Two new therapies—one which uses the gene-editing technology—treat sickle cell anemia.

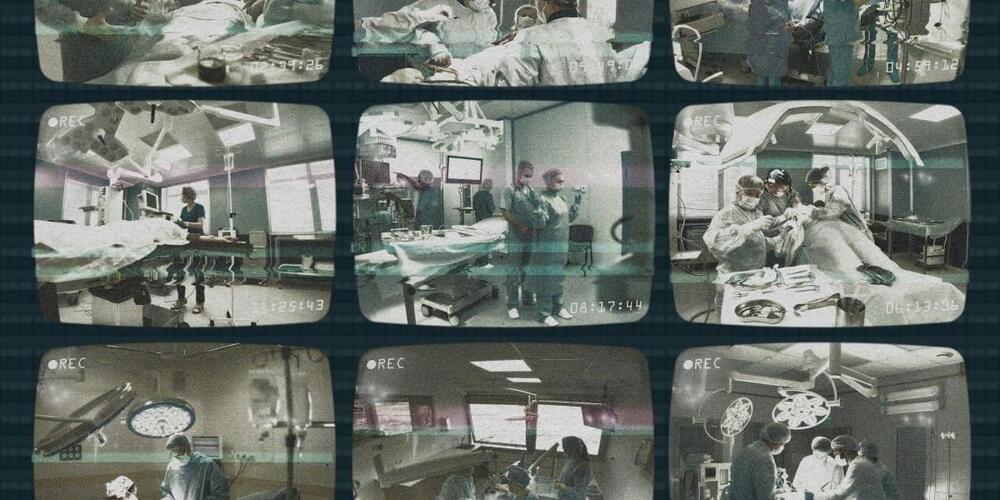
1. Privacy is important, but not always guaranteed. Grantcharov realized very quickly that the only way to get surgeons to use the black box was to make them feel protected from possible repercussions. He has designed the system to record actions but hide the identities of both patients and staff, even deleting all recordings within 30 days. His idea is that no individual should be punished for making a mistake.
The black boxes render each person in the recording anonymous; an algorithm distorts people’s voices and blurs out their faces, transforming them into shadowy, noir-like figures. So even if you know what happened, you can’t use it against an individual.
But this process is not perfect. Before 30-day-old recordings are automatically deleted, hospital administrators can still see the operating room number, the time of the operation, and the patient’s medical record number, so even if personnel are technically de-identified, they aren’t truly anonymous. The result is a sense that “Big Brother is watching,” says Christopher Mantyh, vice chair of clinical operations at Duke University Hospital, which has black boxes in seven operating rooms.
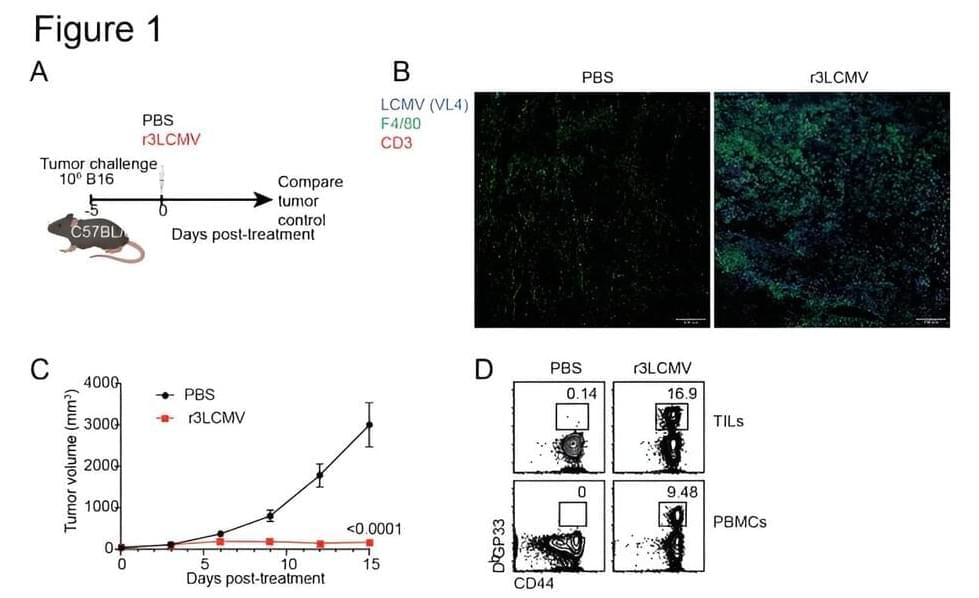
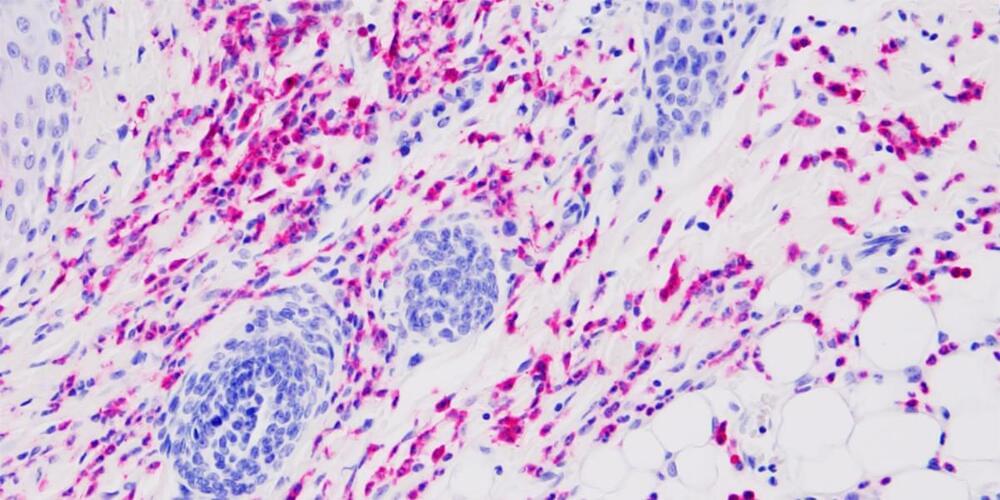
Currently, so-called “oncolytic viruses” such as herpes are used to treat some types of cancer because of their ability to kill cancer cells. But these therapies are not effective with some tumors and their use poses safety concerns, especially in immunosuppressed patients, underscoring the need for safer alternatives, Penaloza-MacMaster said.
In addition to helping clear the tumors, the therapy also helped prevent future cancer in these mice. Healthy mice that were first treated with the LCMV therapy were more resistant to developing tumors later in life.
