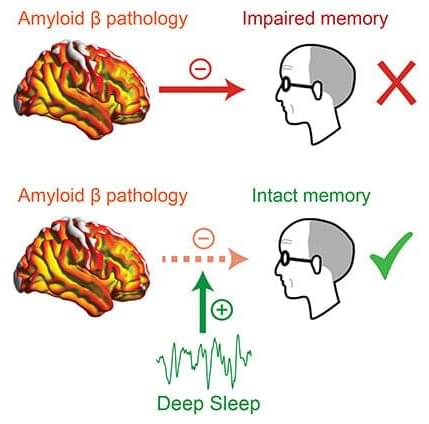
A deep slumber might help buffer against memory loss for older adults facing a heightened burden of Alzheimer’s disease, new research from the University of California, Berkeley, suggests.
Deep sleep, also known as non-REM slow-wave sleep, can act as a “cognitive reserve factor” that may increase resilience against a protein in the brain called beta-amyloid that is linked to memory loss caused by dementia. Disrupted sleep has previously been associated with faster accumulation of beta-amyloid protein in the brain. However, the new research from a team at UC Berkeley reveals that superior amounts of deep, slow-wave sleep can act as a protective factor against memory decline in those with existing high amounts of Alzheimer’s disease pathology —a potentially significant advance that experts say could help alleviate some of dementia’s most devastating outcomes.
“With a certain level of brain pathology, you’re not destined for cognitive symptoms or memory issues,” said Zsófia Zavecz, a postdoctoral researcher at UC Berkeley’s Center for Human Sleep Science. “People should be aware that, despite having a certain level of pathology, there are certain lifestyle factors that will help moderate and decrease the effects.