In a public interview, Chinese biophysicist He Jiankui said he is receiving offers of financial support from figures in the US.



An algorithm developed by Washington State University researchers can better find data anomalies than current anomaly-detection software, including in streaming data.
The work, reported in the Journal of Artificial Intelligence Research, makes fundamental contributions to artificial intelligence (AI) methods that could have applications in many domains that need to quickly find anomalies in large amounts of data, such as in cybersecurity, power grid management, misinformation, and medical diagnostics.
Being able to better find the anomalies would mean being able to more easily discover fraud, disease in a medical setting, or important unusual information, such as an asteroid whose signals overlap with the light from other stars.
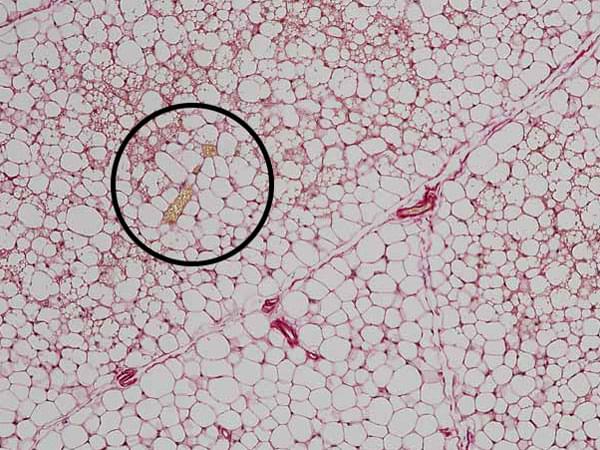
A new study shows that suppressing a protein turns ordinary fat into a calorie burner and may explain why drug trials attempting the feat haven’t been successful.
Researchers at UC San Francisco have figured out how to turn ordinary white fat cells, which store calories, into beige fat cells that burn calories to maintain body temperature.
The discovery could open the door to developing a new class of weight-loss drugs and may explain why clinical trials of related therapies have not been successful.
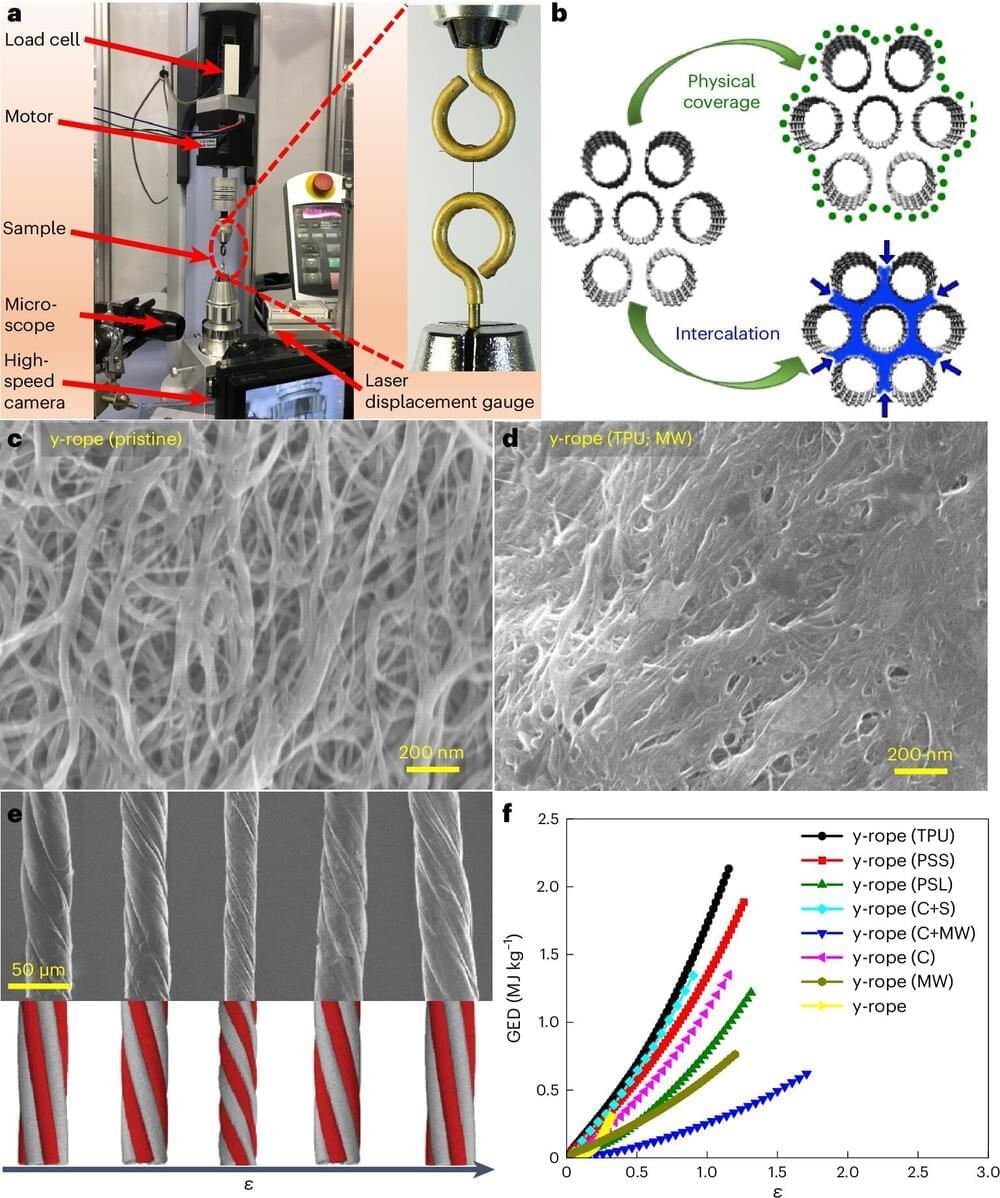
An international team of scientists, including two researchers who now work in the Center for Advanced Sensor Technology (CAST) at UMBC, has shown that twisted carbon nanotubes can store three times more energy per unit mass than advanced lithium-ion batteries. The finding may advance carbon nanotubes as a promising solution for storing energy in devices that need to be lightweight, compact, and safe, such as medical implants and sensors. The research was published recently in the journal Nature Nanotechnology.

