Archive for the ‘biotech/medical’ category: Page 1694
May 12, 2020
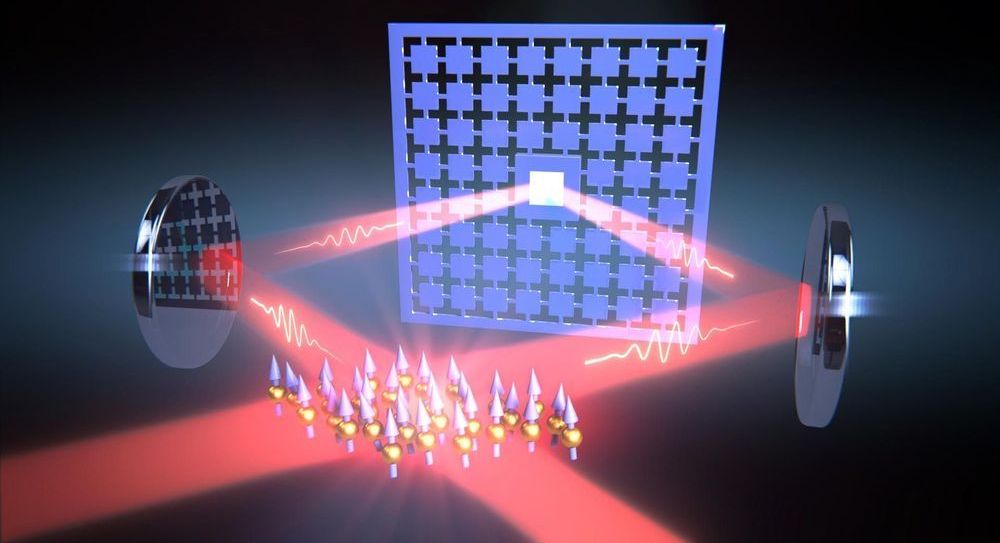
Laser Loop Acts as a Mechanical Spring to Couple Quantum Systems Over a Distance
Posted by Quinn Sena in categories: biotech/medical, computing, nanotechnology, quantum physics
Quantum technology is currently one of the most active fields of research worldwide. It takes advantage of the special properties of quantum mechanical states of atoms, light, or nanostructures to develop, for example, novel sensors for medicine and navigation, networks for information processing and powerful simulators for materials sciences. Generating these quantum states normally requires a strong interaction between the systems involved, such as between several atoms or nanostructures.
Until now, however, sufficiently strong interactions were limited to short distances. Typically, two systems had to be placed close to each other on the same chip at low temperatures or in the same vacuum chamber, where they interact via electrostatic or magnetostatic forces. Coupling them across larger distances, however, is required for many applications such as quantum networks or certain types of sensors.
A team of physicists, led by Professor Philipp Treutlein from the Department of Physics at the University of Basel and the Swiss Nanoscience Institute (SNI), has now succeeded for the first time in creating strong coupling between two systems over a greater distance across a room temperature environment. In their experiment, the researchers used laser light to couple the vibrations of a 100 nanometer thin membrane to the motion of the spin of atoms over a distance of one meter. As a result, each vibration of the membrane sets the spin of the atoms in motion and vice versa.
May 12, 2020
Active machine learning helps drug hunters tackle biology
Posted by Genevieve Klien in categories: biotech/medical, robotics/AI
A growing cadre of startups is pursuing iterative cycles of machine learning, wet-lab experimentation and human feedback to accelerate target drug discovery.
May 12, 2020
This AI tool predicts who’s got COVID-19 without testing
Posted by Genevieve Klien in categories: biotech/medical, health, robotics/AI
A new AI diagnostic tool trained on crowdsourced symptom data can predict whether someone likely has COVID-19 without testing.
The model was trained on data from more than 2.5 million users of the COVID Symptom Study app developed at King’s College London, which anyone can download to report their daily health status.
