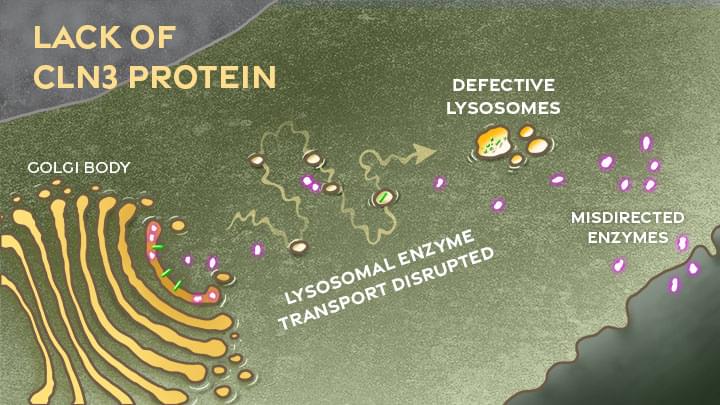
A common theme among parents and family members caring for a child with the rare Batten disease is “love, hope, cure.” While inspiring levels of love and hope are found among these amazing families, a cure has been more elusive. One reason is rooted in the need for more basic research. Although researchers have identified an altered gene underlying Batten disease, they’ve had difficulty pinpointing where and how the gene’s abnormal protein product malfunctions, especially in cells within the nervous system.
Now, this investment in more basic research has paid off. In a paper just published in the journal Nature Communications, an international research team pinpointed where and how a key cellular process breaks down in the nervous system to cause Batten disease, sometimes referred to as CLN3 disease [1]. While there’s still a long way to go in learning exactly how to overcome the cellular malfunction, the findings mark an important step forward toward developing targeted treatments for Batten disease and progress in the quest for a cure.
The research also offers yet another excellent example of how studying rare diseases helps to advance our fundamental understanding of human biology. It shows that helping those touched by Batten disease can shed a brighter light on basic cellular processes that drive other diseases, rare and common.