As more people turn to chat-based AIs for medical advice, it remains to be seen how these tools stack up against—or could complement—human doctors.


Researchers from the National Institutes of Health and their partners have unearthed new findings about healing and aging by studying a tiny sea creature capable of regenerating its entire body using just its mouth. They analyzed the RNA
Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a polymeric molecule similar to DNA that is essential in various biological roles in coding, decoding, regulation and expression of genes. Both are nucleic acids, but unlike DNA, RNA is single-stranded. An RNA strand has a backbone made of alternating sugar (ribose) and phosphate groups. Attached to each sugar is one of four bases—adenine (A), uracil (U), cytosine ©, or guanine (G). Different types of RNA exist in the cell: messenger RNA (mRNA), ribosomal RNA (rRNA), and transfer RNA (tRNA).
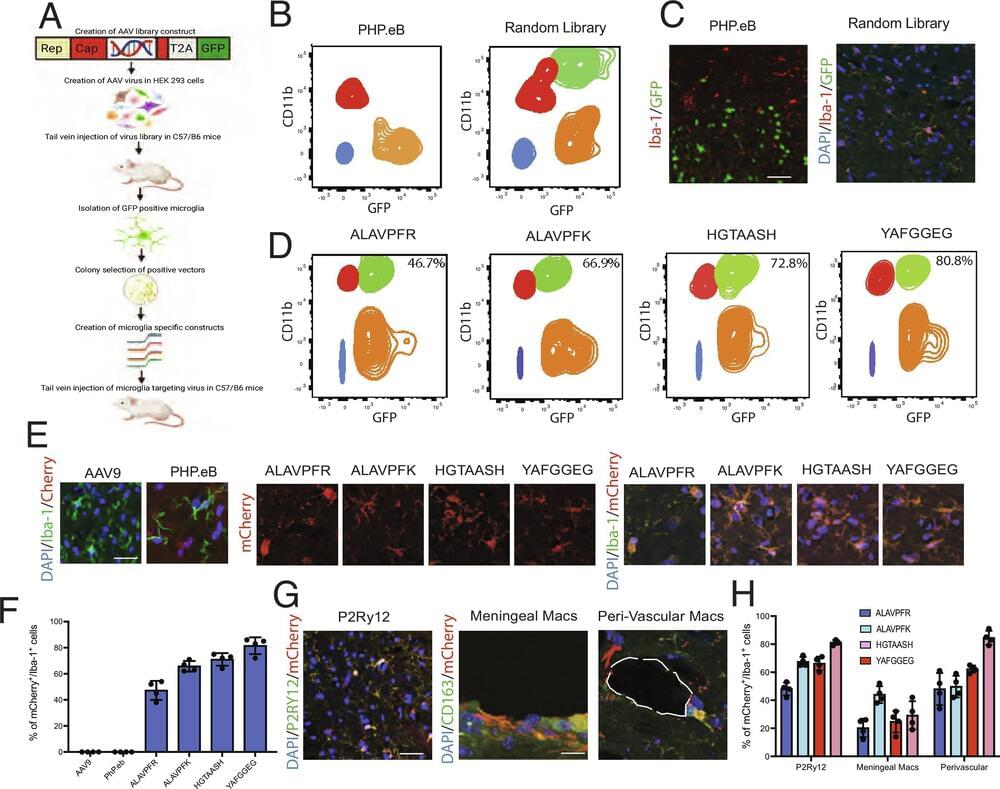
Cool paper that adds a useful tool to the gene therapist’s toolbox! Young et al. utilize an in vivo screening method to develop adeno-associated viruses (AAVs) which target microglia. They show that their AAVs transduce central nervous system microglia as well as tissue macrophages after intravenous injection. #biotechnology
Tissue macrophages, including microglia, are notoriously resistant to genetic manipulation. Here, we report the creation of Adeno-associated viruses (AAV) variants that efficiently and widely transduce microglia and tissue macrophages in vivo following intravenous delivery, with transgene expression of up to 80%. We use this technology to demonstrate manipulation of microglia gene expression and microglial ablation, thereby providing invaluable research tools for the study of these important cells.

