Human writing and drawing dates back at least 30,000 years and incorporates traditional techniques such as carving, engraving, and printing/writing with ink, as well as more novel methods such as electron lithography. Now a team of German physicists has figured out a unique method for writing in water and other fluid substrates, according to a recent paper published in the journal Small.
According to the authors, most classical writing methods involve the same basic approach, in which a line is carved out or ink deposited. On a solid substrate, strong intermolecular forces help the written figures hold their shape, but that’s not the case for surfaces submerged in fluids. Prior research has used scanning probe lithography to “write’ on self-assembled monolayers submerged in fluids, or to bring structures at the micron scale using two-photon polymerization. ” There are now even commercial scuba diver slates available for underwater writing on a substrate,” they wrote.
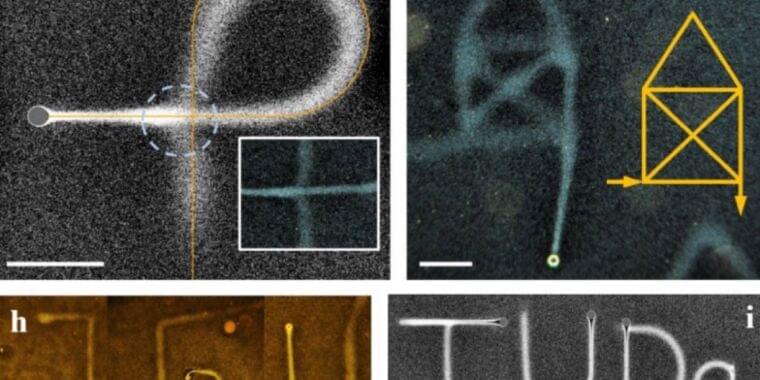
All of these methods still rely on a substrate, however. The German team wanted to devise a means of literally writing into a fluid. Such a method would need to be robust enough to counter the rapid dispersion of drawn lines, and they would need a very tiny pen that didn’t stir up lots of turbulence as it moved through the fluid medium. (The smaller the object moving through a fluid, the fewer vortices, or eddies, it will create.)