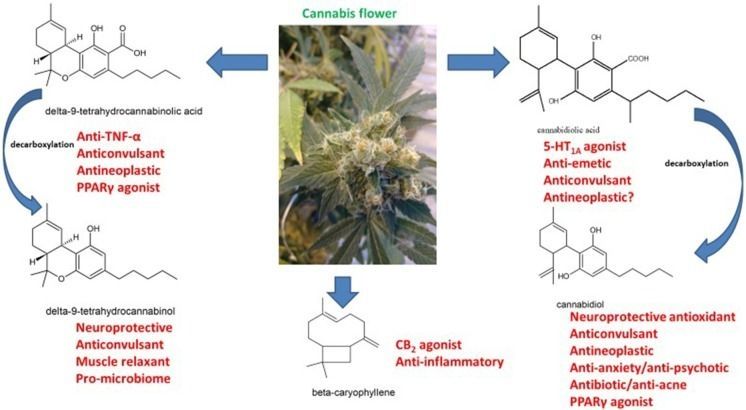
Neurological therapeutics have been hampered by its inability to advance beyond symptomatic treatment of neurodegenerative disorders into the realm of actual palliation, arrest or reversal of the attendant pathological processes. While cannabis-based medicines have demonstrated safety, efficacy and consistency sufficient for regulatory approval in spasticity in multiple sclerosis (MS), and in Dravet and Lennox-Gastaut Syndromes (LGS), many therapeutic challenges remain. This review will examine the intriguing promise that recent discoveries regarding cannabis-based medicines offer to neurological therapeutics by incorporating the neutral phytocannabinoids tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), cannabidiol (CBD), their acidic precursors, tetrahydrocannabinolic acid (THCA) and cannabidiolic acid (CBDA), and cannabis terpenoids in the putative treatment of five syndromes, currently labeled recalcitrant to therapeutic success, and wherein improved pharmacological intervention is required: intractable epilepsy, brain tumors, Parkinson disease (PD), Alzheimer disease (AD) and traumatic brain injury (TBI)/chronic traumatic encephalopathy (CTE). Current basic science and clinical investigations support the safety and efficacy of such interventions in treatment of these currently intractable conditions, that in some cases share pathological processes, and the plausibility of interventions that harness endocannabinoid mechanisms, whether mediated via direct activity on CB1 and CB2 (tetrahydrocannabinol, THC, caryophyllene), peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma (PPARγ; THCA), 5-HT1A (CBD, CBDA) or even nutritional approaches utilizing prebiotics and probiotics. The inherent polypharmaceutical properties of cannabis botanicals offer distinct advantages over the current single-target pharmaceutical model and portend to revolutionize neurological treatment into a new reality of effective interventional and even preventative treatment.
Keywords: cannabis, pain, brain tumor, epilepsy, Alzheimer disease, Parkinson disease, traumatic brain injury, microbiome.
Cannabis burst across the Western medicine horizon after its introduction by William O’Shaughnessy in 1838 (O’Shaughnessy, 1838–1840; Russo, 2017b), who described remarkable successes in treating epilepsy, rheumatic pains, and even universally fatal tetanus with the “new” drug. Cannabis, or “Indian hemp,” was rapidly adopted by European physicians noting benefits on migraine by Clendinning in England (Clendinning, 1843; Russo, 2001) and neuropathic pain, including trigeminal neuralgia by Donovan in Ireland (Donovan, 1845; Russo, 2017b). These developments did not escape notice of the giants of neurology on both sides of the Atlantic, who similarly adopted its use in these indications: Silas Weir Mitchell, Seguin, Gowers and Osler (Mitchell, 1874; Seguin, 1877; Gowers, 1888; Osler and McCrae, 1915).
Read more








