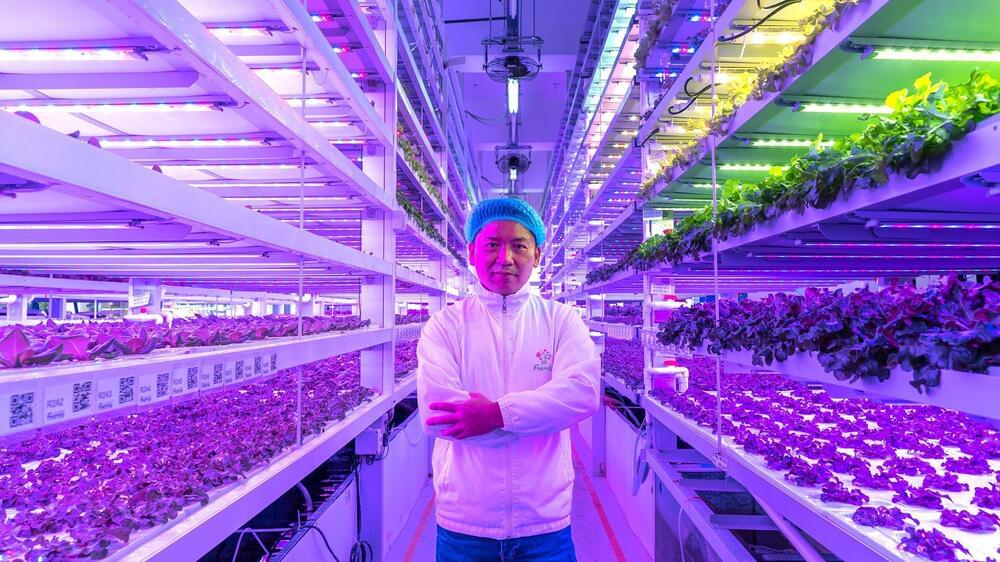
Hong Kong, a densely populated city where agriculture space is limited, is almost totally dependent on the outside world for its food supply. More than 90% of the skyscraper-studded city’s food, especially fresh produce like vegetables, is imported, mostly from mainland China. “During the pandemic, we all noticed that the productivity of locally grown vegetables is very low,” says Gordon Tam, cofounder and CEO of vertical farming company Farm66 in Hong Kong. “The social impact was huge.”
Tam estimates that only about 1.5% of vegetables in the city are locally produced. But he believes vertical farms like Farm66, with the help of modern technologies, such as IoT sensors, LED lights and robots, can bolster Hong Kong’s local food production—and export its know-how to other cities. “Vertical farming is a good solution because vegetables can be planted in cities,” says Tam in an interview at the company’s vertical farm in an industrial estate. “We can grow vegetables ourselves so that we don’t have to rely on imports.”
Tam says he started Farm66 in 2013 with his cofounder Billy Lam, who is COO of the company, as a high-tech vertical farming pioneer in Hong Kong. “Our company was the first to use energy-saving LED lighting and wavelength technologies in a farm,” he says. “We found out that different colors on the light spectrum help plants grow in different ways. This was our technological breakthrough.” For example, red LED light will make the stems grow faster, while blue LED light encourages plants to grow larger leaves.