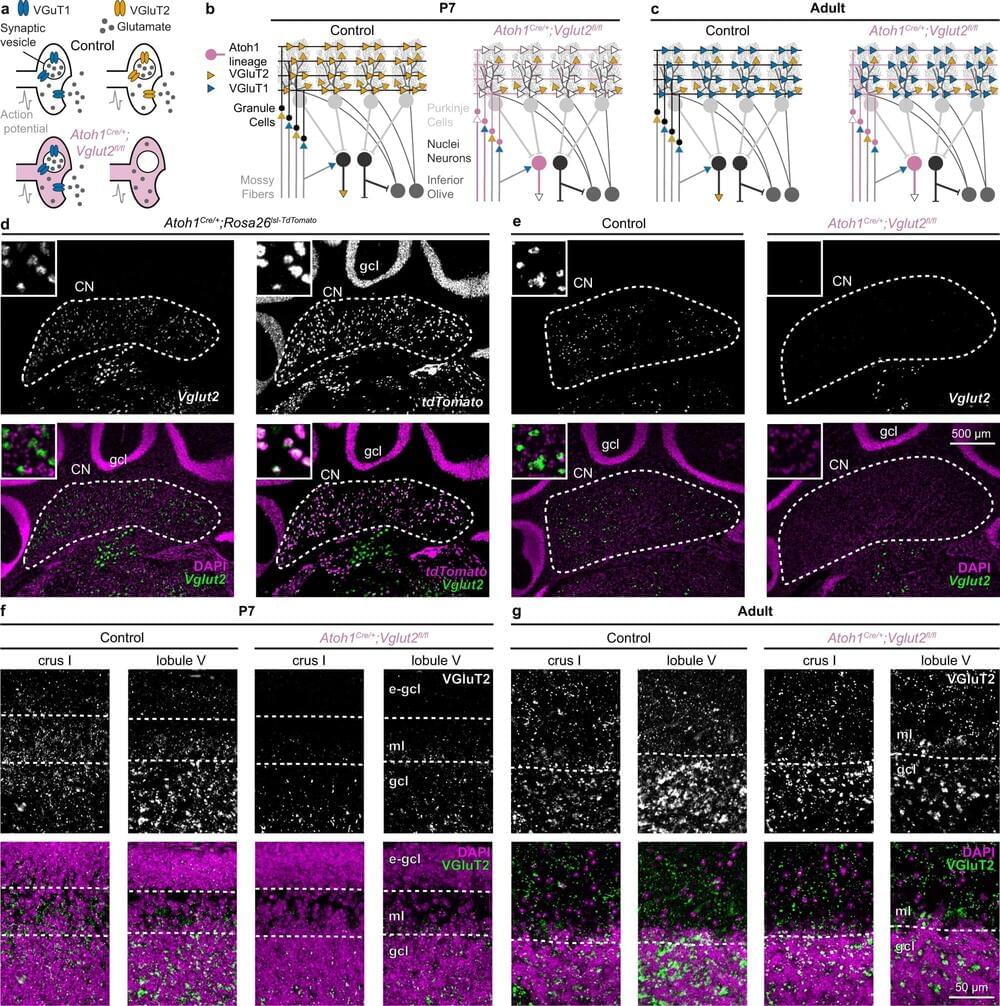
The cerebellum, a major part of the hindbrain in all vertebrates, is important for motor coordination, language acquisition, and regulating social and emotional behaviors. A study led by Dr. Roy Sillitoe, professor of Pathology and Neuroscience at Baylor College of Medicine and investigator at the Jan and Dan Duncan Neurological Research Institute (Duncan NRI) at Texas Children’s Hospital, shows two distinct types of cerebellar neurons differentially regulate motor and non-motor behaviors during development and in adulthood.
The study, published in Nature Communications, provides the first in vivo evidence supporting the critical role of a specific subset of excitatory glutamatergic neurons in acquiring motor and sensory/emotional behaviors. Further, it shows that neurons present in different regions of the cerebellum contribute differently to motor versus non-motor behaviors during development and in adulthood.
The cerebellar nuclei are present in the deepest layer of the cerebellum. These nuclei are encased by an outer highly convoluted sheet of tissue called the cerebellar cortex, which contains most of the other types of neurons in the cerebellum. The cerebellar cortex receives information from most parts of the body and other brain regions. These inputs are integrated by many types of cerebellar neurons and the deep-set cerebellar nuclei—the sole output structures in the cerebellum—then send those signals to the other parts of the brain.