Chip war: China claims breakthrough in silicon photonics that could clear technical hurdle.
A Wuhan-based lab has announced a ‘milestone’ that could help China overcome restraints imposed by traditional chip-design technology.

A team of microchip engineers at Pragmatic Semiconductor, working with a pair of colleagues from Harvard University and another from Qamcom, has developed a bendable, programmable, non-silicon 32-bit RISC-V microprocessor. Their research is published in the journal Nature.
Over the past several years, hardware manufacturers have been developing bendable microprocessors for use in medical applications. A bendable device with bendable components would allow for the creation of 24-hour sensors that could be applied to any part of the body.
For this new project, the research team developed an inexpensive circuit board that could be bent around virtually any curved object. The material was made using indium gallium zinc oxide instead of the more rigid silicon.
Masafumi Oizumi: Unsupervised alignment of qualia structures: Towards direct communication of experience.
Pre-ASSC (2024, June 30, Sun) Satellite Workshop Registration Form: Structural approaches to consciousness: Qualia Structure and Integrated Information Theory.
— program -
Day: June 30, 2024 (Sun)
Time: 9:00–17:00
Place: Ito Hall, Ito International Research Center, University of Tokyo.
Aims:
In this satellite symposium, hosted by the Qualia Structure, we will discuss the current state of the structural approaches to consciousness from empirical, computational and theoretical perspectives. The satellite will be open to any researcher (but registration is required) who are interested in the structural approach to consciousness. A one day event will be a mixture of lectures and poster presentations.
Registration: Free.

The foundation of this simulation, as described by the team, is a well-known cosmological model that describes the universe as expanding uniformly over time. The researchers modeled how a quantum field, initially in a vacuum state (meaning no particles are present), responds to this expansion. As spacetime stretches, the field’s oscillations mix in a process that can create particles where none previously existed. This phenomenon is captured by a transformation that relates the field’s behavior before and after the universe expands, showing how vibrations at different momenta become entangled, leading to particle creation.
To understand how many particles are generated, the researchers used a mathematical tool called the Bogoliubov transformation. This approach describes how the field’s vacuum state evolves into a state where particles can be detected. As the expansion rate increases, more particles are produced, aligning with predictions from quantum field theory. By running this simulation on IBM quantum computers, the team was able to estimate the number of particles created and observe how the quantum field behaves during the universe’s expansion, offering a new way to explore complex cosmological phenomena.
According to the team, the most notable result of the study was the ability to estimate the number of particles created as a function of the expansion rate of the universe. By running their quantum circuit on both simulators and IBM’s 127-qubit Eagle quantum processor, the researchers demonstrated that they could successfully simulate particle creation in a cosmological context. While the results were noisy—particularly for low expansion rates—the error mitigation techniques used helped bring the outcomes closer to theoretical predictions.
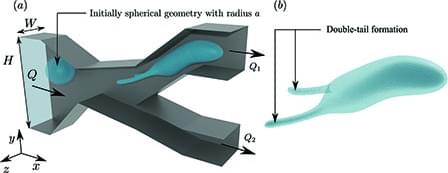
The physics of drop motion in microchannels is fundamental to provide insights when designing applications of drop-based microfluidics. In this paper, we develop a boundary-integral method to simulate the motion of drops in microchannels of finite depth with flat walls and fixed depth but otherwise arbitrary geometries. To reduce computational time, we use a moving frame that follows the droplet throughout its motion. We provide a full description of the method, including our channel-meshing algorithm, which is a combination of Monte Carlo techniques and Delaunay triangulation, and compare our results to infinite-depth simulations. For regular geometries of uniform cross section, the infinite-depth limit is approached slowly with increasing depth, though we show much faster convergence by scaling with maximum vs average velocities. For non-regular channel geometries, features such as different branch heights can affect drop partitioning, breaking the symmetric behavior usually observed in regular geometries. Moreover, non-regular geometries also present challenges when comparing the results for deep and infinite-depth channels. To probe inertial effects on drop motion, the full Navier–Stokes equations are first solved for the entire channel, and the tabulated solution is then used as a boundary condition at the moving-frame surface for the Stokes flow inside the moving frame. For moderate Reynolds numbers up to Re = 5, inertial effects on the undisturbed flow are small even for more complex geometries, suggesting that inertial contributions in this range are likely small. This work provides an important tool for the design and analysis of three-dimensional droplet-based microfluidic devices.
In recent years, quantum physicists and engineers have made significant strides toward the development of highly performing quantum computing systems. Realizing a quantum advantage over classical computing systems and enabling the stable operation of quantum devices, however, will require the development of new building blocks for these devices and other aspects underlying their correct functioning.
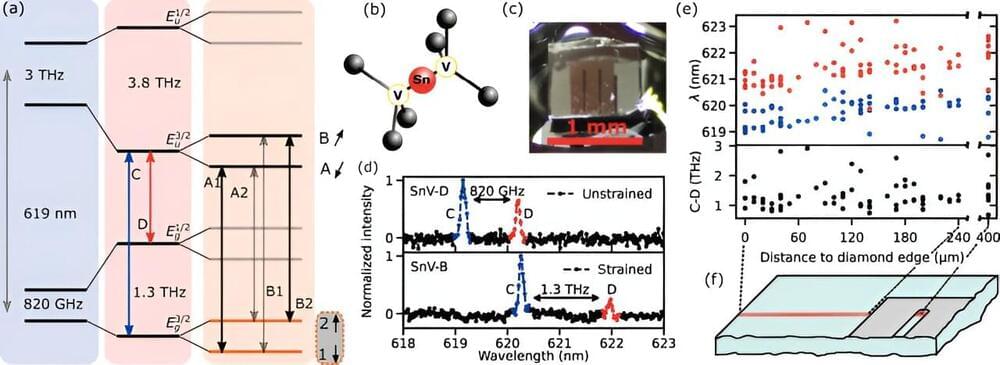
In a first for Germany, researchers at the Karlsruhe Institute of Technology (KIT) have shown how tin vacancies in diamonds can be precisely controlled using microwaves. These vacancies have special optical and magnetic properties and can be used as qubits, the smallest computational units for quantum computing and quantum communication. The results are an important step for the development of high-performance quantum computers and secure quantum communications networks.
