While taking snapshots with the high-speed “electron camera” at the Department of Energy’s SLAC National Acceleratory Laboratory, researchers discovered new behavior in an ultrathin material that offers a promising approach to manipulating light that will be useful for devices that detect, control or emit light, collectively known as optoelectronic devices, and investigating how light is polarized within a material. Optoelectronic devices are used in many technologies that touch our daily lives, including light-emitting diodes (LEDs), optical fibers and medical imaging.
As reported in Nano Letters (“Giant Terahertz Birefringence in an Ultrathin Anisotropic Semimetal”), the team, led by SLAC and Stanford professor Aaron Lindenberg, found that when oriented in a specific direction and subjected to linear terahertz radiation, an ultrathin film of tungsten ditelluride, which has desirable properties for polarizing light used in optical devices, circularly polarizes the incoming light.
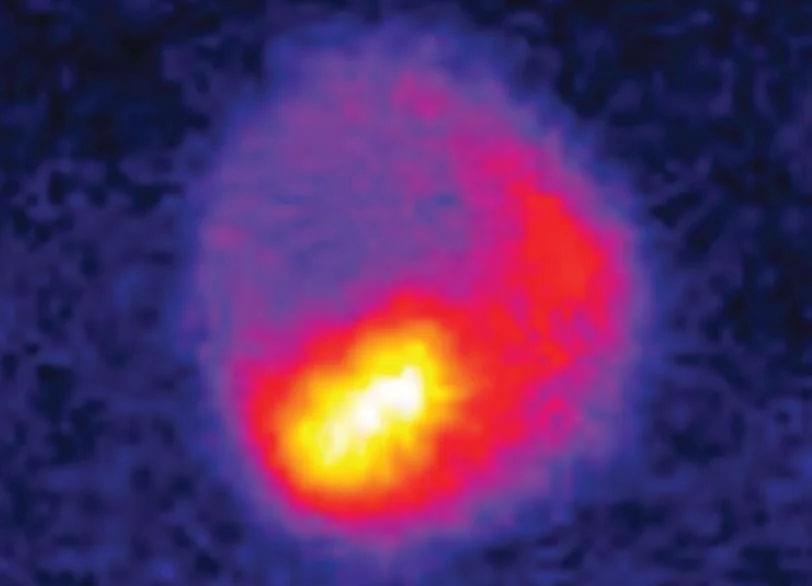
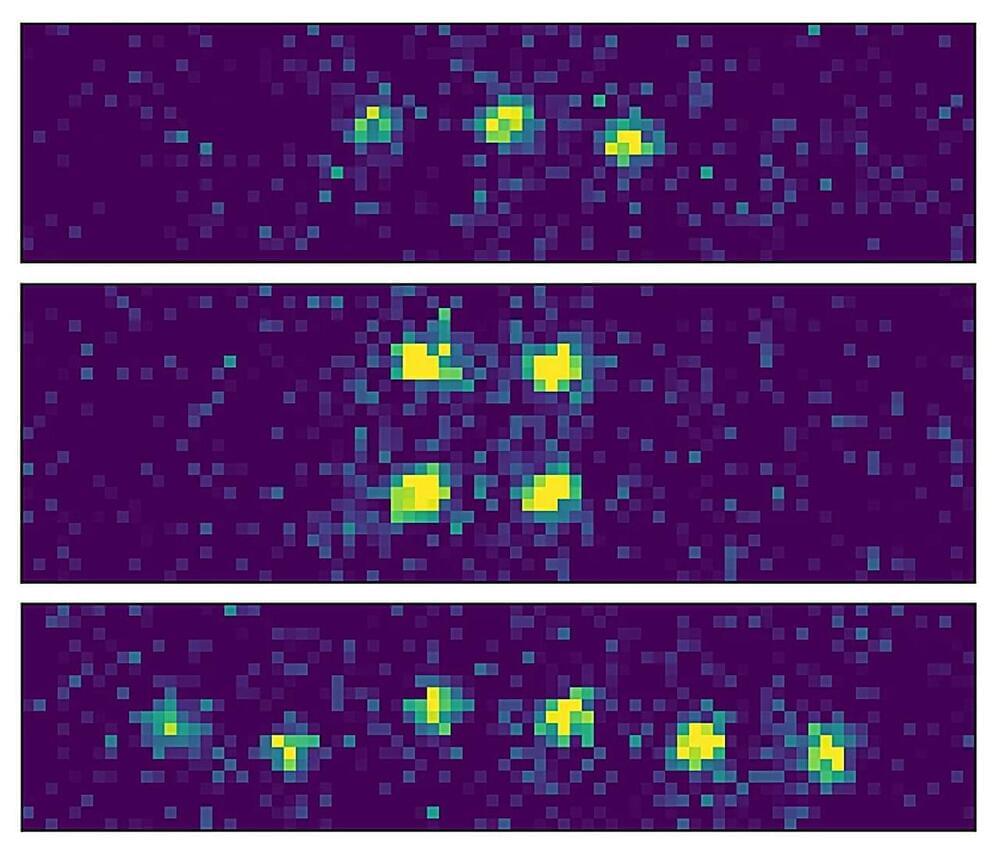
Snapshot taken by SLAC’s high-speed electron camera, an instrument for ultrafast electron diffraction (MeV-UED), showing evidence of circular polarization of terahertz light by an ultrathin sample of tungsten ditelluride. (Sie et al., Nano Letters, 8 May 2024)