The biological roots of autism continue to perplex researchers, despite a growing body of studies looking at an increasing array of genetic, cellular and microbial data. Recently, scientists have homed in on a new and promising area of focus: the microbiome. This collection of microbes that inhabit the human gut has been shown to play a role in autism, but the mechanics of this link have remained awash in ambiguity.
Taking a fresh computational approach to the problem, a study published today, June 26, in Nature Neuroscience sheds new light on the relationship between the microbiome and autism. This research—which originated at the Simons Foundation’s Autism Research Initiative (SFARI) and involved an innovative reanalysis of dozens of previously published datasets—aligns with a recent, long-term study of autistic individuals that centered on a microbiome-focused treatment intervention. These findings also underscore the importance of longitudinal studies in elucidating the interplay between the microbiome and complex conditions such as autism.
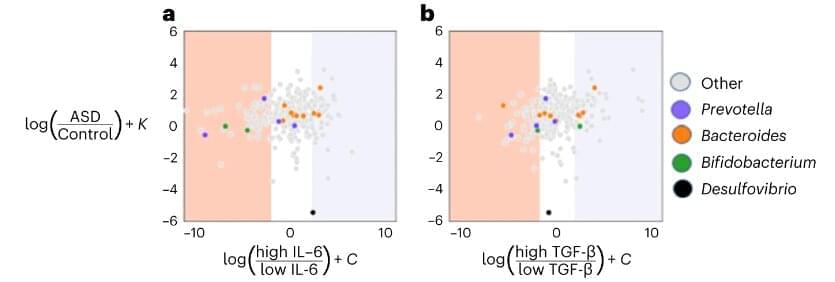
“We were able to harmonize seemingly disparate data from different studies and find a common language with which to unite them. With this, we were able to identify a microbial signature that distinguishes autistic from neurotypical individuals across many studies,” says Jamie Morton, one of the study’s corresponding authors, who began this work while a postdoctoral researcher at the Simons Foundation and is now an independent consultant. “But the bigger point is that going forward, we need robust long-term studies that look at as many datasets as possible and understand how they change when there is a [therapeutic] intervention.”