In addition to providing energy, lipids are also essential building blocks of our cell membranes. However, despite their importance, they remain poorly understood. A research team has revealed for the first time the secrets of their transport within cells. Each lipid uses a limited number of proteins to move from its place of production to its place of action. The team has also compiled an inventory of the proteins involved in the transport of hundreds of lipids.
These findings, published in the journal Nature, provide a better picture of the functioning of our cells, as well as of many genetic and metabolic disorders, such as diabetes and Alzheimer’s disease.
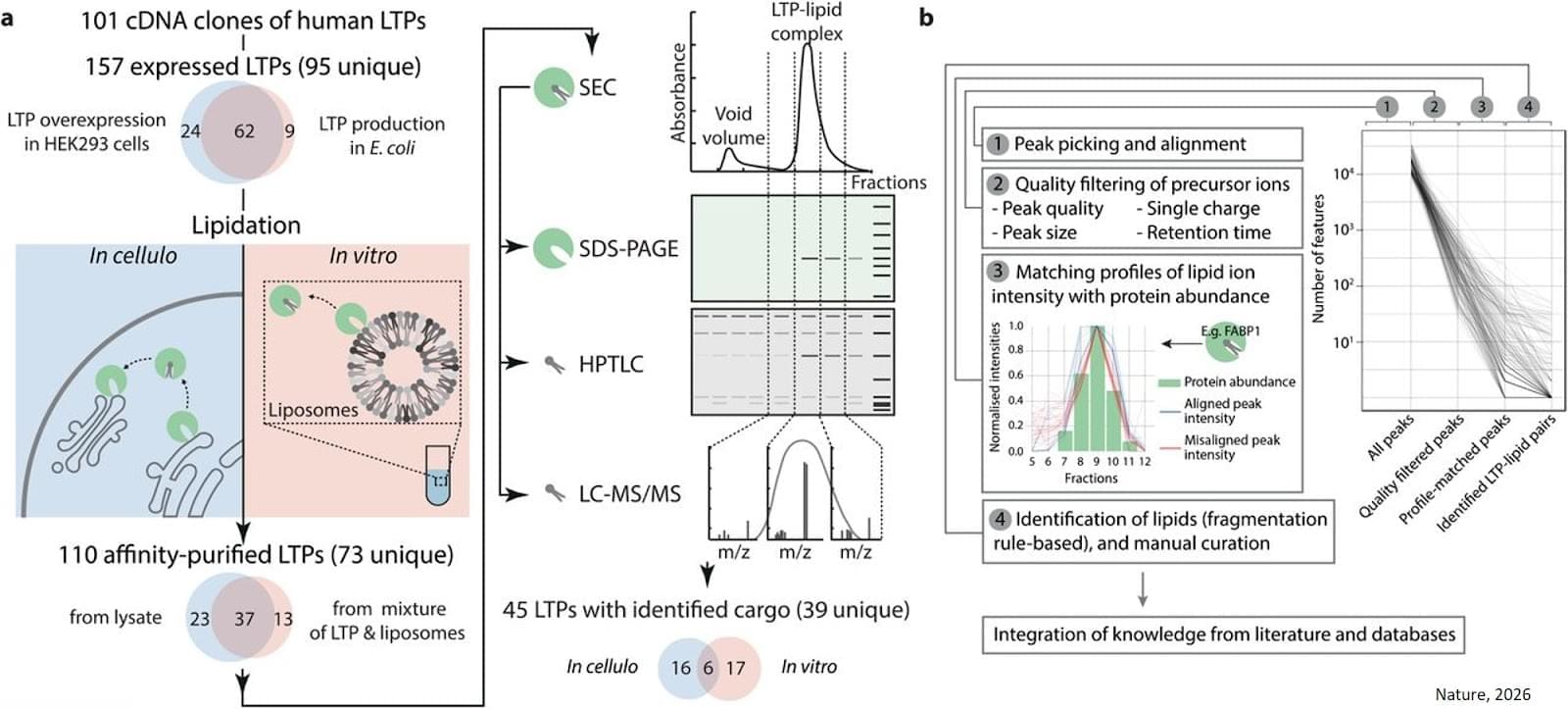
Biologists brought together more than a hundred transfer proteins with hundreds of different lipids. The aim was to obtain the most comprehensive list possible of the ‘pairs’ formed between each protein and the lipids it can carry.
To do this, two experimental methods were combined. The first, carried out in a test tube, provides a highly controlled environment, while the second, which more closely corresponds to the inside of a cell, allows researchers to verify how these bonds are formed under near-real conditions. This is a world first on such a scale and at such a level of complexity. “The ‘‘couples’’ identified show that transfer proteins are not “buses” capable of transporting most lipids, but private chauffeurs with specific characteristics,” explains the senior author.
Scientists have been able to determine, using advanced mathematical models, how three transfer proteins recognise, among all lipids, those that they actually transport. ScienceMission sciencenewshighlights.