A recent study suggests that an ancient, virus-like protein may play a key role in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), a fatal and incurable condition. The finding may lead to new research avenues for ALS treatments.


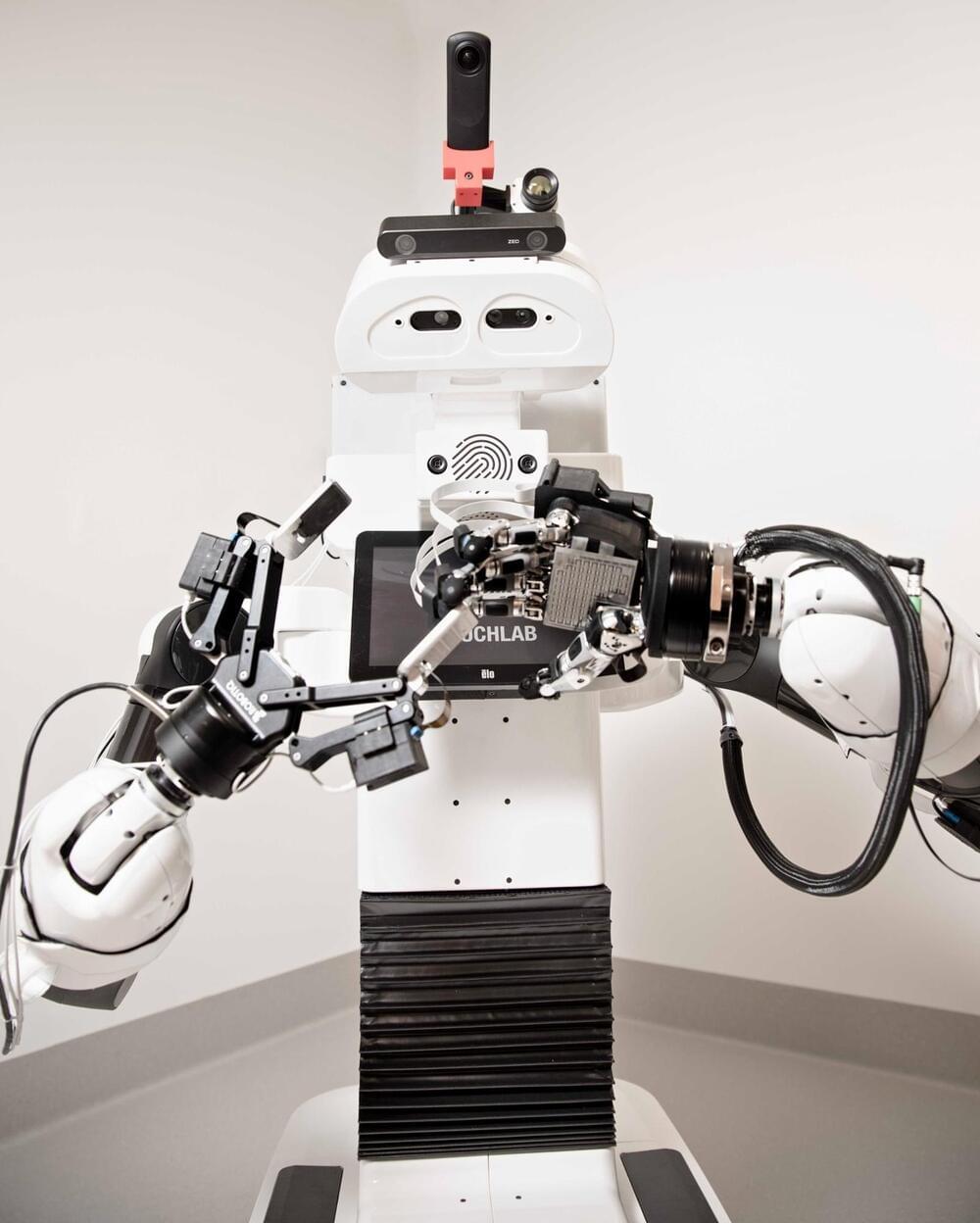
A first-of-its-kind robot which gives clinicians the ability to ‘feel’ patients remotely has been launched as part of a Finnish hospital pilot by deep tech robotics company Touchlab, a new tenant of the world-leading centre for robotics and artificial intelligence the National Robotarium.
Controlled by operators wearing an electronic haptic glove, the Välkky telerobot is equipped with the most advanced electronic skin (e-skin) technology ever developed to transfer a sense of touch from its robotic hand to users. E-skin is a material which is made up of single or multiple ultra-thin force sensors to transmit tactile sensations like pressure, vibration or motion from one source to another in real-time.
