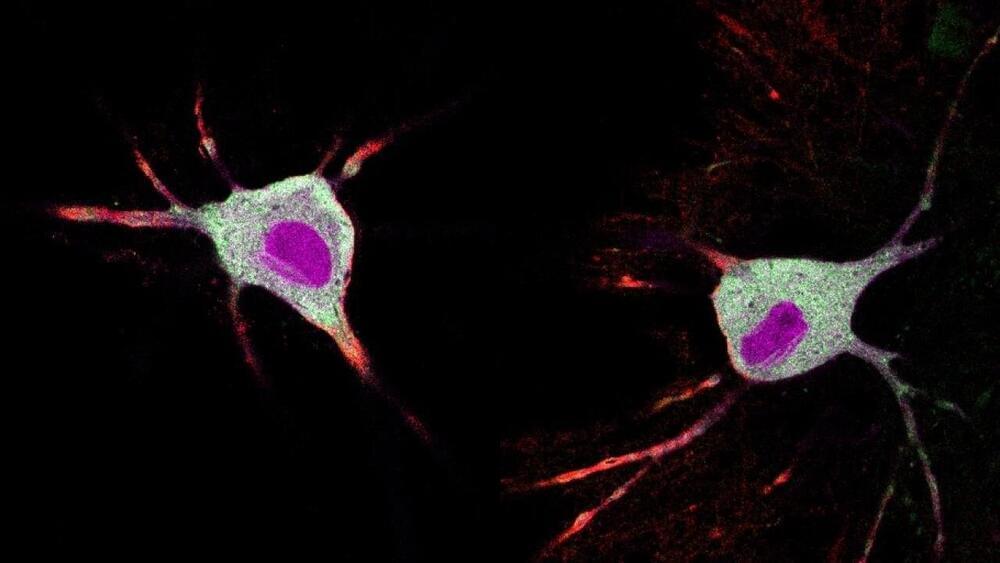
Researchers at the University of California, Davis have developed a rapid, noninvasive tool to track the neurons and biomolecules activated in the brain by psychedelic drugs. The protein-based tool, which is called Ca2+-activated Split-TurboID, or CaST, is described in research published in Nature Methods.
There has been mounting interest in the value of psychedelic-inspired compounds as treatments for brain disorders including depression, post-traumatic stress disorder and substance use disorder. Psychedelic compounds like LSD, DMT and psilocybin promote the growth and strengthening of neurons and their connections in the brain’s prefrontal cortex. The new tool could help scientists unlock the benefits of psychedelic treatments for patients with brain disorders.
“It’s important to think about the cellular mechanisms that these psychedelics act upon,” said Christina Kim, an assistant professor of neurology at the UC Davis Center for Neuroscience and School of Medicine, and an affiliate of the UC Davis Institute for Psychedelics and Neurotherapeutics. “What are they? Once we know that, we can design different variants that target the same mechanism but with fewer side effects.”