The choices we make today, and it’s consequences will shape up this decade. Can we break the current pattern, engage with this new financial system and adapt to new realities? #blockchain
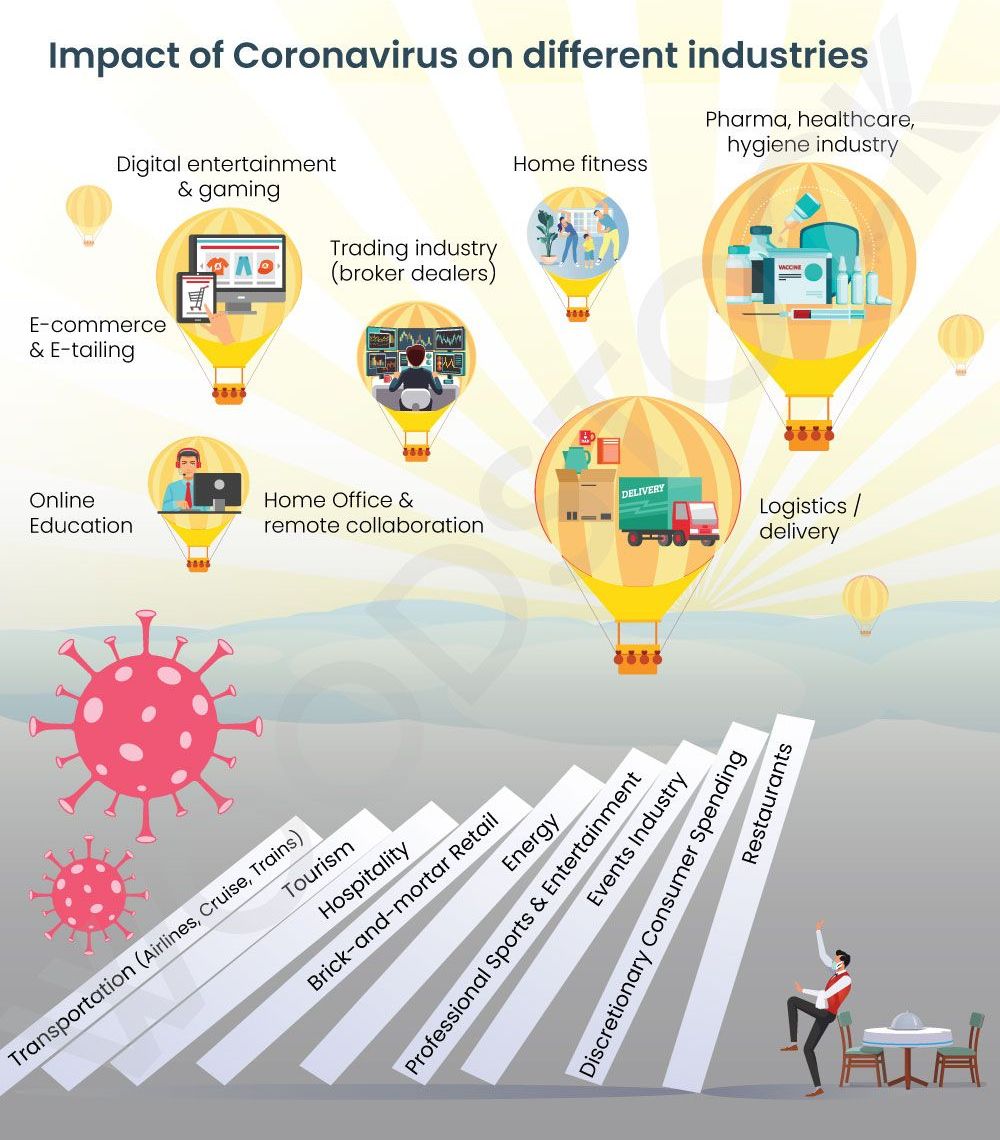
As human beings, we are defined by patterns. Our collective pattern defines society. We are empowered with choices – furthering the patterns, or breaking them or creating new ones. In the physical world, these choices could be social, economic, technological, or ecological. Based on the choices we make – good, bad, or ugly, we enjoy or suffer consequences. COVID-19 escalated the macroeconomic situation leading to liquidity, demand, and supply shocks. Can we break the current pattern and embrace digitization, decentralization and sound money? In turn, making choices that will create affirmative consequences for humanity.
Patterns, Choices & Consequences
On the late evening of 5th July 2004, one of our core team members was driving on Mumbai – Pune highway in a Maruti 800, after an offsite monthly sales review in Mumbai (India). He had to be in Pune for an early morning sales leadership training program. It was getting dark and he was trying his best to get out of Mumbai traffic onto the expressway. Once he reached the expressway, he felt it would be a breeze to get to Pune. This was his usual circuit and he was cruising at about 80 km per hour (not high speed or rash driving by any standards). He was ambitious. Past midway the weather conditions suddenly changed and it started pouring with no visibility beyond two feet. He pushed the accelerator trying to overtake a bus. He hadn’t bothered to check that the tyres were worn out and there was mud sludge on the road. He was ill-prepared and complacent. This lethal combination made his car lose control, spinning and toppling and diving next to a waterlogged canal.