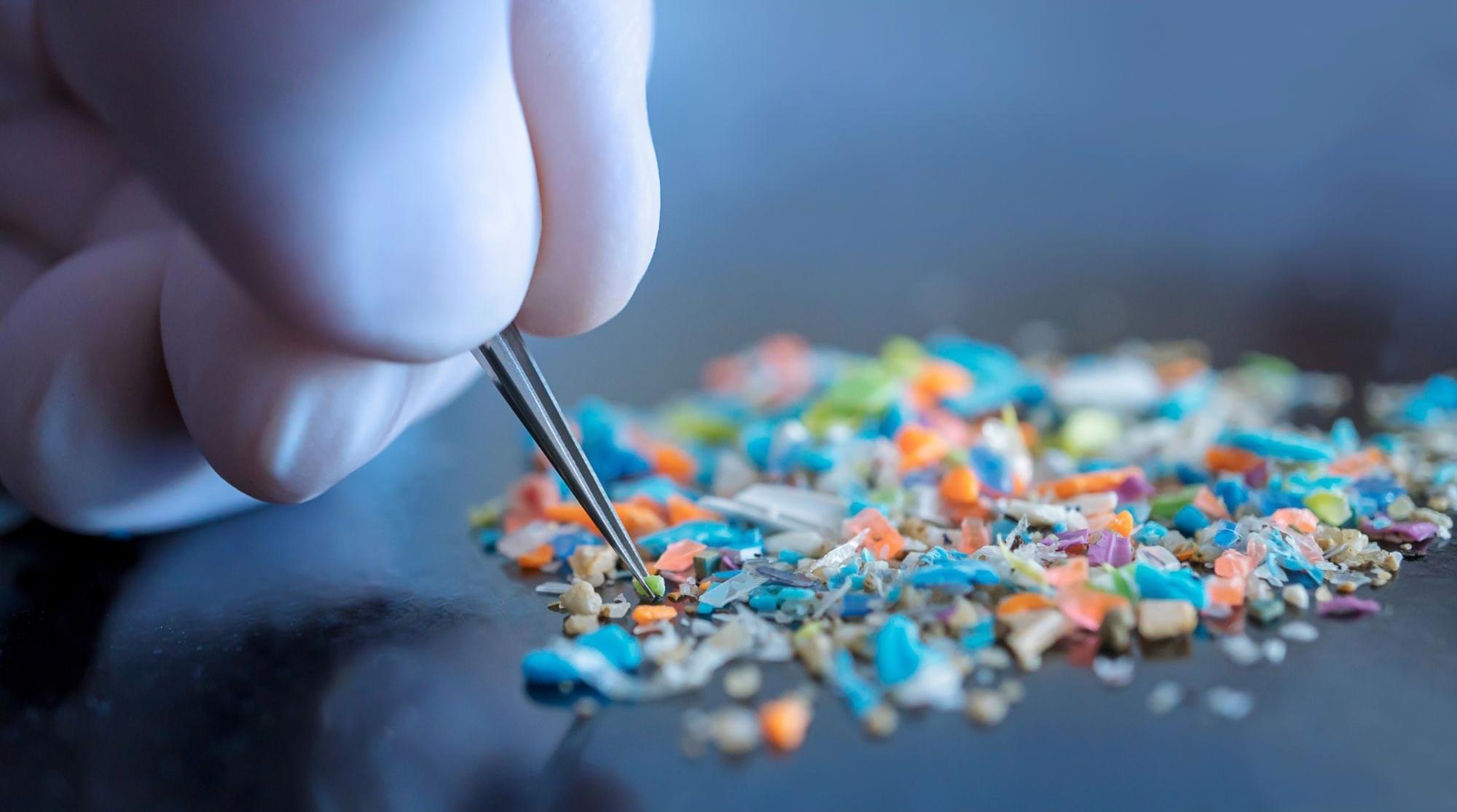
A global study estimates that exposure to the plastic additive DEHP caused over 356,000 heart disease deaths in 2018, with most deaths occurring in rapidly industrializing regions. A new analysis of global population data suggests that daily exposure to certain chemicals used in plastic household
Category: biotech/medical – Page 6
This “DNA origami” may facilitate the transportation of large therapeutic loads into cells
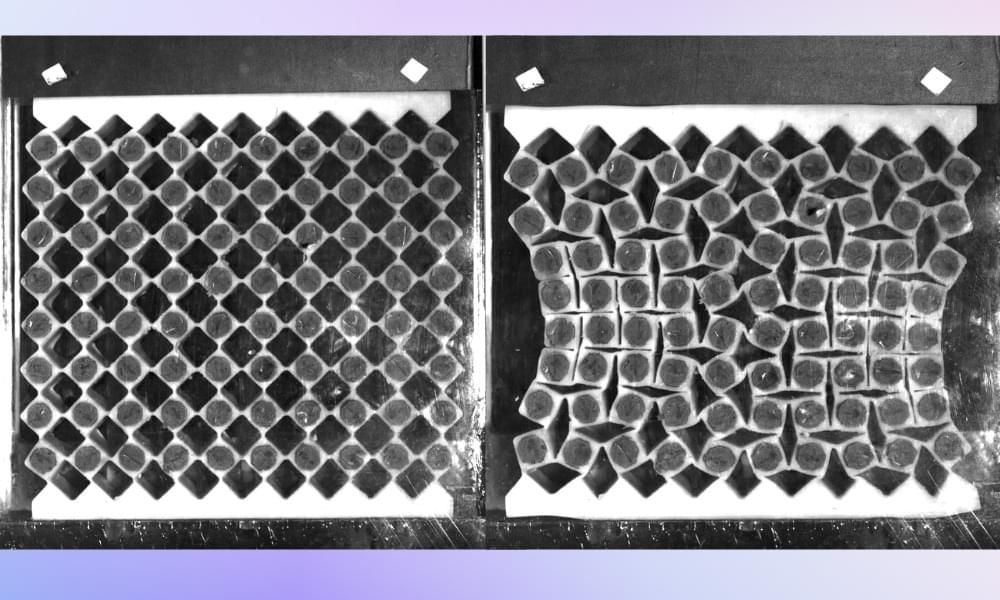
Researchers from Universidad Carlos III de Madrid (UC3M) and Harvard University have experimentally demonstrated that new artificial materials known as metamaterials, with magnetic properties, can have their mechanical and structural behavior reprogrammed without altering their composition. This breakthrough could drive innovations in fields such as soft robotics and biomedicine.
