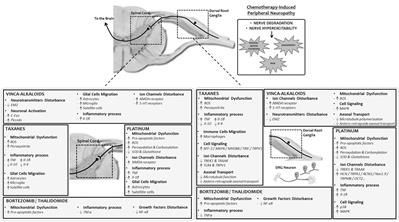
Neurotoxic anticancer drugs, such as platinum-based anticancer drugs, taxanes, vinca alkaloids, and proteasome/angiogenesis inhibitors are responsible for chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy (CIPN). The health consequences of CIPN remain worrying as it is associated with several comorbidities and affects a specific population of patients already impacted by cancer, a strong driver for declines in older adults. The purpose of this review is to present a comprehensive overview of the long-term effects of CIPN in cancer patients and survivors. Pathophysiological mechanisms and risk factors are also presented. Neurotoxic mechanisms leading to CIPNs are not yet fully understood but involve neuronopathy and/or axonopathy, mainly associated with DNA damage, oxidative stress, mitochondria toxicity, and ion channel remodeling in the neurons of the peripheral nervous system. Classical symptoms of CIPNs are peripheral neuropathy with a “stocking and glove” distribution characterized by sensory loss, paresthesia, dysesthesia and numbness, sometimes associated with neuropathic pain in the most serious cases. Several risk factors can promote CIPN as a function of the anticancer drug considered, such as cumulative dose, treatment duration, history of neuropathy, combination of therapies and genetic polymorphisms. CIPNs are frequent in cancer patients with an overall incidence of approximately 38% (possibly up to 90% of patients treated with oxaliplatin). Finally, the long-term reversibility of these CIPNs remain questionable, notably in the case of platinum-based anticancer drugs and taxanes, for which CIPN may last several years after the end of anticancer chemotherapies. These long-term effects are associated with comorbidities such as depression, insomnia, falls and decreases of health-related quality of life in cancer patients and survivors. However, it is noteworthy that these long-term effects remain poorly studied, and only limited data are available such as in the case of bortezomib and thalidomide-induced peripheral neuropathy.
Platinum-based anticancer drugs (i.e., cisplatin, oxaliplatin), proteasome/angiogenesis inhibitors (bortezomib/thalidomide), vinca alkaloids (i.e., vincristine, vinorelbine) and taxanes (i.e., paclitaxel, docetaxel) are the most common anticancer drugs used as first-line chemotherapy for several cancers, including colorectal, gastric, breast and lung cancers, and multiple myeloma. Despite their different action mechanisms, all these anticancer drugs share a common adverse and disabling effect for patients, namely CIPN (Balayssac et al., 2011). CIPN has a considerable impact on cancer treatments and their related symptoms severely affect patients’ daily activities and quality of life. Thus CIPN is often the main adverse effect leading to the reduction or discontinuation of chemotherapy.