May 12, 2020
Supercharged brains and the quest to think better and faster
Posted by Lola Heavey in categories: biotech/medical, neuroscience
Are you taking any pills to enhance performance?
When it comes to the mind, there are a host of drugs that have become popular in various settings as nootropics, from college campuses to high power startups in Silicon Valley. Of these, a few families of drugs have accumulated a collection of research studies suggesting that they could be utilized safety, and also produce a desired effect.
The first such category of such drugs that performance enhancement seekers often try are stimulants. Two common such drugs are methylphenidate and dexamphetamine, which are used routinely and safely to treat attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and narcolepsy. Despite their popularity for off-label use to boost concentration, however, these drugs are not really nootropics. They are actually quite dangerous if you don’t have ADHD or narcolepsy, or some other deficit, because tolerance builds up quickly, leading to dependence. Thus, while methylphenidate can keep you awake overnight or give you a boost in the morning, and possibly move you faster through a pile of non-creative work, they don’t really make you think better, and if you keep taking them you will be back to square one on performance, and with a drug dependence problem. You’d be better off with a strong cup of coffee.
Continue reading “Supercharged brains and the quest to think better and faster” »
May 12, 2020
Germany’s daily coronavirus cases nearly TRIPLE — states bring back tougher lockdown
Posted by Brent Ellman in category: biotech/medical
CORONAVIRUS cases in Germany have almost trebled in the past 24 hours sparking fears of a second wave of COVID-19 infections.
May 12, 2020
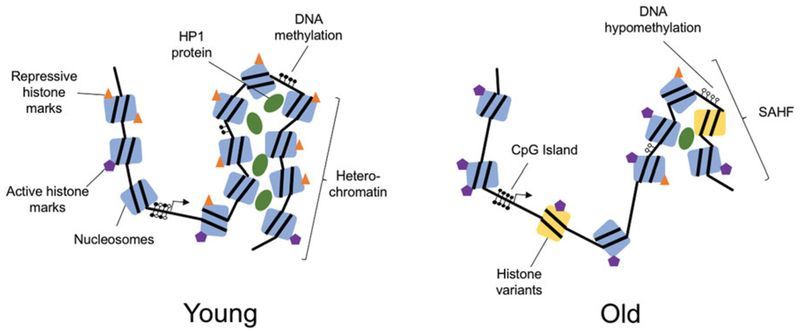
Epigenetic changes during aging and their reprogramming potential
Posted by Mike Diverde in categories: biotech/medical, chemistry, genetics, life extension
If you are interested in age reversal, and you haven’t read Dr David Sinclair (Harvard Medical School) yet, then I’d recommend this research paper.
“Excitingly, new studies show that age-related epigenetic changes can be reversed with interventions such as cyclic expression of the Yamanaka reprogramming factors. This review presents a summary of epigenetic changes that occur in aging, highlights studies indicating that epigenetic changes may contribute to the aging process and outlines the current state of research into interventions to reprogram age-related epigenetic changes.”
The aging process results in significant epigenetic changes at all levels of chromatin and DNA organization. These include reduced global heterochromatin, nucleosome remodeling and loss, changes in histone marks, global DNA hypomethylation with CpG island hypermethylation, and the relocalization of chromatin modifying factors. Exactly how and why these changes occur is not fully understood, but evidence that these epigenetic changes affect longevity and may cause aging, is growing. Excitingly, new studies show that age-related epigenetic changes can be reversed with interventions such as cyclic expression of the Yamanaka reprogramming factors. This review presents a summary of epigenetic changes that occur in aging, highlights studies indicating that epigenetic changes may contribute to the aging process and outlines the current state of research into interventions to reprogram age-related epigenetic changes.
