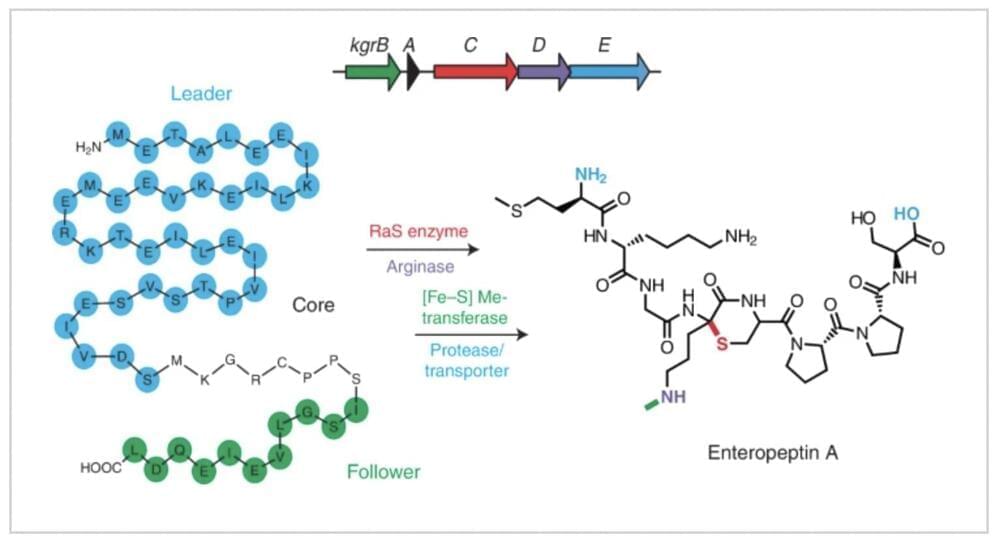
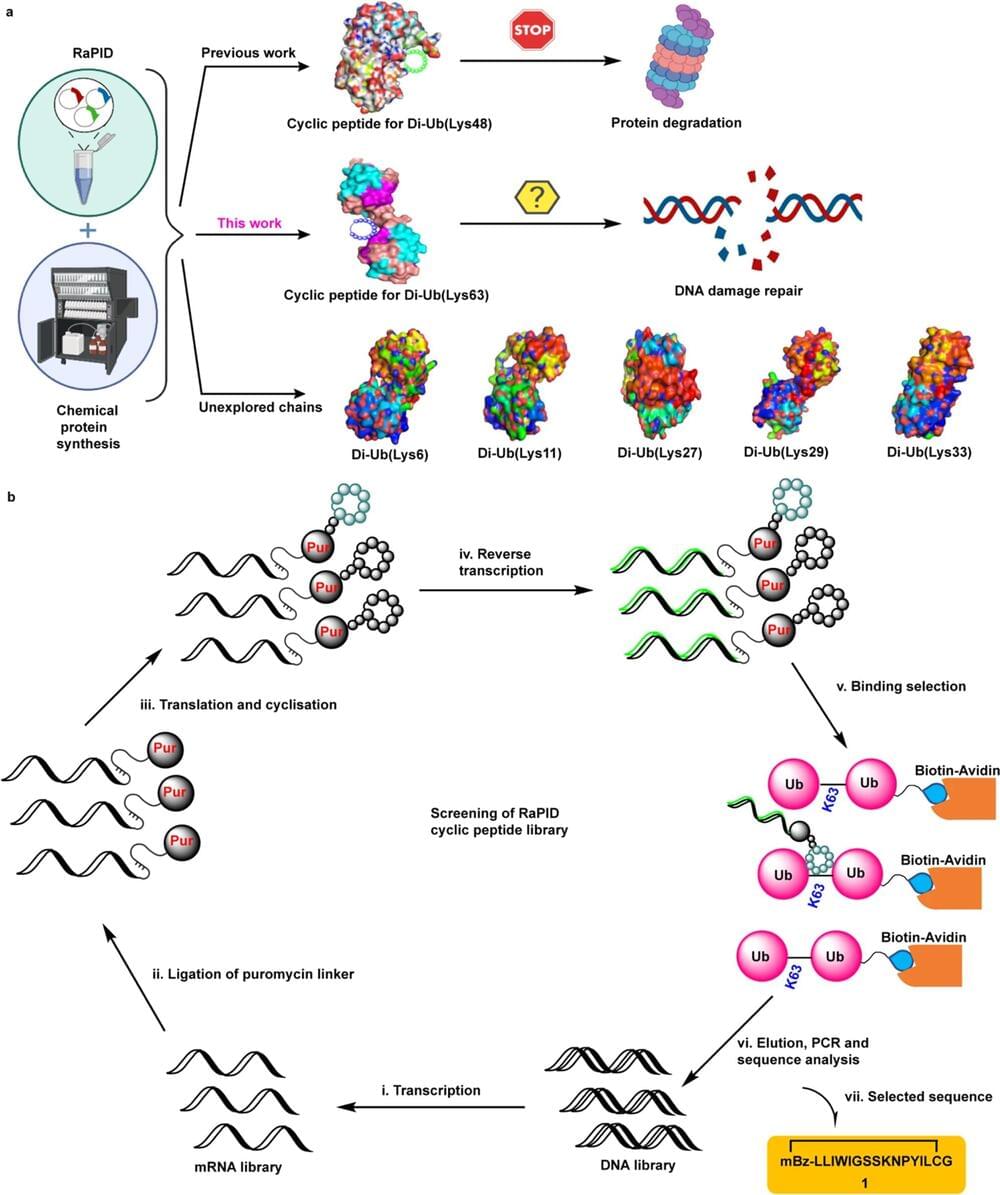
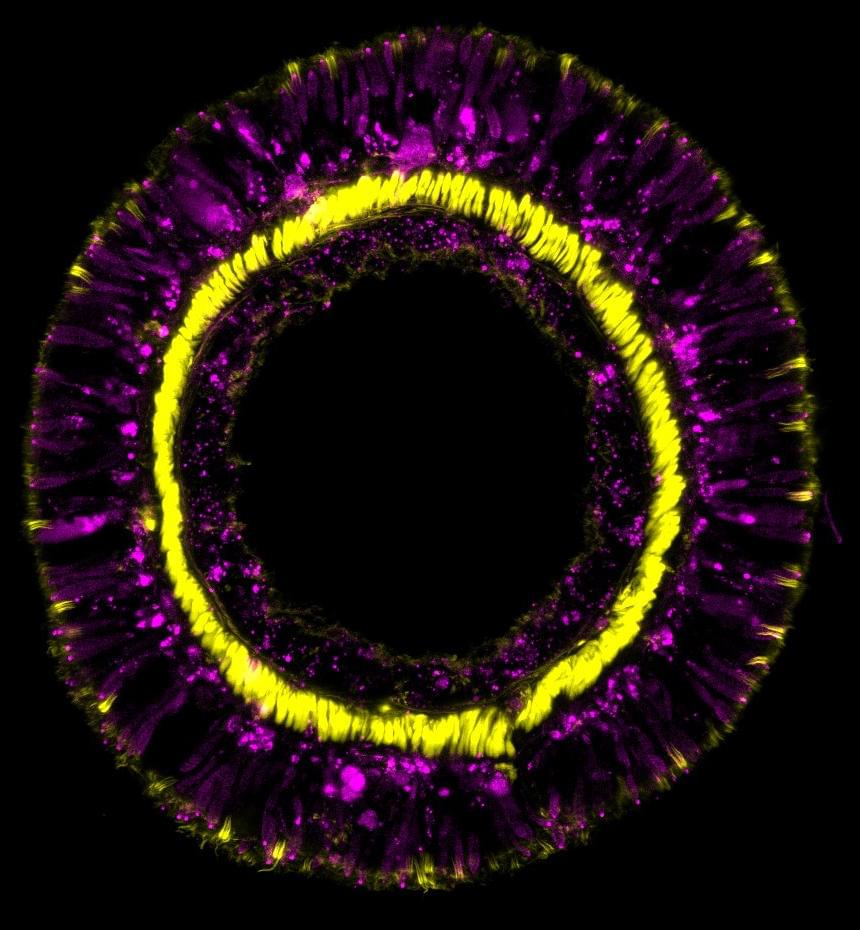
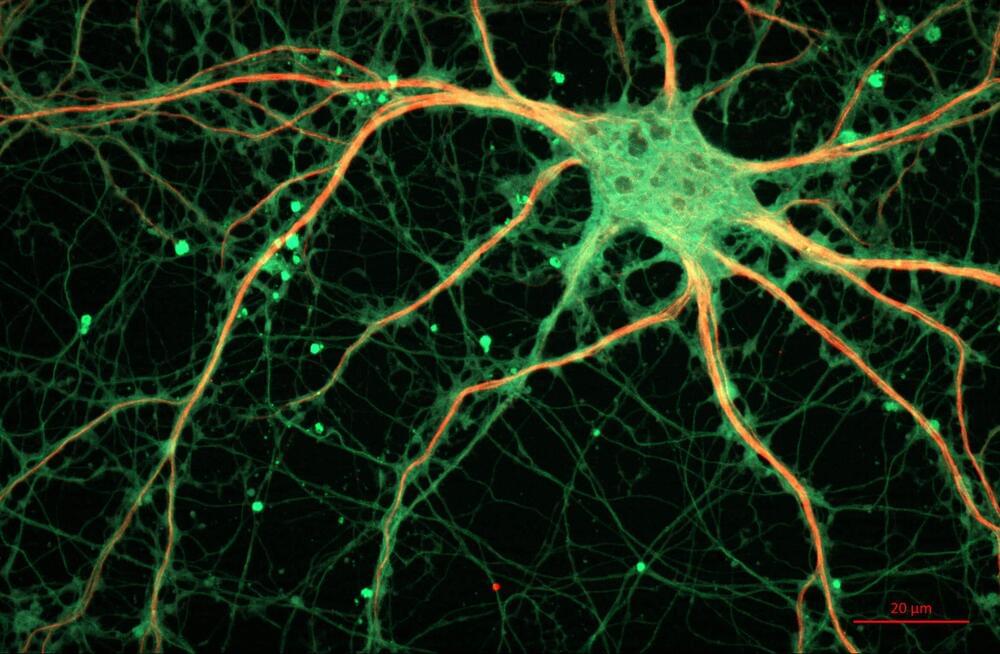
Watch any episode of “CSI,” and a character will use forensic DNA profiling to identify a criminal. A new study from San Francisco State University suggests that these forensic profiles may indirectly reveal medical information—perhaps even those of crime victims—contrary to what the legal field has believed for nearly 30 years. The findings, now published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, could have ethical and legal implications.
“The central assumption when choosing those [forensic] markers was that there wouldn’t be any information about the individuals whatsoever aside from identification. Our paper challenges that assumption,” said first author Mayra Bañuelos, who started working on the project as a San Francisco State undergraduate and is now a Ph.D. student at Brown University.
Law enforcement uses the Combined DNA Index System (CODIS), a system organizing criminal justice DNA databases that uses specific genetic markers to identify individuals. Crime labs from national, state and local levels contribute to these databases and provide profiles from samples collected from crime scene evidence, convicted offenders, felony arrestees, missing persons and more. Law officials can use the database to try to match samples found in an investigation to profiles already stored in the database.