If there’s one phrase the June 2024 U.S. presidential debate may entirely eliminate from the English vocabulary it’s that age is a meaningless number. Often attributed to boxer Muhammad Ali, who grudgingly retired at age 39, this centuries-old idea has had far-reaching consequences in global politics, as life expectancy more than doubled since the start of the 20th century, and presidents’ ages shifted upwards. We say “age is what we make of it” to ourselves and to policymakers, and think it’s a harmless way to dignify the aged. But how true is it? And if it isn’t true, why would we lie?
For centuries, we have confused our narrative of what aging should be with what its ruthless biology is. Yet pretending that biological age does not matter is at best myopic, and at worst, it’s a dangerous story to our governments, families, and economies. In just 11 years — between 2018 and 2029 — U.S. spending on Social Security and Medicare will more than double, from $1.3 trillion to $2.7 trillion per year. As we age, our odds of getting sick and dying by basically anything go up exponentially. If smoking increases our chances of getting cancer by a factor of 15, aging does so 100-fold. At age 65, less than 5% of people are diagnosed with Alzheimer’s. Beyond age 85, nearly half the population has some form of dementia. Biological aging is the biggest risk factor for most chronic diseases; it’s a neglected factor in global pandemics; and it even plays a role in rare diseases.
This explains why in hospitals, if there’s one marker next to a patient’s name, it’s their age. How many birthday candles we have blown out is an archaic surrogate marker of biological aging. Yet it’s the best we have. Chronological age is so telling of overall health that physicians everywhere rely on it for life-or-death decisions, from evaluating the risks of cancer screening to rationing hospital beds.

Geneformer is a recently introduced and powerful AI model that learns gene network dynamics and interactions using transfer learning from vast single-cell transcriptome data. This tool enables researchers to make accurate predictions about gene behavior and disease mechanisms even with limited data, accelerating drug target discovery and advancing understanding of complex genetic networks in various biological contexts.
