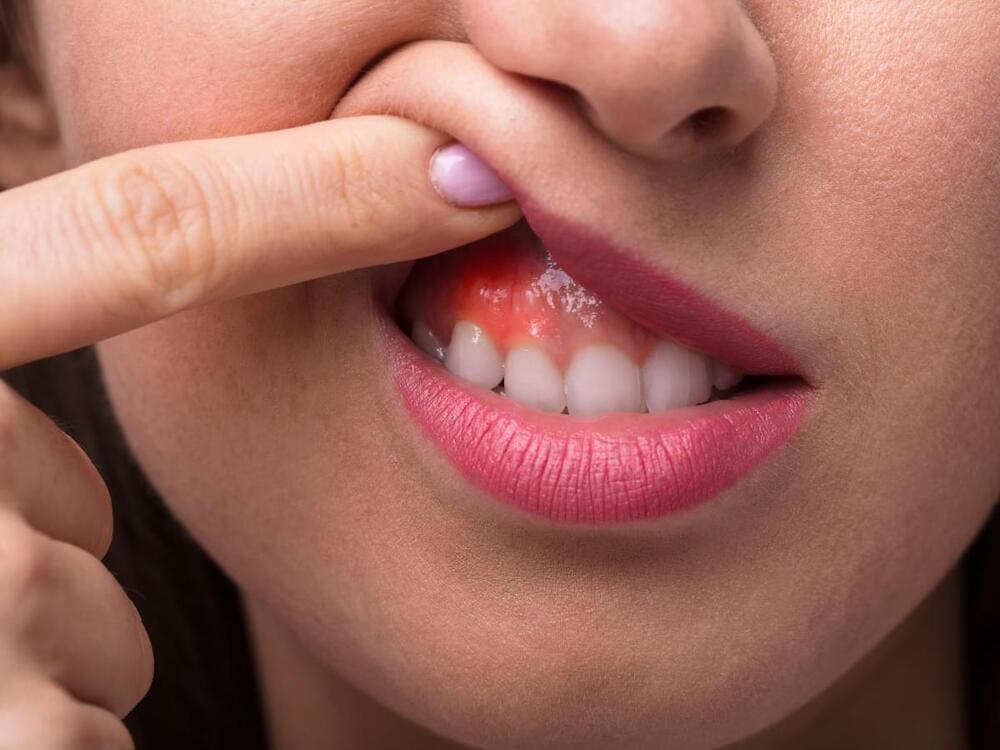
Your gums help to keep your teeth and mouth healthy, but they often get overlooked when it comes to dental care. Gums play an important role in the overall health of your mouth, here’s how to take good care of them.

Inaugurated in 2018, the Human BioMolecular Atlas Program (HuBMAP) endeavours to construct comprehensive spatial maps that feature a range of biomolecules such as RNA, proteins, and metabolites in human organs at single-cell resolution. This collection features the research, datasets, methods and tools generated by this project, accompanied by a Perspective, a News and Views, and links to other resources.
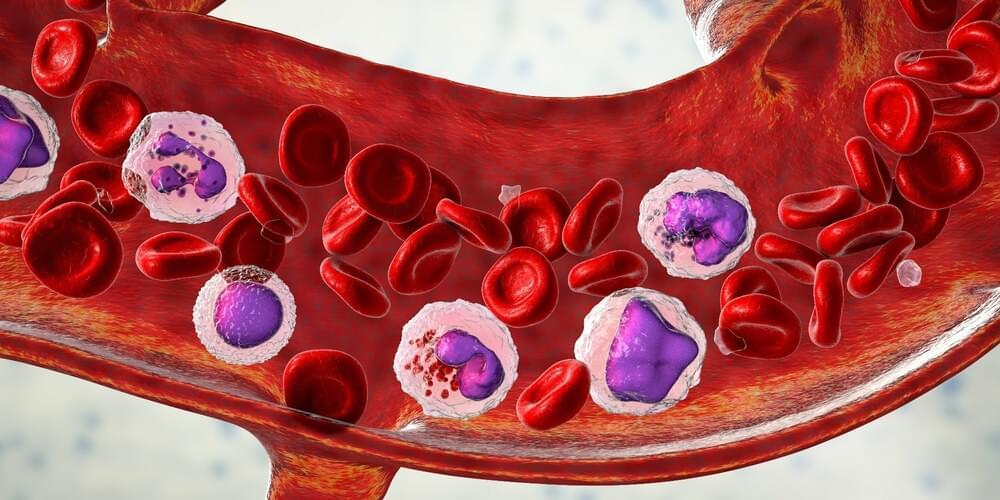
In a recent study published in the Journal of Biomedical Science, researchers investigate whether M2 macrophage-derived exosomes (M2-Exos) could prevent inflammation-associated damage during sepsis-associated acute lung injury (ALI) by modulating abnormal polymorphonuclear neutrophil (PMN) behaviors.
