New technological devices are prioritizing non-invasive tracking of vital signs, not only for fitness monitoring, but also for the prevention of common health problems such as heart failure, hypertension and stress-related complications, among others. Wearables based on optical detection mechanisms are proving an invaluable approach for reporting on our bodies inner workings and have experienced a large penetration into the consumer market in recent years. Current wearable technologies, based on non-flexible components, do not deliver the desired accuracy and can only monitor a limited number of vital signs. To tackle this problem, conformable non-invasive optical-based sensors that can measure a broader set of vital signs are at the top of the end-users’ wish list.
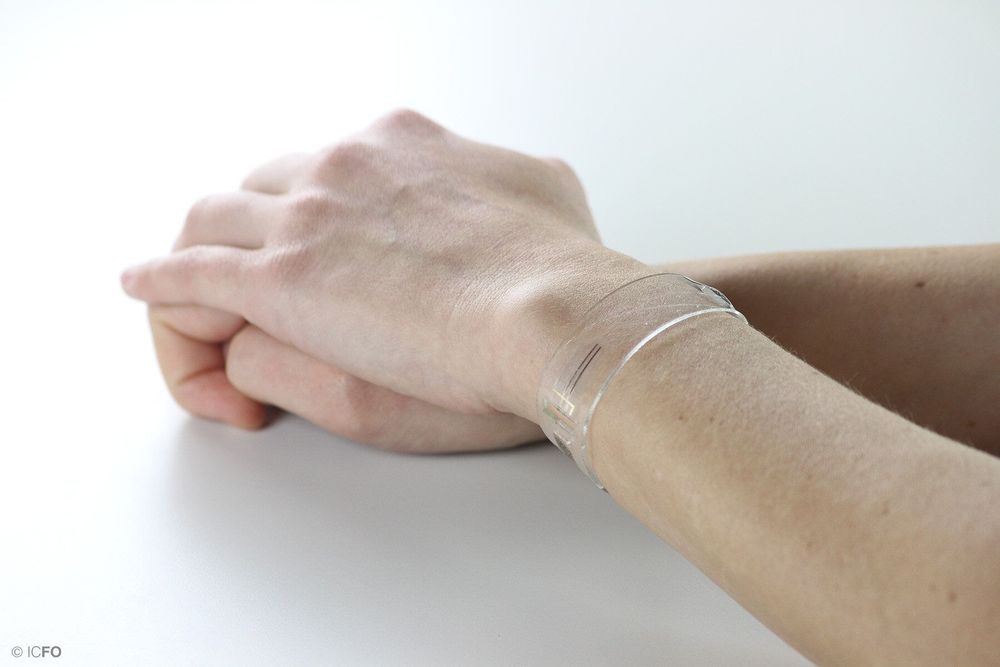
In a recent study published in Science Advances, ICFO researchers have demonstrated a new class of flexible and transparent wearable devices that are conformable to the skin and can provide continuous and accurate measurements of multiple human vital signs. These devices can measure heart rate, respiration rate and blood pulse oxygenation, as well as exposure to UV radiation from the sun. While the device measures the different parameters, the read-out is visualized and stored on a mobile phone interface connected to the wearable via Bluetooth. In addition, the device can operate battery-free since it is charged wirelessly through the phone.
“It was very important for us to demonstrate the wide range of potential applications for our advanced light sensing technology through the creation of various prototypes, including the flexible and transparent bracelet, the health patch integrated on a mobile phone and the UV monitoring patch for sun exposure. They have shown to be versatile and efficient due to these unique features,” reports Dr. Emre Ozan Polat, first author of this publication.