Continue reading “Epigenetic changes during aging and their reprogramming potential” »
May 12, 2020
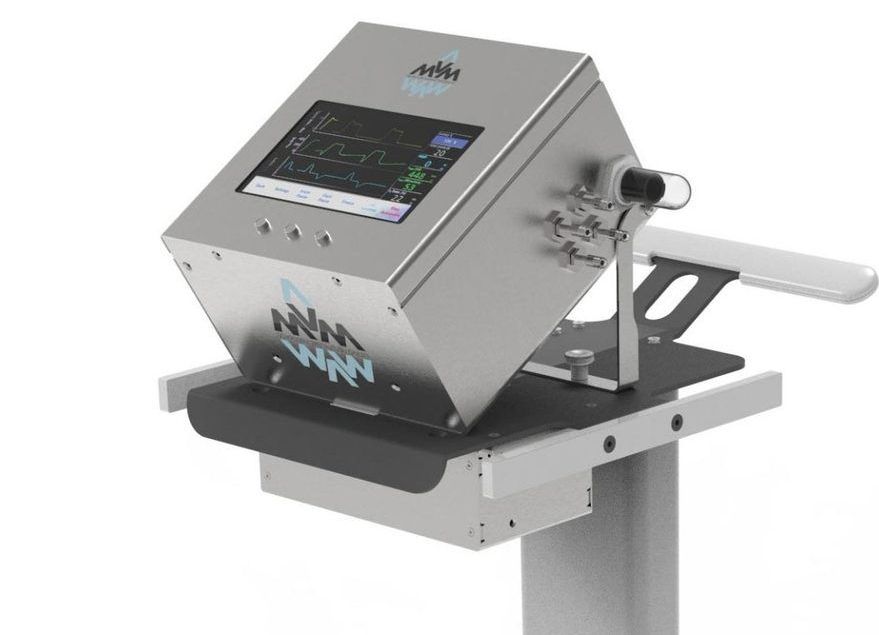
FDA Approval Granted for Simplified Ventilator Design From Particle Physics Community
Posted by Genevieve Klien in categories: biotech/medical, health
In a little over a month, a team of physicists and engineers from around the world took a simplified ventilator design from concept all the way through approval by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. This major milestone marks the ventilator as safe for use in the United States under the FDA’s Emergency Use Authorization, which helps support public health during a crisis.
The Mechanical Ventilator Milano, or MVM, is the brainchild of physicist Cristiano Galbiati. The Gran Sasso Science Institute and Princeton University professor, who normally leads a dark matter experiment in Italy called DarkSide-20k, found himself in lockdown in Milan, a city hit hard by COVID-19. Hearing reports of ventilator shortages and wanting to help, Galbiati reached out to fellow researchers to develop a ventilator with minimal components that could be quickly produced using commonly available parts.
“The sense of crisis was palpable, and I knew the availability of ventilators was critical,” said Galbiati, who obtained his Ph.D from the University of Milan. “We had been doing some complicated projects in physics that required working with gases, and I thought it our duty to find a way to push oxygen into the lungs of patients.”
May 12, 2020
Region rallies to provide NHS with life-saving equipment
Posted by Omuterema Akhahenda in category: biotech/medical
Brackley-based Mercedes has put aside traditional rivalries and joined forces with other F1 teams like Milton Keynes’ Red Bull and manufacturers — to produce a breathing aid called a CPAP that can help keep infected patients out of intensive care.
The device gets oxygen to the lungs without needing invasive treatment.
Watch Rebecca Haworth’s report.
Continue reading “Region rallies to provide NHS with life-saving equipment” »
May 11, 2020
‘Cutting edge’ ventilator enters race to beat coronavirus
Posted by Omuterema Akhahenda in categories: biotech/medical, innovation
A “cutting edge” alternative ventilator for coronavirus patients has been developed by a taskforce. The ‘exovent’ is a reinvention of the traditional iron lung, which saved the lives of countless polio victims during the 20th century.
Unlike the usual ventilators, which are positive pressure ventilators (PPV), the exovent is a non-invasive negative pressure ventilation (NPV) device, which could be used both in intensive care or on an ordinary hospital ward.
www.cambridge-news.co.uk/…/cambridge-coronavirus-ventillato…
Continue reading “‘Cutting edge’ ventilator enters race to beat coronavirus” »