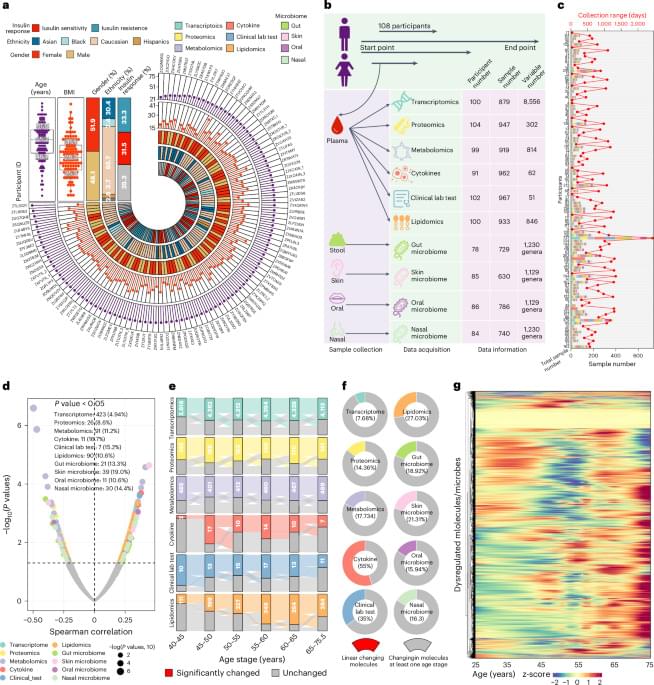
Understanding the molecular changes underlying aging is important for developing biomarkers and healthy aging interventions. In this study, the authors used comprehensive multi-omics data to reveal nonlinear molecular profiles across chronological ages, highlighting two substantial variations observed around ages 40 and 60, which are linked to increased disease risks.