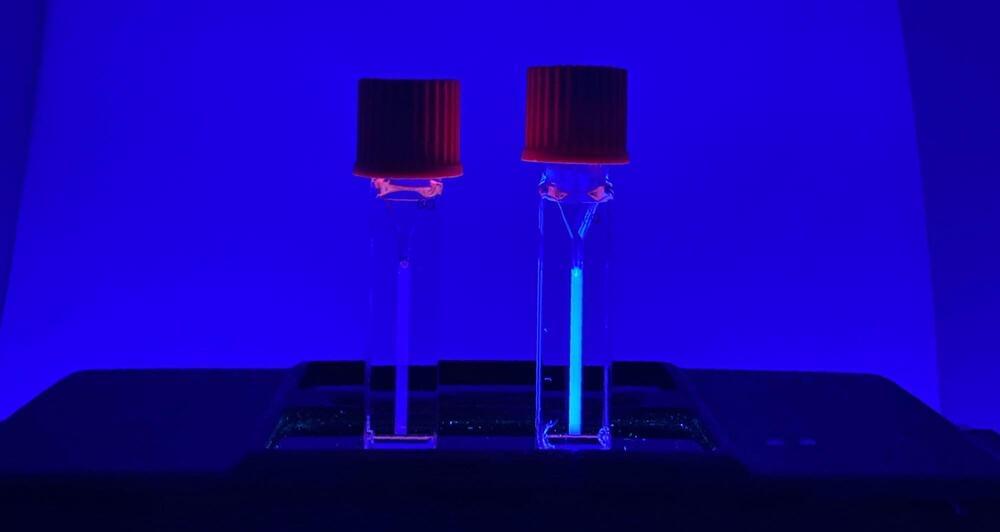
The intricate interplay of gene expression within living cells is akin to a well-orchestrated symphony, with each gene playing its part in perfect harmony to ensure cells function as they should. At the heart of this symphony are transcription factors (TFs), molecular maestros that regulate the expression of genes by binding to specific DNA sequences known as promoters.
Unlocking the secrets of these genome-scale regulatory networks requires a comprehensive collection of gene expression profiles, but measuring gene expression responses for every TF and promoter pair has posed a formidable challenge due to the sheer number of potential combinations, even in relatively simple organisms such as bacteria.
To tackle this challenge, researchers led by Fuzhong Zhang, professor of energy, environmental & chemical engineering in the McKelvey School of Engineering at Washington University in St. Louis, developed a technique called pooled promoter responses to TF perturbation sequencing (PPTP-seq).