Study: Exosomal PGE2 from M2 macrophages inhibits neutrophil recruitment and NET formation through lipid mediator class switching in sepsis. Image Credit: Kateryna Kon / Shutterstock.com.

The Klotho gene has gained increasing attention for its anti-aging properties. In the most recent installment of this series, we explored the promising cognitive benefits of administering Klotho to both mice and monkeys, the results from which may be mirrored in humans. The benefits of this circulating hormone, however, extend beyond the brain.
Klotho was first discovered as the antiaging gene in 1997 when researchers found that enhancing its expression could increase the lifespan of mice by more than 30%. Although a variety of different genes and environmental factors can influence longevity, studies have shown that Klotho-deficient mice not only have shorter lifespans but also experience more age-related complications. Premature aging in these mice often was accompanied by loss of muscle and fat tissue, thinning skin, reduced fertility, cardiovascular complications, movement abnormalities, and bone disease. Since Klotho is primarily produced in the kidneys, it is not surprising that many of these age-related complications often result from kidney dysfunction.
The kidneys generate two types of Klotho: a transmembrane protein that inserts itself into the cell membrane and mediates kidney function, and a secreted hormone that is released into the bloodstream. Individuals with naturally high levels of the hormone in their blood seem to not only live longer and be more resistant to age-related complications but also perform better on learning and memory tasks. In fact, even when a relatively small dose of Klotho is administered, animal studies have shown that the brain undergoes significant changes that allow more connections to be made in the hippocampus, the brain’s learning and memory center.

The researchers were successful in showing the relationship between activin A and bone erosion in cholesteatoma. “Our study showed that targeting activin A is a potential treatment in the management of cholesteatomas,” says senior author Masaru Ishii, MD, PhD, professor.
Currently in clinical settings, the only effective treatment for cholesteatomas is complete surgical removal. However, the discovery of how a cholesteatoma can cause bone erosion in this study offers new hope for developing novel medical treatments as first-line management for cholesteatomas.
“A cholesteatoma can still return or happen again even after its surgical removal, so it is important to know what is actually causing it,” notes lead author Kotaro Shimizu.
This article is an installment of Future Explored, a weekly guide to world-changing technology. You can get stories like this one straight to your inbox every Thursday morning by subscribing here.
The Australian military is funding a project to grow intelligent “mini-brains” in petri dishes. The goal is to use these “DishBrains” to design better AIs — and, eventually, even combine the two, creating AIs merged with processing features of human brain cells.
By creating just the right conditions, scientists can coax stem cells into growing into “organoids,” three-dimensional tissues that resemble the structure and function of different organs — even brains.
