Year 2020 face_with_colon_three
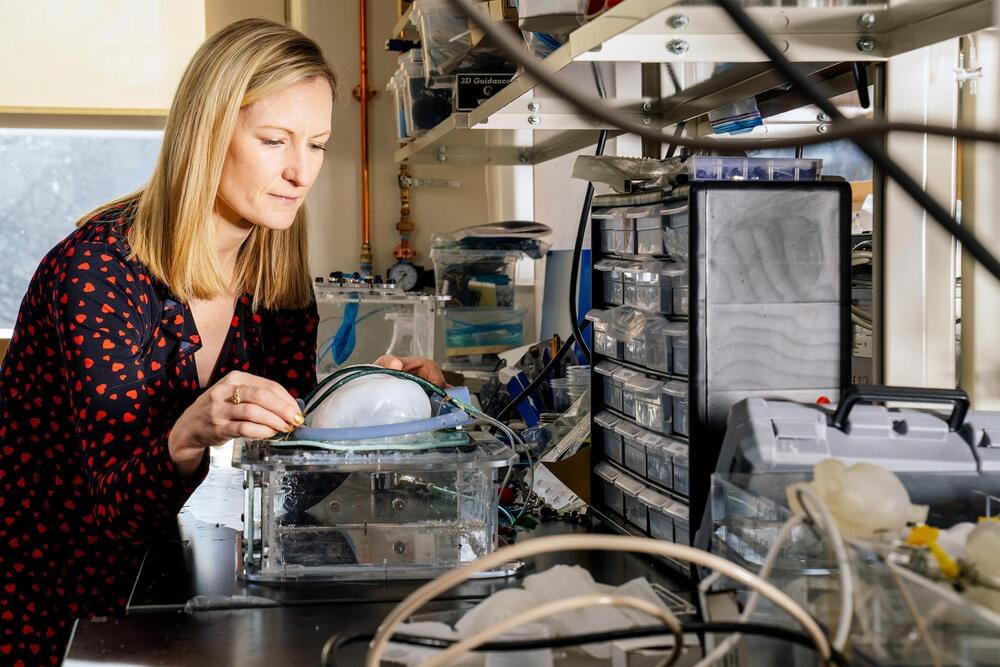
An international team of scientists have restored the vision in blind rats using a nanoparticle-based artificial retina prosthesis that can be injected directly into the eye. The scientific advance has been successfully demonstrated for a period of eight months without the need for surgery. While it is still early days for the research, it suggests it might one day be possible to use the conjugated polymer nanoparticle (P3HT-NP) treatment in humans to correct eye problems –ranging from hereditary retinal dystrophies to the incredibly common age-related macular degeneration.
“In our ‘liquid retina device,’ P3HT nanoparticles spread out over the entire subretinal space and promoted light-dependent activation of spared inner retinal neurons, recovering subcortical, cortical and behavioral visual responses,” Fabio Benfenati, research director at the Italian Institute of Technology, told Digital Trends. “We think that P3HT-NPs provide a new avenue in retinal prosthetics.”
Retinal prostheses refer to implantable devices that are designed to help restore sight in patients with retinal degeneration. They work by introducing visual information into the retina through the electrical stimulation of surviving retinal neurons. While promising, current retinal prostheses have so far been shown to only return low-resolution vision: Useful for things like distinguishing between light and dark or recognizing simple shapes and objects. This new nanotech approach appears far more promising, offering significantly higher resolution. After just one injection, activity in the rats’ visual cortex and visual acuity were the same as those found in healthy rats.