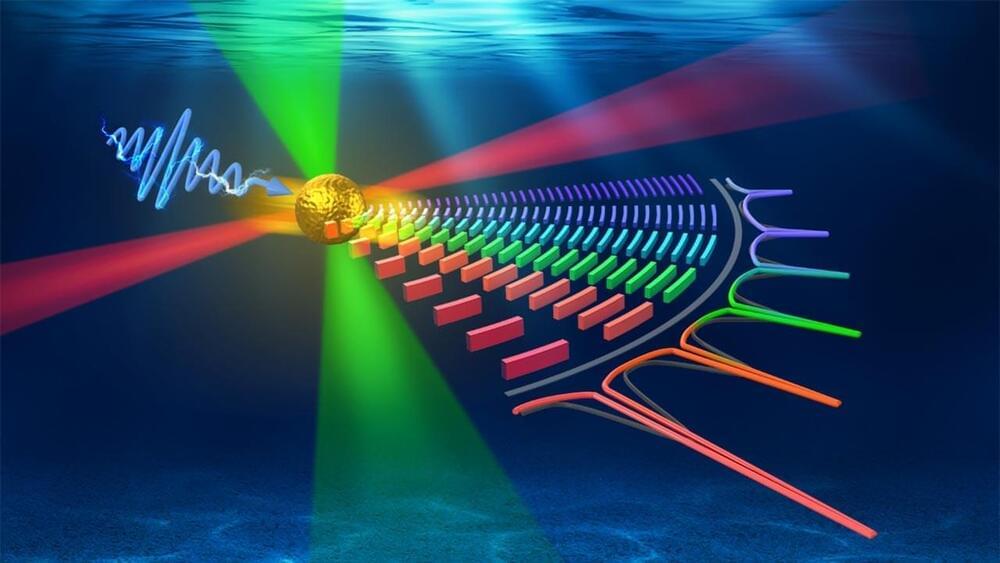
Recent advancements in phonon laser technology, which utilizes sound waves rather than light, show promising new applications in medical imaging and deep-sea exploration.
A novel technique enhances these lasers by stabilizing and strengthening the sound waves, allowing for more precise and powerful outputs. This development not only improves existing uses in medical and underwater applications but also extends potential uses to material science and quantum computing.
Enhancing Phonon Laser Technology
Researchers have developed a promising new optical memory technology using rare earth elements and quantum defects to enable denser and more efficient data storage.
This innovative approach utilizes wavelength multiplexing to increase bit density beyond traditional methods like CDs and DVDs, with theoretical models supporting the potential of near-field energy transfer for long-lasting data retention.
Introduction to Optical Memory Evolution.
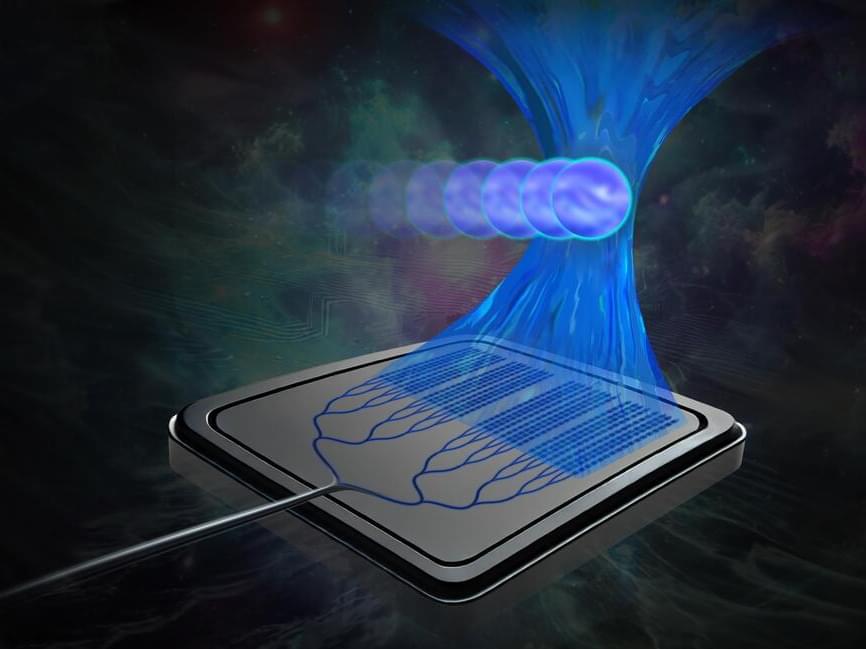
MIT researchers have developed a miniature, chip-based “tractor beam,” like the one that captures the Millennium Falcon in the film “Star Wars,” that could someday help biologists and clinicians study DNA, classify cells, and investigate the mechanisms of disease.
Small enough to fit in the palm of your hand, the device uses a beam of light emitted by a silicon-photonics chip to manipulate particles millimeters away from the chip surface. The light can penetrate the glass cover slips that protect samples used in biological experiments, enabling cells to remain in a sterile environment.
Traditional optical tweezers, which trap and manipulate particles using light, usually require bulky microscope setups, but chip-based optical tweezers could offer a more compact, mass manufacturable, broadly accessible, and high-throughput solution for optical manipulation in biological experiments.