Mar 17, 2023
A scalable and programmable quantum phononic processor based on trapped ions
Posted by Dan Breeden in categories: computing, particle physics, quantum physics
Quantum computing systems have the potential to outperform classical computers on some tasks, helping to solve complex real-world problems in shorter times. Research teams worldwide have thus been trying to realize this quantum advantage over traditional computers, by creating and testing different quantum systems.
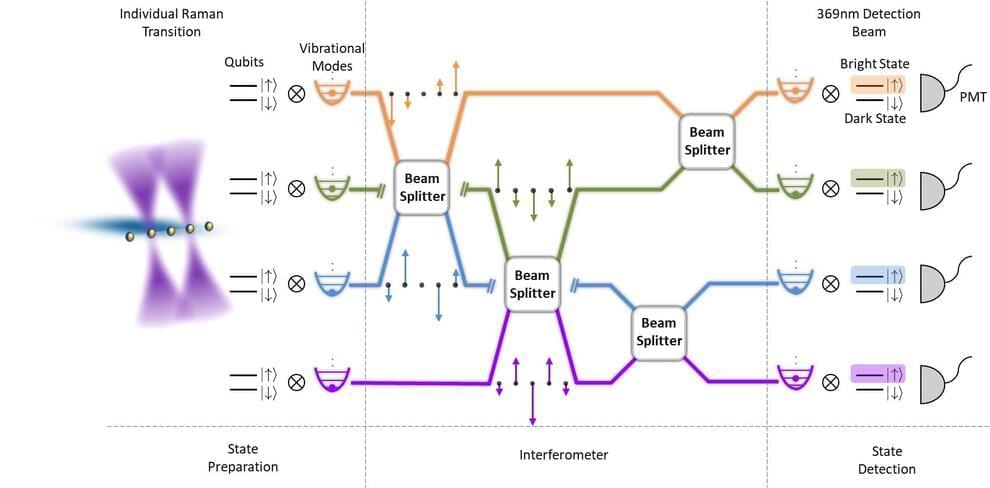
Researchers at Tsinghua University recently developed a new programmable quantum phononic processor with trapped ions. This processor, introduced in a paper in Nature Physics, could be easier to scale up in size than other previously proposed photonic quantum processors, which could ultimately enable better performances on complex problems.
“Originally, we were interested in the proposal of Scott Aaronson and others about Boson sampling, which might show the quantum advantages of simple linear optics and photons,” Kihwan Kim, one of the researchers who carried out the study, told Phys.org. “We were wondering if it is possible to realize it with the phonons in a trapped ion system.”