The study explains how flexible magnets embedded within the structure of mechanical metamaterials can be used to reprogram their behavior.
The integration of flexible magnets in metamaterials allows for reprogrammable structures, offering vast potential in robotics and biomedical engineering.
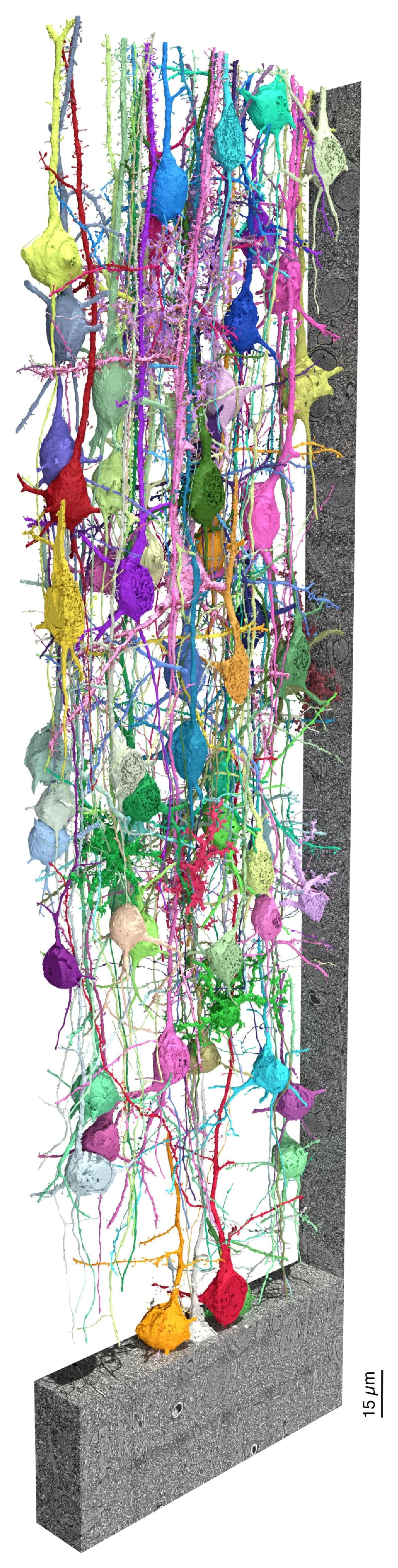
Until now, only expensive and slow electron microscopes could reach this level of detail. But LICONN opens the door for more labs around the world to explore the brain’s cellular “wiring diagram” using tools they already have. It’s like giving everyone a high-powered zoom lens for decoding how the brain works, learns, and perhaps breaks down in disease.