Developed by researchers at the Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard and their collaborators, the AI model Geneformer uses the highest-expressed genes in sc-RNA expression data to generate a dense representation of each cell, which can be used as features for various downstream predictive tasks. What makes Geneformer unique, however, are the capabilities its architecture enables, even when trained on very little data.
Geneformer has a BERT-like transformer architecture and was pre-trained on data from about 30M single-cell transcriptomes across various human tissues. Its attention mechanism enables it to focus on the most relevant parts of the input data. With this context-aware approach, the model can make predictions by considering relationships and dependencies between genes.
Replicating these processes in AI systems is a significant challenge. One of the most exciting applications is in this field. Leveraging OI can help in training AI models more effectively. The dynamic neural networks in organoids can serve as a blueprint for creating more human-like AI systems.
The development of AI-enabled organoids is a promising field that combines AI with organoids to create more precise models of human organ functionality and diseases. This convergence could revolutionize drug discovery, disease diagnosis and the development of advanced treatments. AI helps organoids by guiding them through three crucial dimensions:
1. Hybrid Intelligence: A potential future scenario involves merging OI with traditional AI systems. This fusion could result in a new era of “hybrid intelligence” that combines the analytical power of AI with the nuanced understanding of human-like cognition.
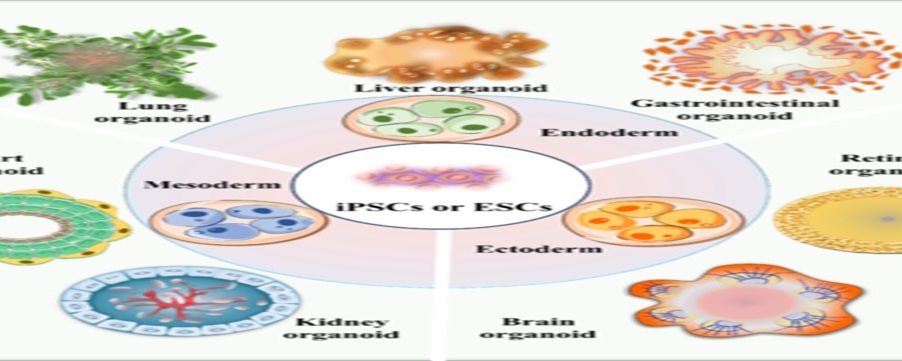
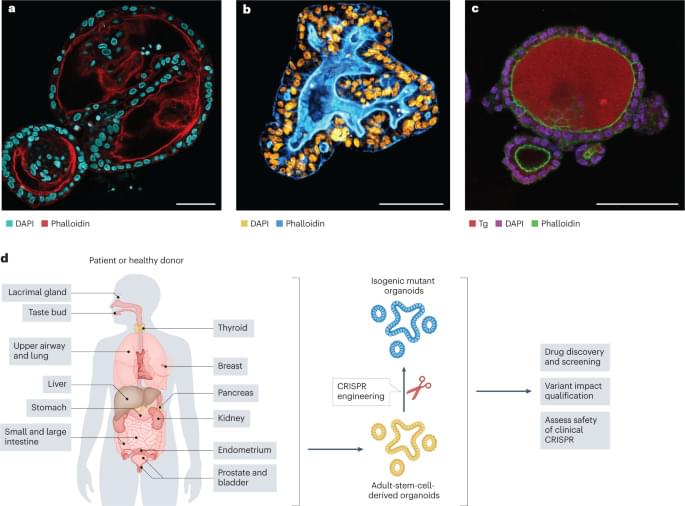
Analyzed the global trends in this area of neuroscience. To identify and further facilitate the development of cerebral organoids, we utilized bibliometrics and visualization methods to analyze the global trends and evolution of brain organoids in the last 10 years. First, annual publications, countries/regions, organizations, journals, authors, co-citations, and keywords relating to brain organoids were identified. The hotspots in this field were also systematically identified. Subsequently, current applications for brain organoids in neuroscience, including human neural development, neural disorders, infectious diseases, regenerative medicine, drug discovery, and toxicity assessment studies, are comprehensively discussed.