This phenomenon might be explained by a poorly understood biological process known as “trained immunity.” Trained immunity occurs when a previous infection enhances the immune system’s ability to respond to different diseases in the future. For example, studies have shown that children who received the tuberculosis (TB) vaccine exhibit improved protection against other microorganisms, not just TB. This differs from the typical vaccine response, such as with the SARS-CoV-2 vaccine, which primarily protects against this specific virus.
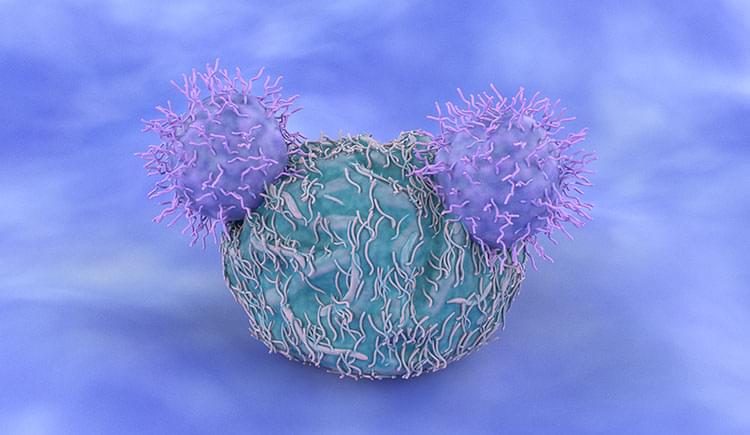
Significance of the work.
CAR T cells are genetically engineered immune cells tailored to respond to a specific molecule found on the surface of tumor cells. These cells are a form of immunotherapy — an approach that harnesses the native ability of the immune system to fight diseases, particularly cancer. CAR T-cell therapy represents a milestone in cancer treatment. It propels cancer therapies beyond traditional chemotherapy and radiation treatments, which are often highly toxic and non-specific.
The four scientists honored with this year’s Warren Alpert Foundation Prize each played key distinct and complementary roles in developing CAR T cells and making their use in the clinic possible. Today, CAR T-cell therapies offer great hope for patients with various B-cell malignancies who have relapsed or failed to respond to other therapies. CAR T cell-based approaches could eventually be used to treat solid tumors, as well as a variety of autoimmune diseases and other conditions.
A map of the entire human brain could help us understand where diseases come from, to how we store memories. But mapping the brain with today’s technology would take billions of dollars and hundreds of years. Learn what GR has already revealed about the brain, and how it’s making it easier for scientists to—someday—reach this goal.