In collaboration with the Institute of Science and Technology Austria (ISTA), we published in Nature the first-ever method for using light microscopy to comprehensively map all the neurons and their connections in a block of brain tissue. The key finding from this validation experiment is that this approach works as well as electron microscopy-based connectomics.
Our brain is a complex organ. Billions of nerve cells are wired in an intricate network, constantly processing signals, enabling us to recall memories or to move our bodies.
Making sense of this complicated network requires a precise look into how these nerve cells are arranged and connected. “LICONN,” a new microscopy method developed by scientists at the Institute of Science and Technology Austria (ISTA) and Google Research, now helps piece together this puzzle.
Light microscopes have been evolving for centuries. Scientists use light microscopy to—literally and figuratively—illuminate the most intricate biological structures. However, unraveling the complex details and architecture of the brain remains a seemingly impossible challenge, considering its billions of densely packed neurons, each linked to other cells via thousands of synapses.
A new study suggests that, in the case of global catastrophe, urban agriculture alone could sustain only about one fifth of the population of a temperate, median-sized city, but the whole city could be fed by also farming land within a short distance of the urban area.
Matt Boyd of Adapt Research Ltd, New Zealand, and Nick Wilson of the University of Otago, New Zealand, present these findings in PLOS One.
Abrupt global catastrophes—such as nuclear wars, extreme pandemics, or solar storms—could severely hamper global trade. Shortages of resources like liquid fuels could disrupt food production and transport, possibly leading to famine. Prior research has suggested that this impact could be mitigated by urban agriculture, which includes such approaches as home, community, and rooftop gardens.
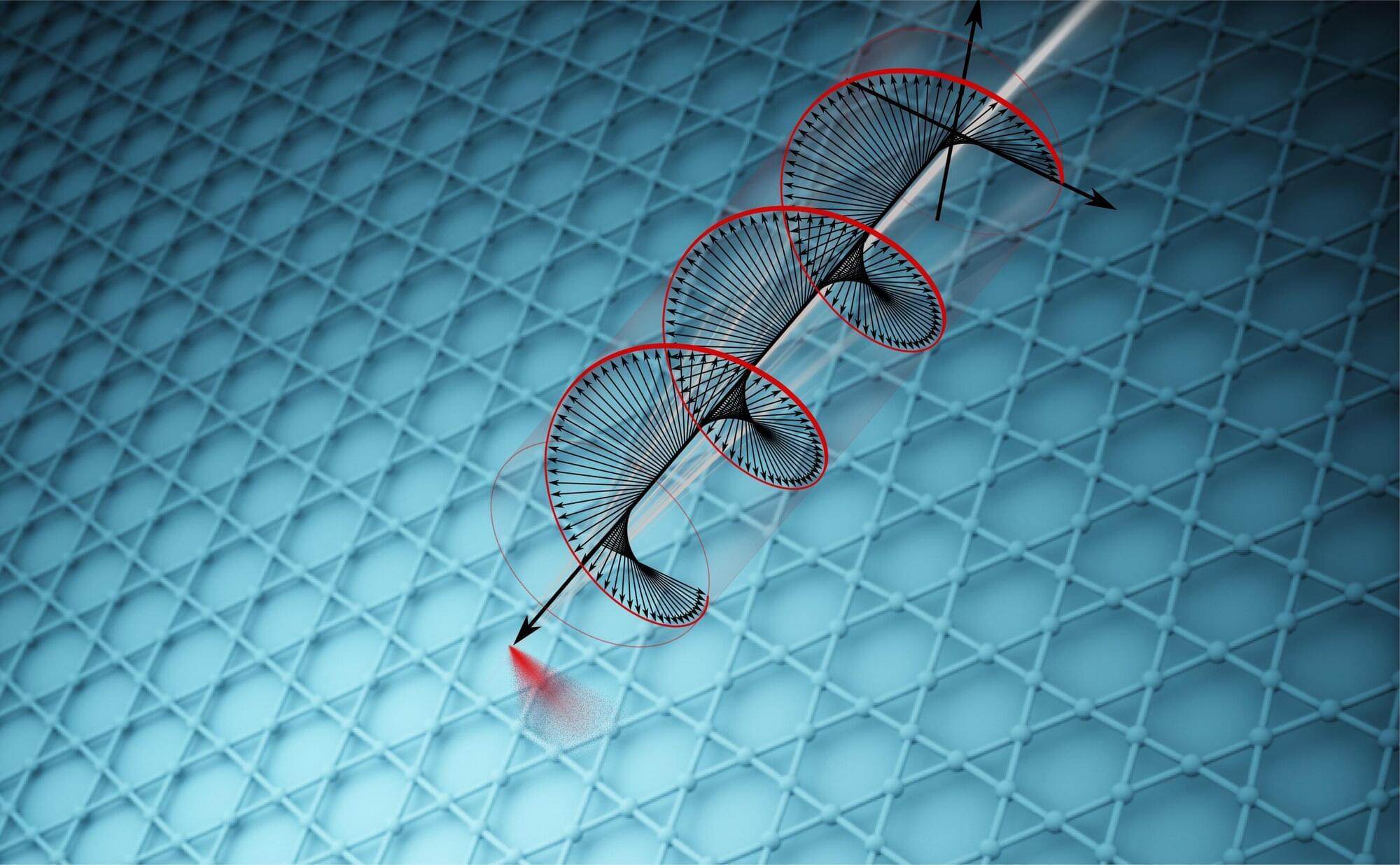
Chirality—the property of an object that is distinct from its mirror image—has long captivated scientists across biology, chemistry, and physics. The phenomenon is sometimes called “handedness,” because it refers to an object possessing a distinct left- or right-handed form. It is a universal quality that is found across various scales of nature, from molecules and amino acids to the famed double-helix of DNA and the spiraling patterns of snail shells.
