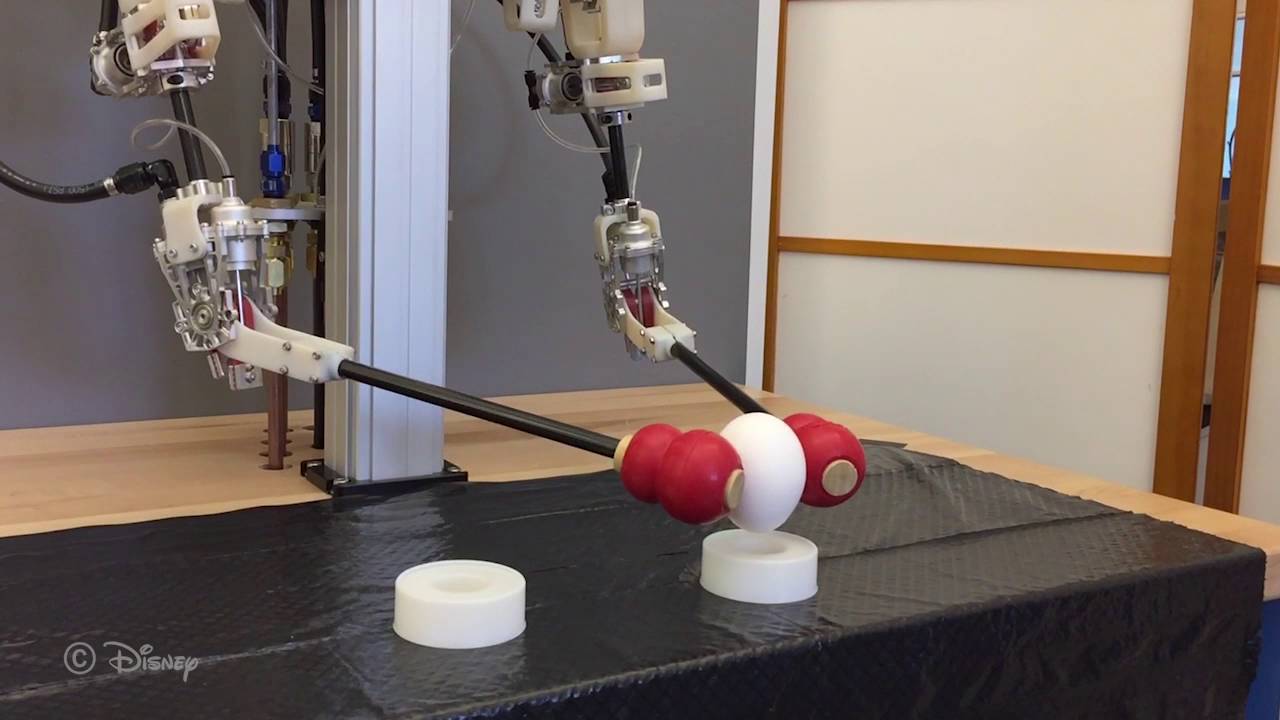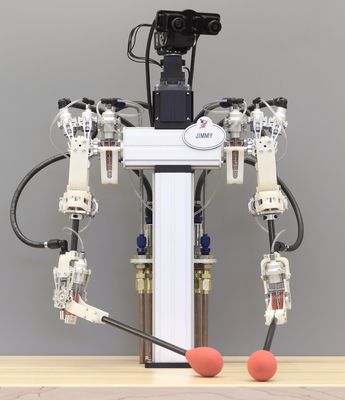
A human-safe lifelike telepresence robot with the delicacy and precision needed to pick up an egg without breaking it or thread a sewing needle has been developed by researchers at Disney Research, the Catholic University of America, and Carnegie Mellon University.
The secret: a hydrostatic transmission that precisely drives robot arms, offering extreme precision with almost no friction or play.
The hybrid transmission design also makes it possible to halve the number of bulky hydraulic lines that a fully hydraulic system would require and allows for making its robotic limbs lighter and smaller, said John P. Whitney, an assistant professor of mechanical and industrial engineering at Northeastern University, who led the development of the transmission while an associate research scientist at Disney Research.