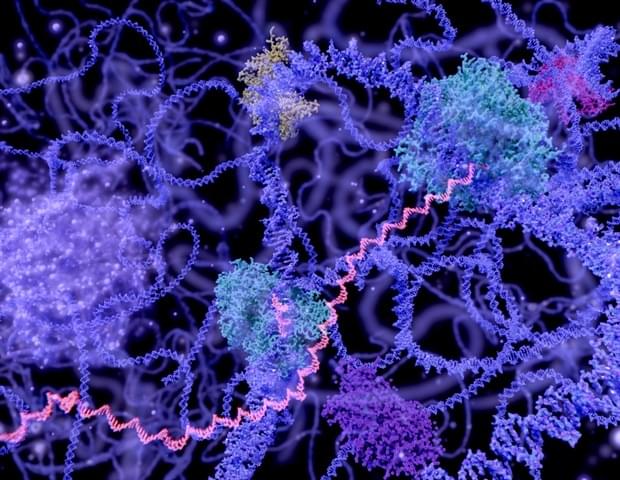
People who owned black-and-white television sets until the 1980s didn’t know what they were missing until they got a color TV. A similar switch could happen in the world of genomics as researchers at the Berlin Institute of Medical Systems Biology of the Max Delbrück Center (MDC-BIMSB) have developed a technique called Genome Architecture Mapping (“GAM”) to peer into the genome and see it in glorious technicolor. GAM reveals information about the genome’s spatial architecture that is invisible to scientists using solely Hi-C, a workhorse tool developed in 2009 to study DNA interactions, reports a new study in Nature Methods by the Pombo lab.
With a black-and-white TV, you can see the shapes but everything looks grey. But if you have a color TV and look at flowers, you realize that they are red, yellow and white and we were unaware of it. Similarly, there’s also information in the way the genome is folded in three-dimensions that we have not been aware of.