The first nonverbal patient to receive Elon Musk’s Neuralink shares a video he edited and narrated using his brain chip
Posted in biotech/medical, computing, Elon Musk, neuroscience | Leave a Comment on The first nonverbal patient to receive Elon Musk’s Neuralink shares a video he edited and narrated using his brain chip
The first nonverbal Neuralink patient to receive the chip implant is offering a glimpse into how he uses the technology — editing and narrating a YouTube video using signals from his brain.
Brad Smith is the third person in the world to get a brain chip implant with Elon Musk’s Neuralink, and the first person with ALS to do so.
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, also known as Lou Gehrig’s disease, is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder that primarily affects motor neurons — the nerve cells in the brain and spinal cord responsible for controlling voluntary muscle movement. Over time, patients lose voluntary control of muscle movements, affecting their ability to speak, eat, move, and breathe independently.
It’s spring, the birds are migrating and bird flu (H5N1) is rapidly evolving into the possibility of a human pandemic. Researchers from the University of Maryland School of Public Health have published a comprehensive review documenting research on bird flu in cats and calling for urgent surveillance of cats to help avoid human-to-human transmission.
The work is published in the journal Open Forum Infectious Diseases.
“The virus has evolved, and the way that it jumps between species—from birds to cats, and now between cows and cats, cats and humans—is very concerning. As summer approaches, we are anticipating cases on farms and in the wild to rise again,” says lead and senior author Dr. Kristen Coleman, assistant professor in UMD School of Public Health’s Department of Global, Environmental and Occupational Health and affiliate professor in UMD’s Department of Veterinary Medicine.
New research shows that AI can identify complex regional pain syndrome (CRPS) with over 90% accuracy by analyzing gut microbiome patterns.