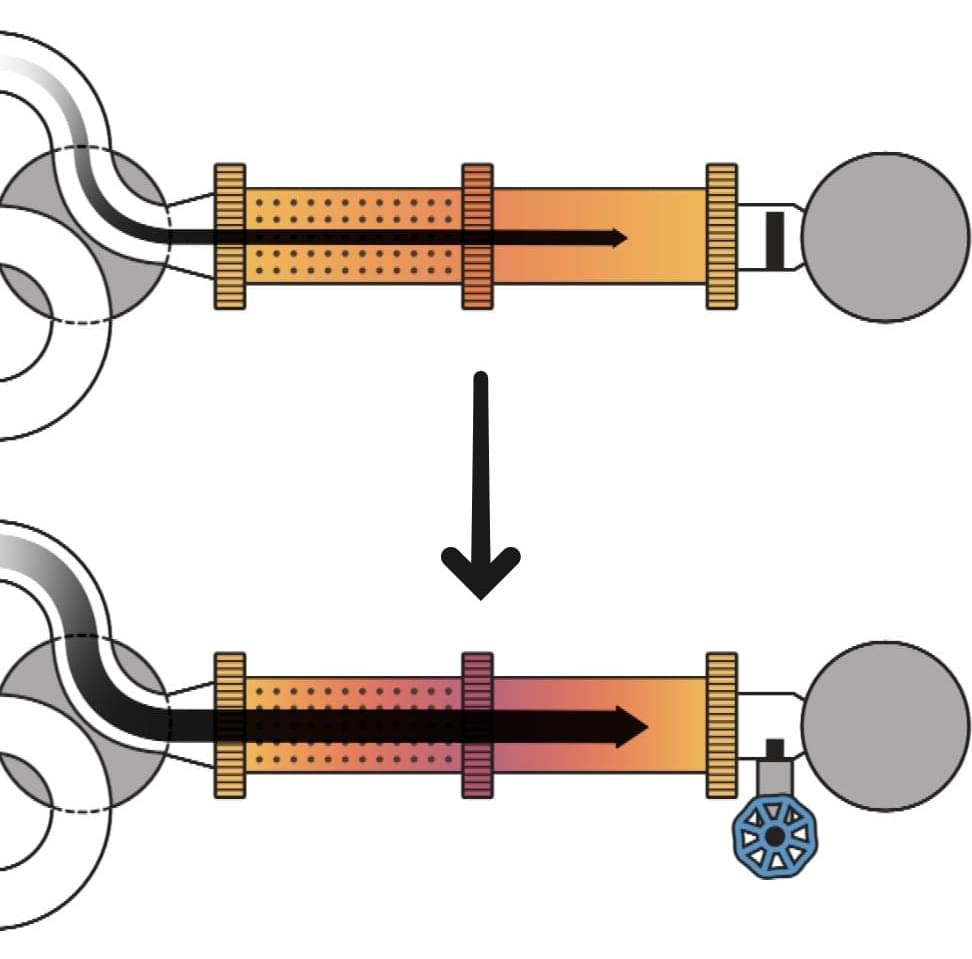
From stabilizing qubits (the basic unit of information in a quantum computer) to maintaining the superconducting properties of materials and keeping NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope cool enough to observe the heavens, ultracold refrigeration is essential to the operation of many devices and sensors. For decades, the pulse tube refrigerator (PTR) has been the workhorse device for achieving temperatures as cold as the vacuum of outer space.
These refrigerators cyclically compress (heat) and expand (cool) high pressure helium gas to achieve the “Big Chill,” broadly analogous to the way a household refrigerator uses the transformation of freon from liquid to vapor to remove heat. For more than 40 years, the PTR has proven its reliability, but it is also power-hungry, consuming more electricity than any other component of an ultralow temperature experiment.