The 3-month pilot at Laakso Hospital in Helsinki, Finland will see a team of purpose-trained nurses explore how robotics systems can help deliver care, reduce workload and prevent the spread of infections or diseases. The pilot at Laakso Hospital is coordinated by Forum Virium Helsinki, an innovation company for the City of Helsinki. The research is part of a wider €7 billion project aimed at developing the most advanced hospital in Europe, due to be completed in 2028.

Getting a colonoscopy is important to screen for colorectal cancer. But how often you should get a colonoscopy depends on several different factors.
Current guidelines suggest that you get your first colonoscopy at age 45 if you are at average risk for colorectal cancer. If no polyps are found, you won’t need another colonoscopy for another 10 years. But in certain situations, you may need a colonoscopy more often.
We spoke with gastroenterologist Mazen Alasadi, M.D., to learn more.
Exploring Mitochondrial Bioenergetics, Optogenetics, Human Health And Aging — Dr. Brandon Berry, Ph.D., University of Washington.
Dr. Brandon Berry, Ph.D. (https://halo.dlmp.uw.edu/people/brandon-berry/) is a postdoctoral researcher in the Kaeberlein Laboratory at University of Washington where his research focuses on how aging and metabolism are linked.
Dr. Berry is interested in how mitochondria, the powerhouses of cells, contribute to and modulate functional decline that occurs during aging, and he is involved in using novel tools, like optogenetics, to precisely control mitochondria and metabolism with light. Through these types of experiments, he can more precisely determine if mitochondrial dysfunction is a cause or a consequence of metabolic aging and may reveal new ways to understand and impact health.
Dr. Berry has BS in Biochemistry from SUNY Geneseo, and an MS and PhD in Physiology from University of Rochester.
Here’s my new article for Aporia Magazine. A lot of wild ideas in it. Give it a read:
Regardless of the ethics and whether the science can even one day be worked out for Quantum Archaeology, the philosophical dilemma it presents to Pascal’s Wager is glaring. If humans really could eradicate the essence of death as we know it—including even the ability to ever permanently die—Pascal’s Wager becomes unworkable. Frankly, so does my Transhumanist Wager. After all, why should I dedicate my life and energy to living indefinitely through science when, by the next century, technology could bring me back exactly as I was—or even as an improved version of myself?
Outside of philosophical discourse, billions of dollars are pouring into the anti-aging and technology fields—much of it from Silicon Valley and the San Francisco Bay Area where I live. Everyone from entrepreneurs like Mark Zuckerburg to nonprofits like XPRIZE to giants like Google is spending money on ways to try to end all diseases and overcome death. Bank of America recently reported that they expect the extreme longevity field to be worth over $600 billion dollars by 2025.
Technology research spending for computers, microprocessors, and information technology is even bigger: $4.3 trillion dollars is estimated to have been spent worldwide in 2019. This amount includes research into quantum computing, which is hoped to eventually make computers hundreds—maybe thousands—of times faster over the next 50 years.
Despite the advancements of the 21st Century, the science to overcome biological death is not even close to being ready, if ever. Over 100,000 people still die a day, and in some countries like America, life expectancy has actually started going slightly backward. However, like other black swans of innovation in history—such as the internet, combustion engine, and penicillin—we shouldn’t rule out that new inventions may make humans live dramatically longer and maybe even as long as they like. As our species reaches for the heavens with its growing scientific armory, Pascal’s Wager is going to be challenged. It just might need an upgrade.
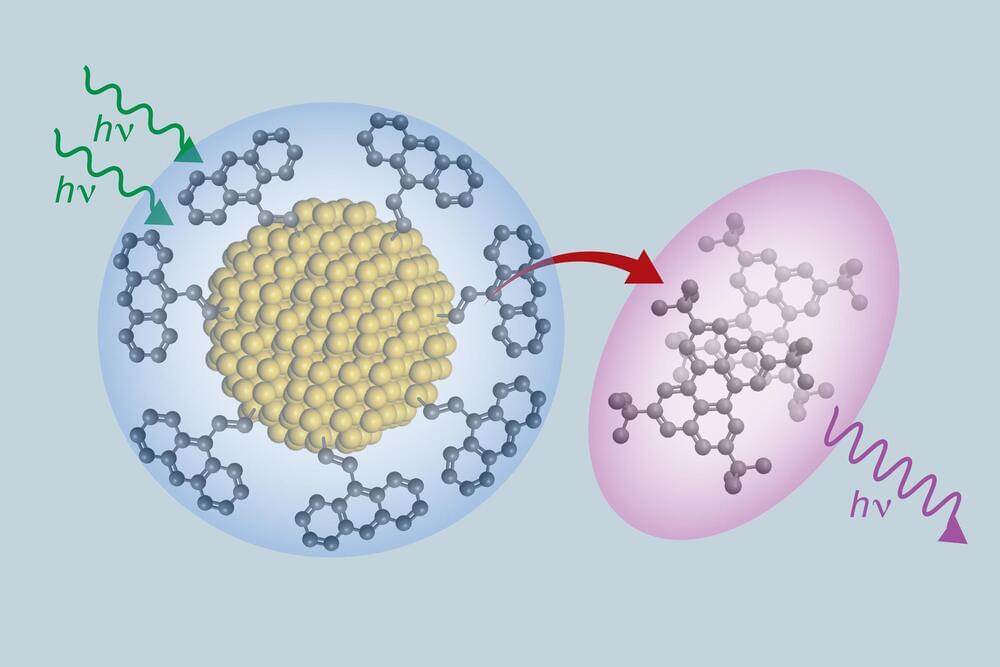
A group of scientists and engineers that includes researchers from The University of Texas at Austin have created a new class of materials that can absorb low energy light and transform it into higher energy light. The new material is composed of ultra-small silicon nanoparticles and organic molecules closely related to ones utilized in OLED TVs. This new composite efficiently moves electrons between its organic and inorganic components, with applications for more efficient solar panels, more accurate medical imaging and better night vision goggles.