New insights into the medical mysteries behind dementia have been revealed this week, with two studies identifying drivers of the brain-degenerating condition.
One study, released on September 11 in the journal General Psychiatry, shows that the shortening of little caps on the end of chromosomes may be linked to increased dementia risk. Another, published in the journal JAMA on September 12, reveals that spending more time sedentary, such as sitting down, may also increase the risk.
These studies may help scientists to further understand the mechanisms behind what causes dementia to develop, and therefore how to stop it.



🏅 R&D 100 Award Winner 🏅
The Noncontact Laser Ultrasound (NCLUS) is a portable laser-based system that acquires ultrasound images of human tissue without touching a patient. It offers capabilities comparable to those of an MRI and CT but at vastly lower cost in an automated and portable platform.
In addition to receiving an R&D 100 Award, NCLUS received the Silver Medal in the Special Recognition: Market Disruptor Products category. Congratulations to the NCLUS team!
Researchers from MIT Lincoln Laboratory and their collaborators at the Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) Center for Ultrasound Research and Translation (CURT) have developed a new medical imaging device: the Noncontact Laser Ultrasound (NCLUS). This laser-based ultrasound system provides images of interior body features such as organs, fat, muscle, tendons, and blood vessels. The system also measures bone strength and may have the potential to track disease stages over time.
“Our patented skin-safe laser system concept seeks to transform medical ultrasound by overcoming the limitations associated with traditional contact probes,” explains principal investigator Robert Haupt, a senior staff member in Lincoln Laboratory’s Active Optical Systems Group. Haupt and senior staff member Charles Wynn are co-inventors of the technology, with assistant group leader Matthew Stowe providing technical leadership and oversight of the NCLUS program. Rajan Gurjar is the system integrator lead, with Jamie Shaw, Bert Green, Brian Boitnott (now at Stanford University), and Jake Jacobsen collaborating on optical and mechanical engineering and construction of the system.
Medical ultrasound in practice
For eons, deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) has served as a sort of instruction manual for life, providing not just templates for a vast array of chemical structures but a means of managing their production.
In recent years engineers have explored a subtly new role for the molecule’s unique capabilities, as the basis for a biological computer. Yet in spite of the passing of 30 years since the first prototype, most DNA computers have struggled to process more than a few tailored algorithms.
A team researchers from China has now come up with a DNA integrated circuit (DIC) that’s far more general purpose. Their liquid computer’s gates can form an astonishing 100 billion circuits, showing its versatility with each capable of running its own program.
Join this channel to get access to perks:
https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCiPW7OlzTfQjR_vLlkYPZCg/join.
Join the Dr. Cellini Family: https://tinyurl.com/DrCellini.
______
CONTACT ME:
📸 Instagram — https://instagram.com/drcellini.
📹 TikTok — @DrCellini.
🐦 Twitter — https://twitter.com/dr_cellini.
📧 Email: TheDrCellini@gmail.com.
———-
https://www.wearfigs.com.
———-
MY TOOLS & GEAR:
🎥 My YouTube Camera Gear — https://www.amazon.com/shop/drcellini?tag=lifeboatfound-20.
⌨️ My Keyboard — Wireless F96 KAT mechanical keyboard — http://iqunix.store/drcellini.
🎵 Where I get ALL of My Music from Epidemic Sound! — https://www.epidemicsound.com/referral/25q7o4/
My Camera: https://amzn.to/2GX4whr.
My Lens: https://amzn.to/2C7NYxt.
Camera Tripod: https://amzn.to/2LUABWf.
Memory Card: https://amzn.to/2LVjtPZ
As an Amazon Associate I earn commission with use of the above links on qualifying purchases
———-
OTHER STUFF: