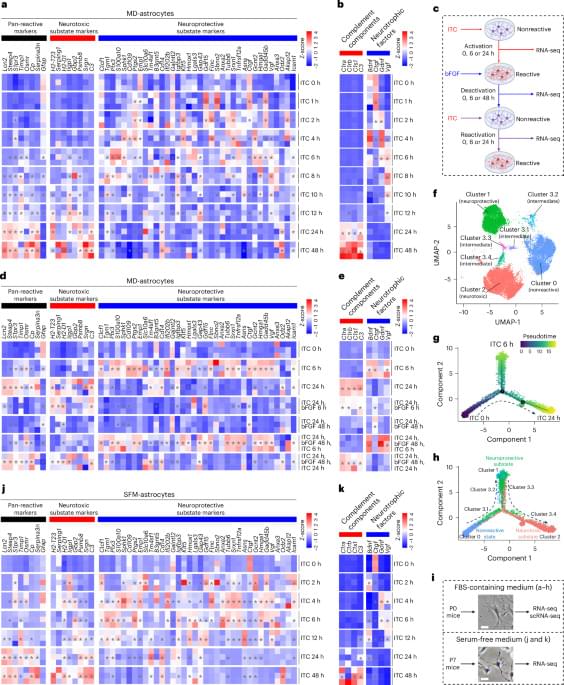
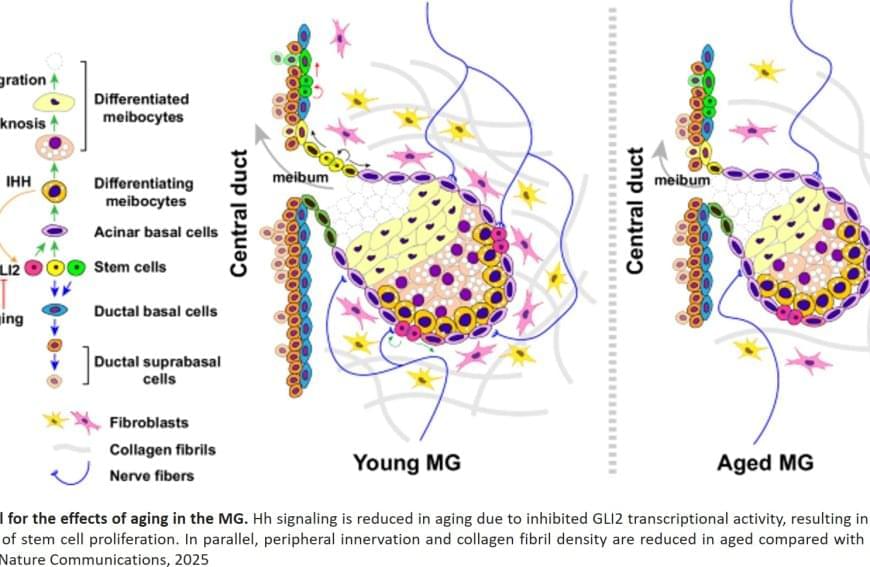
They found that increased Hh signaling is a hallmark of human meibomian gland carcinoma, a rare and aggressive cancer of the eyelid. Furthermore, the team discovered that aged glands show decreased Hh signaling and decreased epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) signaling, as well as impaired innervation and a loss of collagen in niche fibroblasts, suggesting that changes in both glandular epithelial cells and their surrounding microenvironment contribute to age-related degeneration.
These discoveries suggest that targeting Hh and EGFR signaling to stimulate stem cell activity in the meibomian glands could be a potential therapeutic option to treat evaporative dry eye disease.
A team of researchers has identified stem cell populations and mechanisms underlying age-related degeneration in glands that are vital to eye function. The findings, published in Nature Communications, may lead to new therapeutic approaches for evaporative dry eye disease, a common condition in older people.
Meibomian glands, tiny oil glands along the edges of the eyelids, secrete lipid-rich meibum to prevent tear evaporation and protect the eye surface. Aging-related shrinkage of the meibomian glands may result, in part, from stem cell exhaustion and is associated with evaporative dry eye disease, a common condition that causes swollen eyelids, itchy eyes, or blurred vision. Symptoms may be lessened with warm compressions, artificial tears, and thermal pulsation, but these treatments are only partially effective.
The researchers identified markers for stem cell populations that maintain distinct regions of the meibomian glands, and uncovered the hedgehog (Hh) cell-cell signaling pathway, which is broadly important in development and disease, as a key regulator of meibomian gland stem cell proliferation and tissue regeneration.