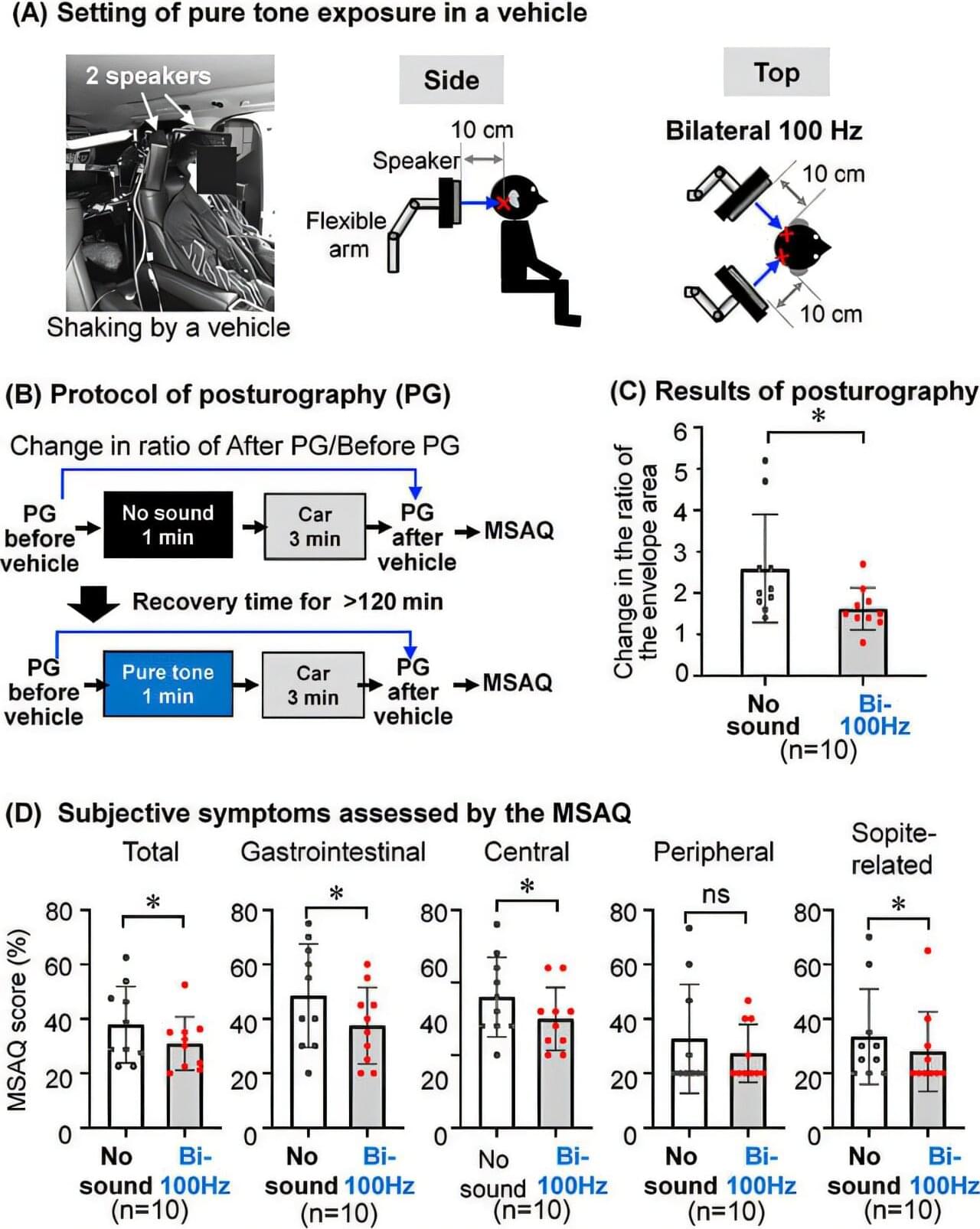
A research group led by Takumi Kagawa and Masashi Kato at Nagoya University Graduate School of Medicine has discovered that using “a unique sound stimulation technology”—a device that stimulates the inner ear with a specific wavelength of sound—reduces motion sickness. Even a single minute of stimulation reduced the staggering and discomfort felt by people that read in a moving vehicle.
The results, published in Environmental Health and Preventive Medicine, suggest a simple and effective way to treat this common disorder.
“Our study demonstrated that short-term stimulation using a unique sound called ‘sound spice’ alleviates symptoms of motion sickness, such as nausea and dizziness,” Kagawa said. “The effective sound level falls within the range of everyday environmental noise exposure, suggesting that the sound technology is both effective and safe.”