#GoogleResearch

How can long-term space flight influence astronaut health, and specifically their organs? This is what a recent study published in Nature Communications hopes to address as a large team of international researchers conducted the most comprehensive study regarding astronaut kidney health and how it’s affected from both microgravity and galactic cosmic radiation (GCR) during long-term space missions. This study holds the potential to help astronauts, space agencies, medical professionals, and the public better understand the health risks associated with sending humans to other worlds, specifically to Mars.
“We know what has happened to astronauts on the relatively short space missions conducted so far, in terms of an increase in health issues such as kidney stones,” said Dr. Keith Siew, who is a Research Fellow in the Department of Renal Medicine at the University of College London (UCL) and lead author of the study. “What we don’t know is why these issues occur, nor what is going to happen to astronauts on longer flights such as the proposed mission to Mars.”
Aside from the 24 Apollo astronauts who traveled to the Moon, with 12 of them walking on the surface, nearly all human space travel has been limited to low-Earth orbit (LEO), totaling almost 700 people having traveled to space. During this time, they are protected by the Earth’s magnetic field, which shields them from harmful solar and cosmic radiation that could cause potentially irreparable harm to their health.
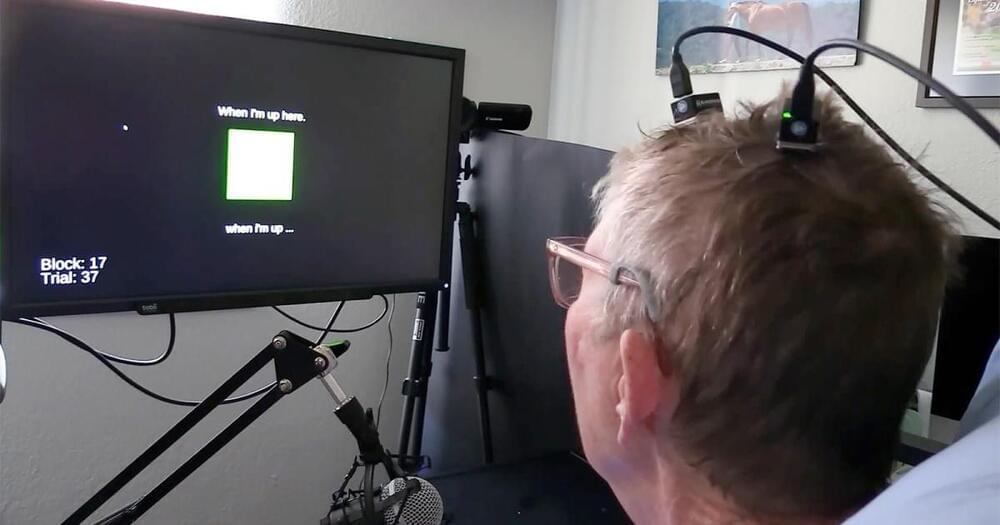

Stanford researchers have developed a speech brain-computer interface (BCI) they say can translate thoughts into text at a record-breaking speed — putting us closer to a future in which people who can’t talk can still easily communicate.
The challenge: “Anarthria” is a devastating condition in which a person can’t speak, despite being able to understand speech and knowing what they want to say. It’s usually caused by a brain injury, such as a stroke, or a neurological disorder, such as Parkinson’s disease or ALS.
Some people with anarthria write or use eye-tracking tech to communicate, but this “speech” is far slower than the average talking speed. People with anarthria due to total paralysis or locked-in syndrome can’t even move their eyes, though, leaving them with no way to communicate.

This interview with Yip Thy Diep Ta, CEO of J3d.ai, delves into AI-driven collective intelligence for decision-making, ethical considerations in AI development (fairness, bias mitigation, diversity), the implications of human-machine integration technologies (e.g., Neuralink), and the evolving role of humans in an AI-driven workforce.
Systain3r Summit: https://www.systain3r.com/
#AI #AGI #Futureofwork.
SingularityNET was founded by Dr. Ben Goertzel with the mission of creating a decentralized, democratic, inclusive, and beneficial Artificial General Intelligence (AGI). An AGI is not dependent on any central entity, is open to anyone, and is not restricted to the narrow goals of a single corporation or even a single country.
The SingularityNET team includes seasoned engineers, scientists, researchers, entrepreneurs, and marketers. Our core platform and AI teams are further complemented by specialized teams devoted to application areas such as finance, robotics, biomedical AI, media, arts, and entertainment.
Website: https://singularitynet.io.