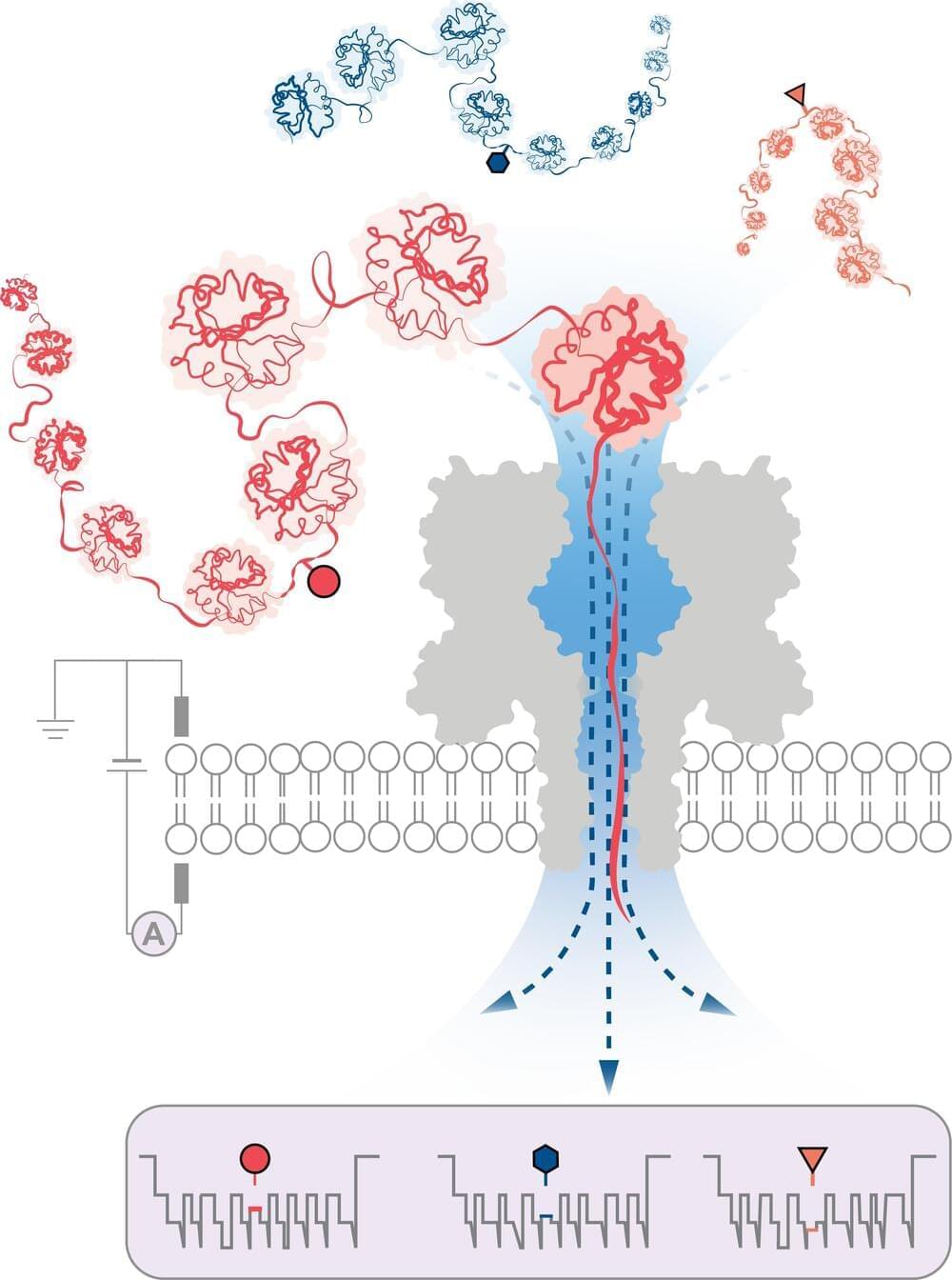
A team of scientists led by the University of Oxford have achieved a significant breakthrough in detecting modifications on protein structures. The method, published in Nature Nanotechnology, employs innovative nanopore technology to identify structural variations at the single-molecule level, even deep within long protein chains.
Human cells contain approximately 20,000 protein-encoding genes. However, the actual number of proteins observed in cells is far greater, with over 1,000,000 different structures known. These variants are generated through a process known as post-translational modification (PTM), which occurs after a protein has been transcribed from DNA.
PTM introduces structural changes such as the addition of chemical groups or carbohydrate chains to the individual amino acids that make up proteins. This results in hundreds of possible variations for the same protein chain.
DEAR MAYO CLINIC: I’ve heard about several people who have experienced sudden cardiac arrest. What is cardiac arrest? And how is it different from a heart attack? What do you do for someone who has this condition?
ANSWER: Cardiac arrest, or sudden cardiac arrest as it is more formally known, is a medical emergency. Think of it as a problem with the heart’s electrical activity. This synchronized electrical activity allows the heart to fill and pump blood normally. Sudden cardiac arrest can happen unexpectedly and quickly, and the heart stops working. It’s not the same as a heart attack, but it is just as critical that treatment occurs rapidly.
Cardiac arrest is when the heart cannot fulfill its duties, such as pumping oxygenated blood around the body to reach critical areas such as the brain and the rest of the body. It is sometimes called “sudden” because it seems to happen without warning. A person suddenly loses all heart activity, stops breathing and becomes unconscious. Without immediate treatment, sudden cardiac arrest can lead to death.
Researchers at Uppsala university have developed a new method to find mutations in brain tumors in children. They also showed that the mutations change how cancer cells respond to a cancer drug. These findings could lead to better diagnostics and more individualized treatment of children with brain tumors. The study is published in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
Medulloblastoma is the most common malignant brain tumor in children. It usually develops in the cerebellum and although modern treatment has improved the prognosis so that more than 70% of patients now live more than five years, not all patients can be cured. The aggressive cancer treatment also causes severe side effects such as balance problems and impaired learning abilities in cancer survivors.
Numerous studies have explored the less than 2% of human DNA that gives rise to proteins, and much less is known about the rest of the genome. In a cancer, such as medulloblastoma, 98% of the mutations thus occur in the less studied part of the genome. There could be thousands of mutations, and it is difficult to separate the ones driving the cancer from those without importance.