Sep 15, 2020
The human story of how ventilators came to breathe for us
Posted by Christopher Field in categories: biotech/medical, ethics
Medical Ethics and “Futility” (Note: Listen here function)
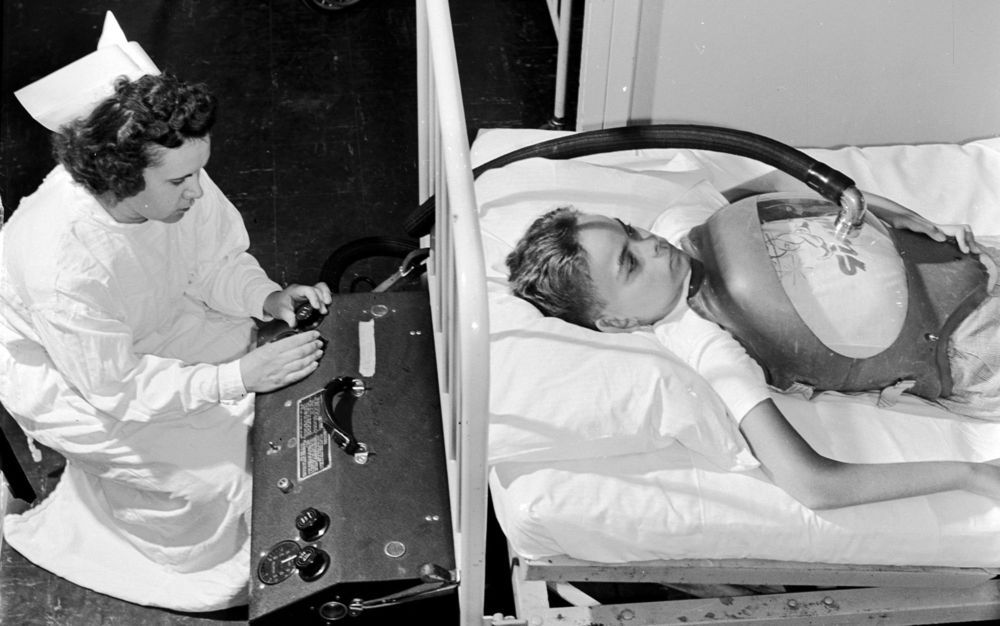
We breathe about 12 to 20 times a minute, without having to think. Inhale: and air flows through the mouth and nose, into the trachea. The bronchi stem out like a wishbone, and keep branching, dividing and dividing, and finally feeding out into the tiny air sacs of alveoli. Capillaries – blood vessels thinner than hairs – twine around each alveolus. Both the air sac and the blood vessel are tiny, delicate, one cell thick: portals where blood (the atmosphere of the body) meets air (atmosphere of the world). Oxygen passes from air to blood; carbon dioxide, from blood to air. Then, the exhale pushes that carbon dioxide back out the mouth and nose. Capillaries channel newly oxygenated blood back to the heart. That oxygen fuels the body. That’s why we breathe.
Today, these basics of human respiration and metabolism feel obvious – and ventilators, the machines that breathe for sick people, do, too. We have so many medical devices, so of course we’d need, and have, machines that help us to breathe. But there’s a strange, and deeply human, story behind how we learned to breathe for each other. It starts long ago, when we didn’t understand breathing at all. When the body’s failure to breathe was incomprehensible, incurable, and fatal. When we had no way of knowing how badly we needed ventilators to keep people alive through those moments of vulnerability, lest those moments be their last.
Continue reading “The human story of how ventilators came to breathe for us” »