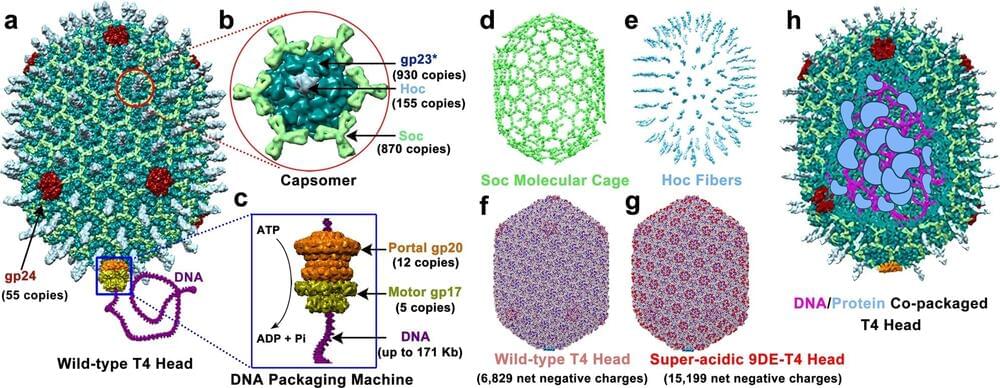
A team of medical scientists at The Catholic University of America, in Washington, D.C., working with a colleague from Purdue University, has developed a way to engineer the bacteriophage T4 to serve as a vector for molecular repair. The study is reported in the journal Nature Communications.
Prior research has shown that many human ailments arise due to genetic mutations: cystic fibrosis, Down syndrome, sickle cell disease and hemophilia are just a few. Logic suggests that correcting such genetic mutations could cure these diseases. So researchers have been working toward developing gene editing tools that will allow for safe editing of genes.
One of the most promising is the CRISPR gene editing system. In this new effort, the research team took a more general approach to solving the problem by working to develop a vector that could be used to carry different kinds of tools to targeted cells and then enter them to allow for healing work to commence.