The material is described in a new paper in Nature Chemistry.
“This process gives us a whole new way of designing materials,” said Sean Roberts, an associate professor of chemistry at UT Austin. “It allows us to take two extremely different substances, silicon and organic molecules, and bond them strongly enough to create not just a mixture, but an entirely new hybrid material with properties that are completely distinct from each of the two components.”
A nice Tesla Video. Hope it’s not censored.
#TeslaFans #teslanews #teslamotorfans #gigaberlin.
Please Subcribe my channel: http://bit.ly/3clkTm6
=====
Tesla Giga Shanghai Production Speed 38 Seconds, Changes Everything!
Huge thank to:
CCTV https://www.youtube.com/c/cctv.
wu wa https://www.youtube.com/c/%E7%83%8F%E7%93%A6
Jason Yang https://www.youtube.com/c/JasonYang.
====
Tesla’s Giga Shanghai is a trump card for the EV revolution of Tesla.
Recently, Elon Musk revealed how fast Giga Shanghai could produce a car in just 38 seconds.
So how did that change everything?
The first video includes a ten-minute and five-minute segment of the Model Y leaving the workshop.
And during the 10-minute segment, 16 new cars were completed, which would be 38 seconds per car on average.
7 cars were completed in the following 5-minute segment, translating to an average of 44 seconds per car.
We will not count it to double-check, but the peak rate may be amazingly high. Of course, not necessarily constant and simultaneous for both models.
Based on production and statistics, we can completely believe in the super-fast production speed of Giga Shanghai.
This is the carmaker’s first Gigafactory outside the United States, with an industrial chain localization rate of more than 95 percent and 99.99 percent of the employees being Chinese.
Especially, Giga Shanghai’s production and sales volume reached a new record.
This $2 billion US factory produced nearly 300,000 cars in the first half of this year.
Tesla delivered a record high of 77,938 vehicles in China in June, up 177 percent yearly.
It’s a big step for Tesla though it has faced unprecedented delays in vehicle production due to pandemic-related supply chain disruptions. Giga Shanghai was shut down for over three weeks in April, and no vehicles were exported to other territories.
Tesla says its Giga Shanghai is now the most productive EV factory in the world. It saw a projected annual capacity increase from just 450,000 vehicles to a whopping 750,000 from Q1 to Q2 2022.

Cancer remains one of the leading causes of death in the US at over 600,000 deaths per year. Cancers that form solid tumors such as in the breast, brain, or skin are particularly hard to treat. Surgery is typically the first line of defense for patients fighting solid tumors. But surgery may not remove all cancerous cells, and leftover cells can mutate and spread throughout the body. A more targeted and wholistic treatment could replace the blunt approach of surgery with one that eliminates cancer from the inside using our own cells.
Dennis Discher, Robert D. Bent Professor of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, and postdoctoral fellow Larry Dooling provide a new approach in targeted therapies for solid tumor cancers in their study, published in Nature Biomedical Engineering. Their therapy not only eliminates cancerous cells, but teaches the immune system to recognize and kill them in the future.

One California-based startup, Varda Space Industries, is betting that big business will lie in relatively unassuming satellites that will spend days or months in Earth’s orbit quietly carrying out pharmaceutical development. Its research, company officials hope, could lead to better, more effective drugs — and hefty profits.
“It’s not as sexy a human-interest story as tourism when it comes to commercialization of the cosmos,” said Will Bruey, Varda’s CEO and cofounder. “But the bet that we’re making at Varda is that manufacturing is actually the next big industry that gets commercialized.”
Varda is expected to launch its first test mission Monday aboard a SpaceX rocket. A window for take-off from Vandenberg Space Force Base in California begins at 2:19 p.m. PT.