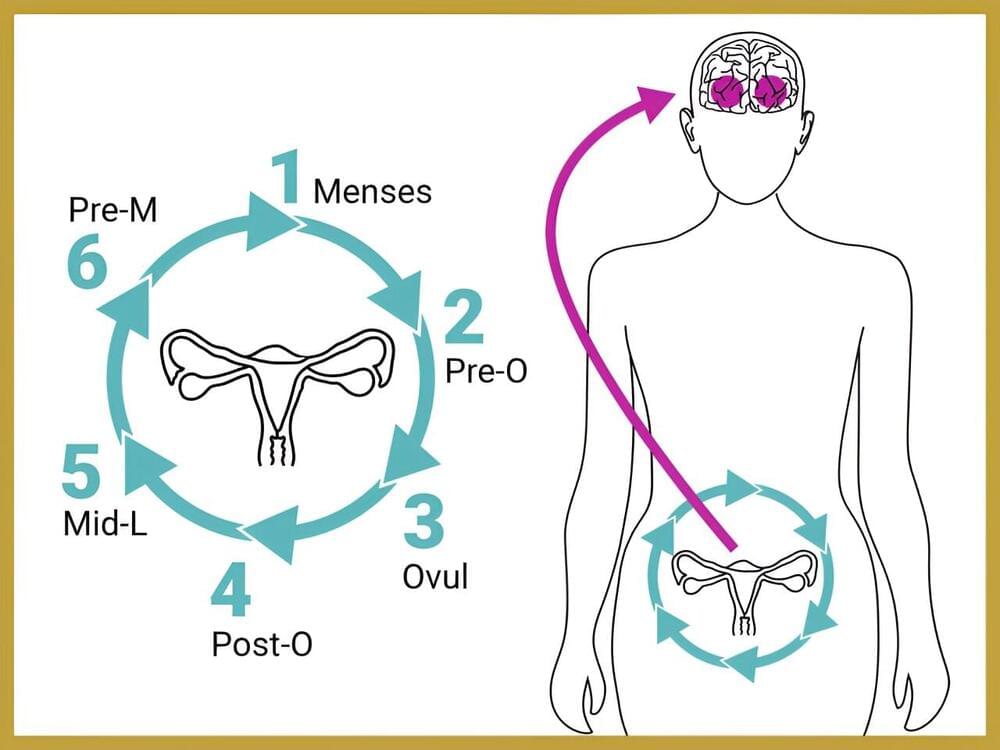
Central learning and memory hubs change in response to sex hormones. A new study in Nature Mental Health by Rachel Zsido and Julia Sacher of the Max Planck Institute for Human Cognitive and Brain Sciences and the University Clinic in Leipzig, Germany, links rhythmic oscillations in ovarian hormone levels in women during the menstrual cycle to changes in brain structure.
Ovarian hormones have significant effects on the brain, and early menopause may be associated with an increased risk of accelerated brain aging and dementia later in life. However, the effects of ovarian hormone fluctuations on brain structure earlier in life are less defined. In their current study, Zsido and Sacher show that fluctuations in ovarian hormones affect structural plasticity in key brain regions during the reproductive years.
To do this, the scientists collected blood samples from 27 female study participants, used ultrasound to track follicle growth in the ovaries to pinpoint ovulation timing, and utilized ultra-high field 7 Tesla MRI to zoom into subregions of the medial temporal lobe and hippocampus. That’s because these regions are dense with sex hormone receptors and are critical for cognitive function, such as episodic memory.